Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
At present, we do not know the cause of Parkinsons disease. In most people there is no family history of Parkinsons Researchers worldwide are investigating possible causes, including:
- environmental triggers, pesticides, toxins, chemicals
- genetic factors
- combinations of environment and genetic factors
Patient Selection And Diagnostic Criteria
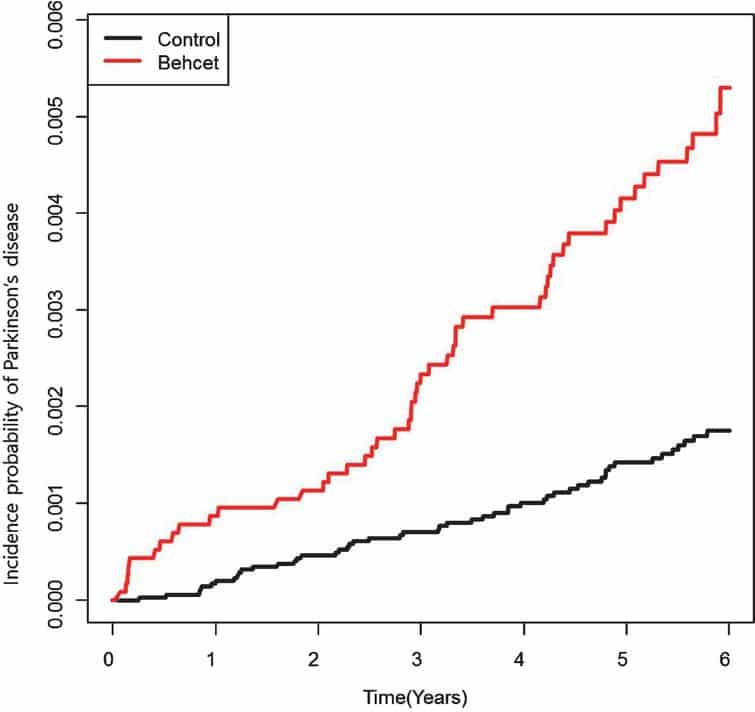
We selected all PD patients registered in the RID program during the 6-year study period. The diagnostic criteria for PD established by the NHI in the RID program are similar to the UK PD society brain bank clinical diagnostic criteria, and are as follows: 1) diagnosis of Parkinsonian syndrome : mild or worse bradykinesia and at least one of the following: muscular rigidity, rest tremor, postural instability 2) the exclusion criteria for PD: history of strokes, head injury, definite encephalitis, drug side effects, and hypoxia 3) supportive prospective positive criteria for PD: three or more required for diagnosis of definite PD in combination with step one: unilateral onset, rest tremor present, progressive disorder, persistent asymmetry affecting the side of onset most, excellent response to levodopa, severe levodopa-induced chorea, levodopa response for 5years or more, clinical course of 10years or more.
The database did not contain any personal identifiers as all identifiable personal information in the database was removed to comply with the privacy rules of the health insurance portability and accountability act. Informed consent was not required for this study as all the data was obtained from medical records. This study was performed based on the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki of the World Medical Association. All procedural and ethical aspects of this study were approved by the Institutional Review Board of Korea University Ansan Hospital .
Can We Turn The Tide
The study authors believe that the key to transforming this seemingly inevitable rise in Parkinsons disease is activism.
Conditions such as HIV and breast cancer have benefited widely from this approach. For example, many focus on raising awareness, amassing funds, improving treatments, and changing policy.
Stopping the production and use of certain chemicals that may increase the risk of Parkinsons is essential. As the authors write:
We have the means to prevent potentially millions from ever experiencing the debilitating effects of Parkinson disease.
Also crucial, as ever, is financial backing. More research is needed to understand why the condition appears and how it progresses, and this type of scientific investigation is never cheap.
In particular, scientists need to develop better medications. Currently, the most effective therapy is levodopa, which is 50 years old and not without its issues, including both psychological and physical side effects.
While this recent analysis is worrying, the authors leave the reader with some positivity, concluding that he Parkinson pandemic is preventable, not inevitable.
Also Check: How To Take Mannitol For Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s Disease By Ethnicity
Parkinson’s disease affects people of all races and geographic regions worldwide. The incidence is higher among White Americans than among Black and Asian Americans. It is higher among Hispanics than among White Americans.
It is not known whether the different incidence and prevalence rates among people of different ethnic backgrounds are due to environmental or genetic factors.
The Rise Of Parkinson’s Disease
Neurological disorders are the worlds leading cause of disability. And the fastest growing of these conditions is not Alzheimers but Parkinsons disease.
QUICK TAKE
- The number of people with Parkinsons disease more than doubled from 1990 to 2015 and could double again by 2040. An aging population alone does not account for this rise.
