Possible Neuroprotective Mechanisms Of Vitamin D In Pd
VDR belongs to the intranuclear receptor superfamily, composing of eight coding exons and three alternative 5 noncoding exons, spanning over 105kb, on chromosome 12 . The most widely studied biallelic polymorphic sites are BsmI, TaqI, ApaI, and FokI. Substantial researches have been carried out to explore the relationship between these allelic variations and PD. Kim et al. detected VDR gene BsmI polymorphisms in over 300 Korean individuals . The frequency of VDR genotype bb was significantly increased in the PD patients than that in the controls . The bb genotype was more common in PD patients with postural instability and gait difficulty than in the PD patients with tremor . A meta-analysis showed that VDR BsmI and FokI polymorphisms were associated with the risk of PD , and VDR FokI genotype was associated with the severity and cognitive decline of PD . Muscular and motor impairments, which can seriously affect the motor behaviour, were found in the VDR-knockout mice , indicating that vitamin D may be involved in the pathogenesis of PD.
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor is a protein that is essential for the maintenance and survival of dopaminergic neurons and can inhibit microglial activation . Many animal studies showed that 1,25-2-D3 could enhance the endogenous GDNF expression in vitro and in vivo and inhibit the glial cell activation to protect dopaminergic neurons from immune inflammation .
Also Check: What Are The Complications Of Parkinsons Disease
Green Tea And Coffee To Reduce The Risk Of Developing Pd
Green tea is prepared from the leaves of the Camellia Sinensis plant and contains phenolic compounds such as -Epigallocatechin-3-gallate a potent antioxidant and neuroprotective compound. Preclinical clinical and self-report studies suggest that green tea may prevent PD . However, the therapeutic mechanism of green teas potential protective actions in PD is unclear. It is feasible that green teas phenolic compounds are modulating critical neuroprotective signaling pathways in the brain . On the other hand, green tea could exert its effects via caffeine-induced inactivation of the adenosine receptor.
Effect Of Cellular Maturity On Transplant Survival And Function
To evaluate the effect of cellular maturity on transplant survival, we injected grafts of D17, D24, D37, or G418 cells into the striatum bilaterally of intact athymic rats. At 3 months post-transplantation , coronal sections stained for human-specific neural cell adhesion molecule revealed relatively small G418 and D37 grafts, with few hNCAM-ir fibers innervating the host striatum. In contrast, large hNCAM-ir grafts, and their processes, were visible in animals engrafted with either D17 or D24 cells. While all grafts contained TH-ir neurons, only D17 grafts were cytoarchitecturally arranged in a manner similar to what is characteristically seen with fVM implants, with dopaminergic cell bodies localized at the periphery of the grafts.
After verifying that our modified differentiation protocol produced cells that are viable in the immunocompromised intact rat brain, we performed a long-term functional study. Rats with unilateral 6-OHDA-induced medial forebrain bundle lesions confirmed by repeated d-amphetamine-induced rotations were transplanted with vehicle control or D17, D24, D37, or G418 cells and sacrificed 6 months post-injection. A summary table describes the histological and behavioral findings for each cell type and dosing group.
Table 1 Summary Table.Fig. 3: Graft survival and function.Fig. 4: Visualization of dopaminergic phenotype in vivo.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s And Kidney Problems
Study Screening And Selection Criteria
Types of Participants
We included studies of participants with PD in the early stages .
Types of Interventions
We included studies of DAs, levodopa, monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors, and catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors to treat motor symptoms of PD in the early stages of the disease.
Comparison Group
We included studies using active comparators only.
Types of Studies
For clinical questions 1 through 6, we included only randomized controlled trials. For clinical questions 7 and 8, we included randomized controlled trials, population-based epidemiologic studies, and prospective cohort studies.
Types of Outcome Measures
The preferred outcome measure was the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale part III, which measures motor symptoms. To determine the change in motor symptoms, the authors calculated the raw mean difference between scores on the UPDRS part III at baseline and at follow-up. To determine the change in dyskinesia, hallucinations, adverse event related discontinuation, and impulse control disorders , the risk differences were calculated.
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
If you have Parkinsons disease, the best thing you can do is follow the guidance of your healthcare provider on how to take care of yourself.
- Take your medication as prescribed. Taking your medications can make a huge difference in the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. You should take your medications as prescribed and talk to your provider if you notice side effects or start to feel like your medications aren’t as effective.
- See your provider as recommended. Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule for you to see them. These visits are especially important to help with managing your conditions and finding the right medications and dosages.
- Dont ignore or avoid symptoms. Parkinsons disease can cause a wide range of symptoms, many of which are treatable by treating the condition or the symptoms themselves. Treatment can make a major difference in keeping symptoms from having worse effects.
Read Also: Rbd And Parkinson’s Disease
Proliferation Gliosis And Serotonergic Contamination In The Grafts
Importantly, in agreement with our previous studies, we observed low levels of continued proliferation in the grafts after 6 months, as determined via unbiased stereology performed on sections stained for hKi-67 . We estimated 2402±1006 hKi-67-ir cells in MFD grafts 1038±741 in high-dose grafts 532±745 in medium-dose grafts and 0±5 hKi-67-ir cells in low-dose grafts, representing 0.4, 0.4, 1.2, and 0.0% of estimated hNuclei-ir cells, respectively. We calculated significant differences for MFD compared to high , medium , and low dose as well as low compared to high and medium dose groups for total number of hKi-67-ir cells and for percentages of low compared to high and maximum feasible dose using KruskalWallis and Dwass, Steel, Critchlow-Fligner method. Again, we report no evidence of teratoma formation.
Fig. 8: Non-dopaminergic cell types observed in grafts.
Representative A micrographs of graft sections stained for hKi-67 and B stereological estimates for each group. C Representative images of graft sections stained for hGFAP , D, Iba1 , and E 5-HT . Scale bar A=100M C=200 M D=500M E=1mm =25M. P< 0.05 for medium vs. low dose P< 0.005 for all other comparisons by KruskalWallis test with Dwass, Steel, Critchlow-Fligner method. *p< 0.05 **p< 0.001.
Dopaminergic Input And Organizational Features Of The Dorsal And Lateral Striatum
As reviewed above, it is generally accepted that dysfunction in PD stems from the degeneration of SNc neurons , which leads to motor dysfunction and the loss of VTA neurons , which leads to behavioral dysregulation, including demotivation, anhedonia, and depression within PD . While both pathways have been studied extensively across an array of conditions and pathologies, the modulatory mechanisms of the nigrostriatal pathway neurons have been fairly well described while the varied mechanisms and roles of VTA efferents continue to be elucidated. Within the nigrostriatal pathway, GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the dorsal/lateral striatum receive excitatory glutamatergic signals that can be modulated via dopaminergic inputs originating from the SNc. MSNs are moderately sized cells with large, multi-structured dendritic arbors that constitute a staggering 95% of all postsynaptic nigrostriatal neurons . Local circuit interneurons of the dorsal striatum are also actively involved in regulating MSN activity and can be subdivided into cholinergic interneurons and aspiny GABAergic interneurons known as low-threshold, fast-spiking neurons . Striatal cholinergic and MSNs express several neurotransmitter receptors including the -aminobutyric acid , glutamate, DA, adenosine, serotonin, opioids, and substance P receptors .