- Air pollution, metal production, certain industrial chemicals, and some synthetic pesticides are linked to Parkinsons. Yet we are doing little to manage known risk factors.
- The authors contend that the United States should ban trichloroethylene, paraquat, and other chemicals linked to Parkinsons, which many other countries have already done.
From 1990 to 2015, the number of people living with Parkinsons more than doubled from 2.6 million to 6.3 million, according to a 2015 study in Lancet Neurology. By 2040, the number is projected to double again to at least 12.9 million, a stunning rise .
The number of people with Parkinsons disease more than doubled between 1990 and 2015 and is projected to double again by 2040.
Figure adapted from E. R. Dorsey and B. R. Bloem, 2018.
Figure adapted from R. Dorsey et al., 2020.
The number of people who succumb to Parkinsons each year has been increasing steadily.
Data from: U.S. National Center for Health Statistics, National Vital Statistics System, Mortality Data.
Christophe Vander Eecken / Reporters / Science Source
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s Disease Hereditary Or Genetic
Prevalence Of Parkinsons State
Western and Southern states appear to have lower rates of Parkinsons disease, while Northeastern and many Midwestern states have higher rates . Mississippi and Montana have the lowest rates of Parkinsons, at 5.1 per 10,000. Vermont has the highest rate of Parkinsons at 9.9 per 10,000.
Exhibit 2: Prevalence of Parkinsons Disease, by geography
General Comments On Methodology
This analysis identified many potentially important differences in the incidence of PD, which could possibly be attributed to environmental or genetic factors. However, as this meta-analysis contains studies with a range of methodological strategies, the differences between age- and gender-specific incidence may also be due to methodological differences or potential population confounders. Ideally, only studies using the same methods of case ascertainment would be combined in the meta-analysis. However, only 27 studies of PD incidence were found, with only 14 providing data that could be combined in the meta-analysis. There were only a few studies that used identical methodologies for case ascertainment. As all methods of case ascertainment have drawbacks, including attrition, misclassification, and nonresponse, the quality of individual studies may be equally as important as the method of case ascertainment in determining PD incidence. Therefore, we chose to combine studies using different methodologies and examine closely for heterogeneity using the I2 statistic calculated from the Cochrane Q chi-square test for heterogeneity. I2 values showed low to moderate heterogeneity in the female age groups from 40 to 70, with considerable heterogeneity in those 70-79 and 80+. Similarly, heterogeneity increased with age in males, though considerable heterogeneity was found in all age groups over 50.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Case Study Example
The Impact Of Parkinsons Disease On Overall Health
Based on the Blue Cross Blue Shield Health Index, the overall health of those affected by Parkinsons is significantly lower than the general population. In 2017, the average BCBS Health Index for someone aged 30-64 with Parkinsons was 57, compared to 88 for the entire commercially insured population in this age range. This translates to an average of 10.7 years of healthy life lost for those with the condition compared to 3.4 years for the 30-64 population as a whole.4
Caring for someone with Parkinsons Disease
The majority of Parkinsons patients are cared for by informal caregivers, such as a family member. The physical, mental and emotional work this requires can be significant. The Impact of Caregiving on Mental and Physical Health found that caregivers have 26% poorer health compared to a benchmark population, as measured by the BCBS Health Index. In addition, a national survey conducted by the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association found that 1 in 4 unpaid caregivers are feeling more stress trying to balance work and family due to COVID-19.5
Incidence And Prevalence Mf Ratios
Among 457027 persons with at least one reimbursement of antiparkinsonian drugs in 2010, 188562 persons were predicted as being treated for PD, of whom 10723 died in 2010. The corrected number of prevalent cases was 149672 . Among persons treated for PD in 2010, 29940 were new cases. The corrected number of incident cases was 25438 . There were no important sex differences among prevalent and incident PD cases for characteristics included in the prediction model .
Systematic review of age-specific male-to-female incidence ratios of Parkinson’s disease. Circles represent observed male-to-female incidence ratios for each study by age-by-sex strata, estimated by modelling incidence through Poisson regression their size is proportional to the variance of the male-to-female incidence ratios, and more precise estimates are represented by larger circles. Solid line, linear regression of male-to-female incidence ratios weighted by the inverse of their variance on age . Dashed line, 95% CIs of the linear regression.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Someone Live With Parkinson’s Dementia
Whats Causing The Increase
The increase is due to a growing and ageing population.
Our analysis suggests that 1 in every 37 people will be diagnosed with Parkinsons in their lifetime.
The growth in Parkinsons diagnoses shown in this report is a huge challenge. It is now more urgent than ever that we give people affected by Parkinsons the support they need, drive better care and find new treatments and a cure.