Don’t Miss: How To Be Tested For Parkinson’s Disease
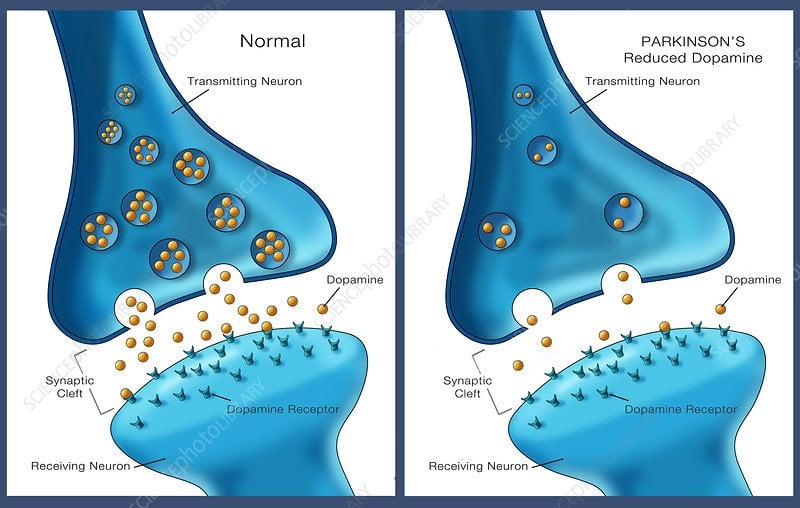
Understanding Dopamine And Parkinsons Disease
- Dopamine is a neurotransmitter responsible for sending signals in the brain to coordinate movement.
- In Parkinsons disease, the cells responsible for making dopamine die off, causing movement problems and other symptoms.
- Treatments are available to increase levels of dopamine in the brain and alleviate symptoms.
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disease caused by low levels of dopamine and improper signaling in the brain, which leads to movement symptoms. Parkinsonism is a set of movement disorders characterized by tremors, muscle stiffness, coordination issues, and slowed movements .
Parkinsons is treated with medications that increase the levels of dopamine in the brain, called dopaminergic treatments. Over time, these medications may cause side effects like dyskinesia that can interfere with daily life.
What Is Dopamines Connection To Parkinsons Disease
For people with Parkinsons disease, dopamine levels are too low. As the dopamine starts to fall, signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease will begin to reveal themselves. That means the smooth, controlled body movements may be replaced by symptoms like tremor or stiffness in limbs. Fluid motions may become slow, shaky, and halted.
Dopamine levels may be significantly reduced by the time these symptoms are noticeable. Some of the earliest signs of Parkinsons disease arent as obvious, and they may occur years before the more significant motor problems arise. These symptoms include:
- difficulty concentrating
Its not clear why dopamine levels drop off in people with Parkinsons disease, but the lower the level of dopamine, the more likely you are to experience symptoms of the disorder.
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke , the symptoms of Parkinsons disease typically begin to appear when a persons brain has lost 60 to 80 percent of their dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra. That means the drop in dopamine may be happening long before symptoms are recognized and your doctor begins the work of trying to determine whats causing issues.
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s A Prion Disease
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Transplantation is not the only application for iPSC cells. Scientists are making iPSCs from patients with Parkinsons and using them in the lab for disease modelling purposes. These neurons act as a powerful tool to study the neuropathology of Parkinsons and they can be used to test substances developed into new drugs to effectively treat the condition.
The MRC Centre for Regenerative Medicine, University of Edinburgh
Dr Tilo Kunaths laboratory in Edinburgh is leading the way here and Cure Parkinsons is providing funding for this research. Dr Kunath is producing pure batches of dopamine neurons under a highly technical process that only a few laboraties in the world are capable of doing safely and effectively to better differentiate and characterise the cell lines which are planned to be used for transplantation.
In addition, Cure Parkinsons is also funding a study led by Prof. Roger Barker, which involves converting a person with Parkinsons own skin cells directly into neurons. These cells are called induced neuronal cells . The goal of the study is to provide a rapid method of growing patient specific cells, which would allow for a more personalised form of testing potential therapies.
Important news updates
Note:
Data Synthesis And Confidence In Evidence Statements For Levodopa Vs Das
-
1. In people with early PD, what is the comparative efficacy of levodopa vs DAs vs MAO-B inhibitors for motor symptoms?
-
2. In people with early PD, what is the comparative risk of adverse effects of levodopa vs DAs vs MAO-B inhibitors?
UPDRS Part III Score
The change in the UPDRS part III score from baseline to endpoint was extracted from studies comparing levodopa to DAs and the RMD between treatments was calculated . Negative values favored levodopa. Where possible, estimates were combined using meta-analysis at specific time points. The minimal clinically important difference in the UPDRS part III score was determined by consensus to be 3 points changes of 1 point or less were considered unimportant.
Long-Acting vs Immediate-Release Levodopa: Change in Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Part III Score From Baseline to Endpoint, Risk of Dyskinesia, Hallucinations, and Adverse EventRelated Discontinuation
The available evidence is insufficient to make conclusions regarding the relative efficacy of long-acting vs IR levodopa for improvement in motor function or the risk of hallucinations. There do not appear to be major differences between long-acting and IR levodopa in the risk of dyskinesia or AE-related discontinuation.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Life Center Of Southern New Jersey
Glucagonlike Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists And Other Antidiabetic Agents
Biological processes involved in PD share common features with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus , including the dysregulation of insulin signaling in the brain. The term brain insulin resistance has been suggested to describe decreased sensitivity of CNS pathways to insulin, followed by disturbances in synaptic, metabolic and immune response functions . Strategies to normalize insulin sensitivity in neurons have thus been in the spotlight of clinical trials aiming to establish whether they may provide neuroprotective actions.
The neuroprotective effect of GLP-1 RAs is assumed to be mediated by improved brain insulin sensitivity however, human studies evaluating their biological effect in the CNS are limited. Functional MRI imaging studies have primarily focused on investigating brain networks involved in the anorectic effect of GLP-1 RAs , but sparse mechanistic data are available for understanding neuroprotective effects of these drugs. In a more recent trial of exenatide in PD, disease modifying effects measured by nigrostriatal dopamine transporter imaging were reported . Subsequently, brain insulin and Akt signaling pathways were also evaluated in neuronal-derived exosomes and it was shown that exenatide treatment, but not placebo, activated these pathways . This significant, secondary analysis of the trial increases understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying the treatment effect and provides a possible biomarker to measure target engagement.
Where Is It Made In The Brain
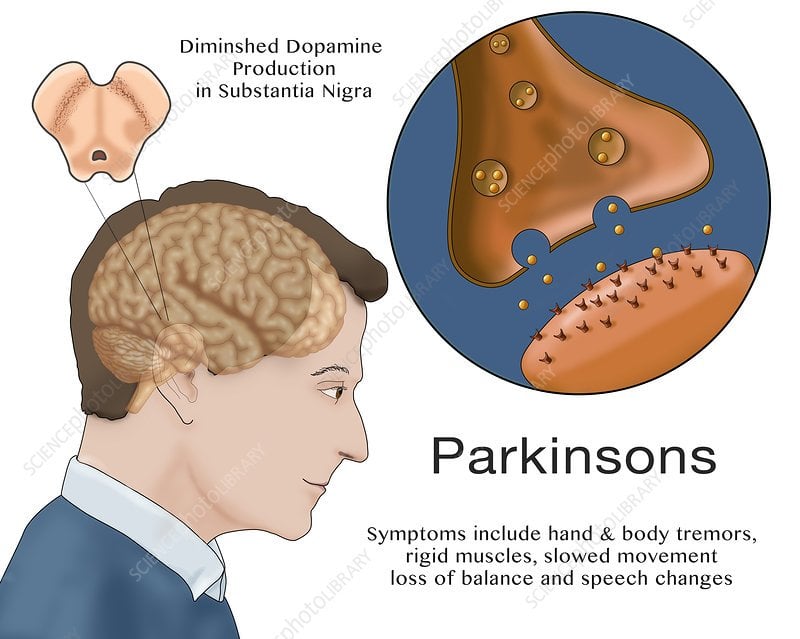
Dopamine is produced in the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, and hypothalamus.1 You may not remember these complicated names. That is fine! It is probably more important to know what these areas of the brain do:1,4-6
- The substantia nigra is part of the brain known as the basal ganglia. This part of the brain is responsible for making movement possible.
- The ventral tegmental area is the part of the brain that is responsible for reward and reinforcement.
- The hypothalamus has many functions. It is responsible for sleep, appetite, body temperature, and sexual arousal, among other things. The hypothalamus helps control the autonomic nervous system.