Parkinsons Disease Is A Global Pandemic
PD is an age-related disorder symptoms typically begin to first appear at varying stages in patients in their mid-60s.
PD had been a rare disorder, however, demography and the by-products of industrialisation are now contributing to an impending PD pandemic. It is currently understood to affect 12% of individuals aged 65 years and older worldwide.
Recommended Reading: Wearable Technology For Parkinson Disease
Other Studies Of Interest
Three high-quality papers were found but not included in the meta-analysis as they did not report age- and gender-specific incidence rates or proportions. These studies provided information on Asian and Eastern European populations that were not well represented in the meta-analysis.
Das et al. was the only study that examined PD in a south Asian Indian population, reporting average annual incidence rates for males and females in different age categories. AAIRs peaked earlier for males, than females. Male AAIRs peaked at 60-69 years female AAIRs continued to rise in 70-79 years before dropping off in the 80+ age group. Hristova et al. and Kyrozis et al. both provided incidence rates not stratified by gender and age and therefore could not be included in the meta-analysis. Both represented unique European populations and found peak incidence between 70 and 80 years.
Screening And Early Detection
There is no specific test that can tell in advance whether someone will one day develop Parkinsons disease. Most of the time, people who develop the condition did not have any early signs in the years before the disease started to cause symptoms. Many people with Parkinsons disease had a physically active lifestyle before the disease started to have any effects.
Parkinsons disease is diagnosed based on a physical examination, which includes a comprehensive neurological examination. Sometimes brain imaging or other tests are ordered to see whether another brain condition, such as a stroke, brain injury, or a tumor, could be causing the symptoms.
There is no definitive laboratory test or other test to confirm a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease.
Don’t Miss: How To Make A Donation To Parkinson’s Disease
Incidence Of Parkinsons Disease
The overall crude incidence rate of PD between 2006 and 2016 as defined by the four case definitions was 57 per 100,000 PYAR using PD diagnosis Read codes and at least 2 prescriptions of antiparkinsonian medication 70 per 100,000 person years at risk using solely PD diagnosis Read codes 75 per 100,000 PYAR using PD diagnosis OR symptom Read codes 140 per 100,000 PYAR using PD diagnosis OR symptom Read codes OR at least one prescription of antiparkinsonian medication- .
Table 1 Incidence of Parkinsons disease from 2006 to 2016 by sociodemographic factors, calendar year, and region using the broadest case definition .
The incidence of PD was slightly lower in people from the most deprived areas compared to those from the least deprived areas. For the broadest case definition, the IRR was 0.98 with an IR of 133.86 per 100,000 PYAR in the most deprived quintile and of 147.12 in the least deprived quintile. .
Impact On Families And Carers
Informal carers spendmany hours dailyproviding care for people living with PD.This can be overwhelming. Physical, emotional and financial pressures can cause great stress to families and carers, and support is required from the health, social, financial and legal systems. Useful support resources from other conditions can be drawn upon, such as WHOs iSupport programme for dementia.
Don’t Miss: What Foods Are Good For Parkinson’s Disease
Availability Of Data And Materials
Data is available from the Korea National Health Insurance Sharing Service Institutional Data Access / Ethics Committee for researchers who meet the criteria for access to confidential data. Researchers can apply for the National Health Insurance data sharing service upon approval by the Institutional Review Board of their institution. After a review by the Korea National Health Insurance Sharing Service Institutional Data Access / Ethics Committee, authors are required to pay a data access fee and confirm that other researchers will be able to access the data in the same manner as the authors.
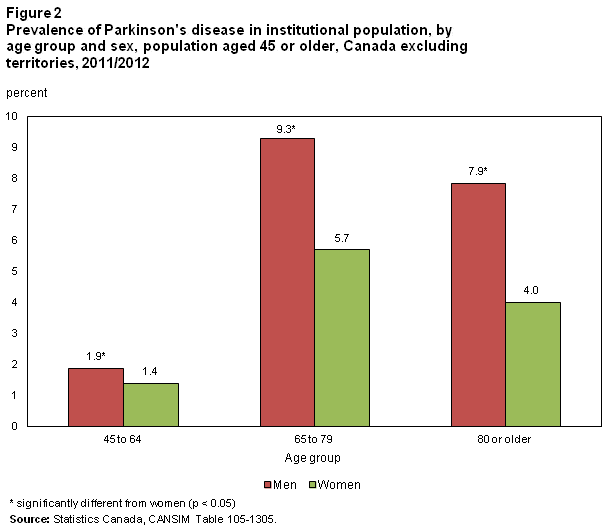
Parkinson’s Disease By Age And Gender
Parkinsons disease generally affects people who are over 60 years old. Early-onset Parkinsons disease is defined as beginning before age 50. The prevalence of Parkinsons disease increases with increasing age, and it is estimated to affect 1 in 40 people who are 85 to 89 years old.
People who begin to have symptoms at an older age generally have more severe symptoms and also have more comorbid conditions , such as heart disease, lung disease, or diabetes.
Parkinsons disease is more common among males than females, affecting approximately twice as many males.
Also Check: Parkinson’s And Alcohol Use
The Ghosts Of Pesticides Past
Over the past half century, we have begun to identify the worst risks and address them. The insecticide DDT was once considered a miracle compound. In the 1930s, the Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Müller was looking for a chemical that could kill insects that were destroying crops and spreading diseasewithout harming the plants. Müller, a nature lover, tested hundreds of chemicals before coating the inside of a glass box with DDT, a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless nerve toxin. He placed houseflies into the container, and they bit the dust. Müller had found his answer.
In the 1940s DDT was considered harmless to humans and regularly sprayed on neighborhoods here children play in the sprays at the beach in New York. Even though DDT was banned half a century ago, it persists in the environmentand in our food supply. It becomes more concentrated as it makes its way up the chain to human consumption. The pesticide is then stored in fatty tissues, including the brain. DDT has been linked to Parkinsons disease. Because of the widespread use of the pesticide, DDT and its breakdown products are detectable in nearly everyone in the United States. It has also been found in the breast milk of women living in Spain, Nicaragua, Taiwan, and the Spanish Canary Islands as recently as 2014.
Pictorial Press Ltd/Alamy Stock Photo
We eat fruits, vegetables, nuts, and grains every day that have been doused in pesticides. What kind of risk are we all exposed to? We do not know.
Systematic Review And Meta
In order to examine whether our findings were consistent with those from studies conducted in other settings using other methods, we undertook a systematic review of PD incidence studies. Two authors sought studies published before 31 January 2015, using Medline we also searched reference lists of papers identified by this search and previous reviews for additional references.,,
Studies were eligible for the meta-analysis if they included PD incidence data broken down by age and sex with at least two of three following parameters available for each age-by-sex strata in order to be able to perform calculations: number of PD cases, person-years, incidence rate. If several publications were based on the same population, we selected the most recent report.
Read Also: Social Security Disability Parkinson’s
Analysis Of The Influential Factors Of Eapc
The ASR in 1990 served as the disease reservoir at baseline, and the HDI reflected the level of human development, and the availability of health resources in settings, including regions and countries. The EAPCs of the incidence, prevalence, and YLDs had a negative association with the corresponding ASRs in 1990 . Meanwhile, only the EAPCs of incidence had a positive association with HDI in 2019 , which further explained that the trends of the ASIR increased pronouncedly in the high SDI regions and countries from 1990 to 2019.
Figure 7. The association s between EAPCs and ASRs in 1990 at the national level. EAPCs of incidence , prevalence , YLDs had negative associations with ASR in 1990, respectively. The association was calculated with Pearson correlation analysis. The size of circle is increased with the numbers in 1990. EAPC, estimated annual percentage change ASR, age-standardized rate YLDs, years lived with disability.
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease And Risk Factors
Parkinsons disease is caused by low dopamine activity in certain areas of the brain. Its associated with degeneration of the substantia nigra, a small area of the brain that produces dopamine, a neurotransmitter that mediates motor movements and other body functions.
The underlying cause or trigger for these changes is not known, although some people have a family history of the condition.
Many potential risk factors have been examined as possible triggers, including exposure to chemicals, but no environmental or lifestyle factors have been confirmed as causing Parkinsons disease.
Also Check: Botox For Parkinson’s Videos
Trends In The Pd Incidence
Globally, the incident number of PD was 1,081.72 × 103 in 2019, which increased 159.73% since 1990. The overall age-standardized incidence rate was 13.43/100,000 in 2019, and it increased with an annual average of 0.61% from 1990 to 2019 . Compared to female patients, male patients had a larger incident number, and a higher increasing trend in ASIR . Among the age groups, the high incident numbers of PD were observed in the patients aged over 65 years, and the largest increasing percentage occurred in the age group of over 80 years .
Table 1. The changes in incidence and prevalence of Parkinson’s disease worldwide, and in sexes, SDI areas, and regions, 19902019.
Figure 1. Trends in the ASR of incidence, prevalence, and YLDs of Parkinson’s disease in global, SDI areas and geographic regions from 1990 to 2019. ASR, age-standardized rate SDI, sociodemographic index YLDs, years lived with disability.
Figure 2. The distribution of Parkinson’s disease incidence in age groups, SDI areas and geographic regions from 1990 to 2019. was the incident number in age groups was the ASIR in SDI areas was the incident number in geographical regions. ASIR, age-standardized incidence rate SDI, sociodemographic index.