Recommended Reading: Questions About Parkinson’s Disease
Are There Side Effects From Dopamine Agonists
Side effects from DA medications can vary depending on the medication , dose, how long the medication is used, and individual traits.
If youre experiencing side effects which are bothersome, dont stop taking the medication on your own. Talk to your doctor about treatment options available to help improve your condition. This includes non-medication options too.
Side effects might be mild and go away after a few days or they may be important enough to need either a dose change or to stop the medication. DA medications can cause withdrawal symptoms or worsening of the condition if theyre suddenly stopped.
This is not a full list of side effects. Ask your pharmacist or doctor about specific concerns related to your medication.
side effects
Side effects for dopamine agonists include:
- drowsiness
- heart valve problems, heart failure
- headache
- trouble with memory or concentration
- movement-related problems
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Pivotal Pathological Mechanism Of Parkinsons Disease
Mitochondria are complex cytosolic organelles of eukaryotic cells whose primary function is the generation of cellular energy in the form of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Mammalian mitochondria contain between 2 and 10 mitochondrial DNA molecules encoding 22 transfer RNAs, two ribosomal RNAs, and 13 polypeptides, each of which is part of the respiratory chain and the oxidative phosphorylation system . The mitochondrial respiratory chain contains four protein complexes that form the site of oxidative phosphorylation. This site is responsible for NADH and FADH2 oxidation, co-occurring with the movement of protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space. This movement produces an electrochemical gradient denoted as mitochondrial membrane potential . This gradient stimulates the ATP synthase to reduce molecular oxygen and synthesize ATP. This step is fundamental in aerobic metabolism and constitutes the primary provider of ATP at the final stage of cellular respiration . Nevertheless, the biological function of mitochondria goes far beyond energy production and includes the metabolism of lipids and amino acids and the support of intermediate metabolic pathways, such as the Krebs cycle.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get Disability For Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s Disease: Why Dopamine Replacement Therapy Has A Paradoxical Effect On Cognition
- Date:
- University of Montreal
- Summary:
- Dopamine replacement therapy, which is used to manage motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease, can, at times, adversely affect cognition. Now researchers have identified the reasons why.
Dopamine replacement therapy, which is used to manage motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease, can, at times, adversely affect cognition. Dr. Oury Monchi, Ph. D. in neuronal modeling and Head of the Neurophysiological and Neuroimaging Research theme at the Centre de recherche de l’Institut universitaire de gériatrie de Montréal , which is affiliated with the Université de Montréal, and Dr. Penny A. MacDonald, Neurologist and postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Monchi’s laboratory, have identified the reasons why within the framework of a clinical study recently published in Brain: A Journal of Neurology.
Until now, the effect of dopamine replacement therapy on cognition in individuals with Parkinson’s disease was controversial. The purpose of this study however, was to further investigate. This led to a series of laboratory tests and neuroimaging studies that allowed researchers to clearly define the distinct cognitive functions performed by the dorsal and ventral striatum, thereby shedding some light on the issue.
Summary of the Research
Parkinson’s disease
The authors are grateful for the support provided by the IUGM Foundation and the Canadian Institutes of Health Research.
Story Source:
What Are The Side Effects Of Parkinson’s Drugs
The most common reactions include nausea, vomiting, dizziness , sleepiness and visual hallucinations.
In the last few years, levodopa and dopamine agonists in particular have been associated with the emergence of behavioral changes such as impulse control disorders. These are characterized by failure to resist an impulse to perform certain actions.
Impulse control disorders include a range of behaviors such as compulsive gambling or shopping, hypersexuality, binge eating, addiction to the Internet or to other recreational activities. These activities are often pleasant in the moment, but over time may become harmful to you or to others. If you are experiencing these behaviours, tell your neurologist/doctor. Often the medication can be adjusted which can reduce or control the behaviour.
Care partners can play an important role in helping to identify when these behaviours occur. If you are a care partner, tell the person if you have noticed a change in his/her behaviour or personality and encourage him/him/her to speak with the doctor immediately so medication can be adjusted.
Recommended Reading: Possible Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease