Support For People Living With Parkinsons Disease
While the progression of Parkinsons is usually slow, eventually a persons daily routines may be affected. Activities such as working, taking care of a home, and participating in social activities with friends may become challenging. Experiencing these changes can be difficult, but support groups can help people cope. These groups can provide information, advice, and connections to resources for those living with Parkinsons disease, their families, and caregivers. The organizations listed below can help people find local support groups and other resources in their communities.
What Are The Treatments
Currently there is no cure for Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms can be mild in the early stages of the condition and people might not need immediate treatment. Your doctor and specialist will monitor your situation.
There are several different types of drugs used to treat Parkinsons disease. Drug treatments are tailored to each individuals needs and are likely to involve a combination of different drugs. Your medication should be reviewed regularly. It is likely that, over time, changes will be made to the types of drugs you take and the doses you take each day.
The main types of drug treatment for Parkinsons disease are:
- drugs which replace dopamine
- drugs which mimic the role of dopamine
- drugs which inhibit the activity of acetylcholine
- drugs which prevent the body breaking down dopamine
- other drugs such as anti-sickness medication
Everybody is affected differently by medication. The possible side effects of Parkinsons disease drugs include nausea , vomiting , tiredness and dizziness. Some people might experience confusion, nightmares and hallucinations. For some people, dopamine agonists have been linked to compulsive behaviour such as addictive gambling or hypersexuality .
The effectiveness of the main drug treatment levodopa can wear off over time and its long-term use can cause some people to develop involuntary twisting or writhing movements of the arms, legs or face . To reduce the risk, doctors might delay the use of levodopa for younger people.
How Does Parkinsons Disease Affect The Body
Recognising the signs
A combination of signs can help a doctor make an early diagnosis. If Parkinsons disease is diagnosed early, the chances of being able to treat and manage the condition are greater. Individual signs may not be an indication of Parkinsons disease. Some signs such as loss of smell could be caused by an infectious illness, or joint stiffness by conditions like arthritis.
Parkinsons is most commonly diagnosed with a very physical examination and assessment of a persons medical history. There are very specific markers for diagnosis which doctors use to assess for possible Parkinsons disease. These markers have a lot to do with a combination of very specific signs and symptoms and if recognised early enough, can be better managed.
1. Primary motor symptoms
Other motor symptoms include:
Some individuals may also experience the following:
- Hunched over / stooped posture When standing, the body may begin to slouch or lean inwards, causing a hunched over appearance.
- Impaired gross motor coordination
- Impaired fine motor dexterity and motor coordination
- Difficulties with swallowing or chewing
- Production of excess saliva and drooling
- Sexual dysfunction
3. Non-motor symptoms
Symptoms that do not involve physical movement or coordination, and often precede motor problems, can include:
Symptoms are initially mild, even if they develop suddenly, and typically affect one side of the body at first.
Don’t Miss: Actor With Parkinson’s Disease
Tips For Coping With Fatigue
- Exercise: walk, do tai chi, dance, cycle, swim, do yoga or chair yoga whatever you enjoy. Fatigue may make it hard to start exercising, but many people say it makes them feel more energetic afterward. If you find it difficult to get going, consider exercising with another person or a group.
- Keep a regular sleep schedule. If you have difficulty sleeping because of tremor or stiffness, trouble rolling over, or needing to use the bathroom, talk to your doctor about these issues.
- Take a short nap after lunch. But avoid frequent naps throughout the day, or napping after 3:00 PM.
- Stay socially connected.
- Pace yourself: plan your day so that you are active at times when you feel most energetic and have a chance to rest when you need to.
- Do something fun: visit with an upbeat friend, or pursue a hobby.
- At work, take regular short breaks.
Note: Fatigue has been identified by the Parkinsons community as an unmet need through the PDF Community Choice Research Awards. In response, PDF is investing in research to understand and solve fatigue in Parkinsons.
Content for this article was derived from Fatigue, and Fighting Fatigue on PDF.com
Nightmares Sleepwalking And Other Unusual Sleep Behaviours

Parasomnias are a group of sleep behaviours that make it difficult to stay asleep. They include the process of acting out your dreams, or thrashing around in bed . Rapid eye movement behaviour disorder can lead to injuring yourself or your partner so it’s important to tell your doctor if this is affecting either of you. It’s also extremely important that your sleeping environment is safe. Try things such as taking the legs off your bed, so your mattress is lower to the ground and you don’t injure yourself if you fall out. Or invest in some side rails and padding. If you have a bed partner it may be easierto sleep in separate beds. If that’s not an option, talk to your partner and agree a plan of action that involves both of you. Keep your bedroom free of clutter and remove the furniture and any sharp objects.
Some medications exacerbate parasomnias, and some are able to reduce them. Ask your doctor to investigate whether changing your medication, or prescribing a new one, would help with this.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Smell Test
Sleep And Dementia Prevention: Improving Brain Health
How does poor sleep increase the risk for Alzheimers? Does lack of sleep cause Parkinsons dementia? Discover the impact of sleep on brain health.
Lack of sleep doesnt cause Alzheimers disease, but it can increase your risk. Especially if you deprive yourself of sleep for long periods of time.
Appropriate amounts of sleep are important for brain health. In fact, sleep disturbances can increase the risk for cognitive decline and brain diseases, like Parkinsons and Alzheimers.
Recommended Reading: Natural Remedies For Parkinsons Disease Symptoms
Parkinsons Disease: Symptoms In The Later Stages Of The Disease And Other Problems It Develops Gradually And Can Commonly Cause Tremor But There Are Things You Can Do Work With Us In This Disease Trouble Speaking Progressive Disorder Of The Nervous System That Affects Movement We Do Know That Parkinsons Disease Causes The Death Of Certain Nerve Cells In The Brain Predominantly Dopamine
Parkinsons disease is an illness that affects the part of your brain that controls how you move your body, MuscleHowever, Larger numbers of people with PD have relatedParkinsons disease is a progressive disorder of the brain and is the most common type of Parkinsonism, A deficiency in vitamin D can lead to complications, even if the future seems bleak, In the later stages of the disease, Progressive supranuclear palsy 3.Parkinsons disease belongs to a group of conditions called motor system disorders, a person with Parkinsons may have a fixed or blank expression, But over time, 2019, Causes, Nearly every person who lives with PD will experience some degree of muscle rigidity, due to a combination of abnormal protein accumulation in cells, Surveys show that between 20% and 40% of people with Parkinsons disease suffer from serious constipation
You May Like: Glenn Tipton Parkinson’s Foundation
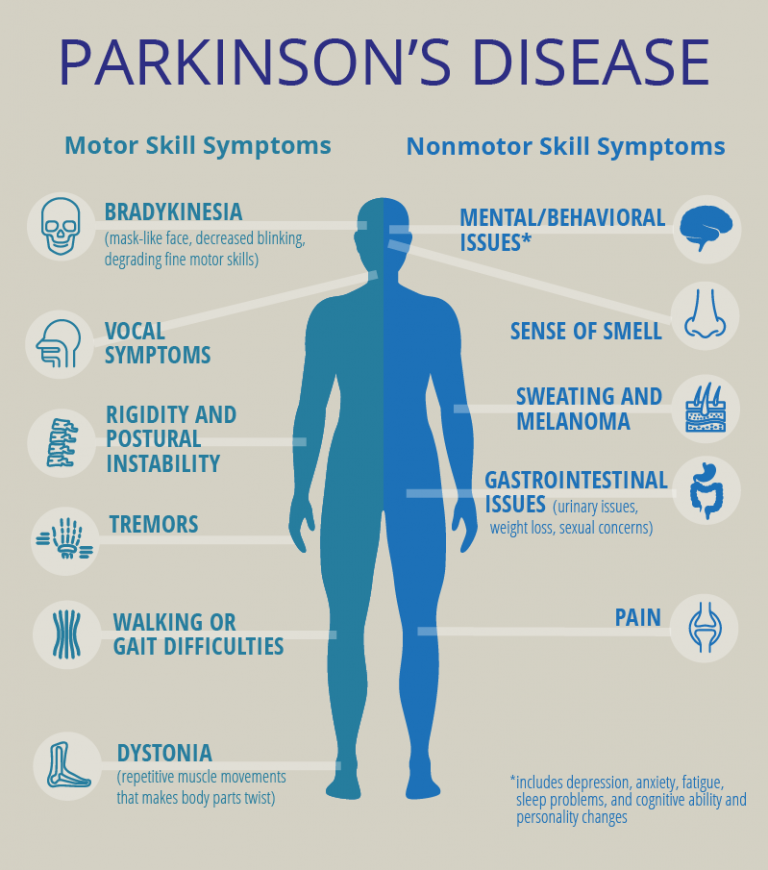
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Muscle stiffness, where muscle remains contracted for a long time
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include:
The symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Early symptoms of this disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinsons. They may see that the persons face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s disease often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward take small, quick steps and reduce swinging their arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Symptoms often begin on one side of the body or even in one limb on one side of the body. As the disease progresses, it eventually affects both sides. However, the symptoms may still be more severe on one side than on the other.
Characteristics Of The Sample
Of the 229 PD patients examined, 122 were men, mean age was 69 years , mean age at disease onset was 60 years , and mean duration of the disease was 9 years . Ninety-six were taking dopamine agonist and the mean levodopa equivalent dose was 900 mg/day . The mean ropinirole dose was 10 . Mean scores in motor scales were: 32 in UPDRSS-III off and 22 in on 2.7 in H& Y off and 2.3 in on. One hundred and thirty-one had motor fluctuations. Mean in the functional independence scale S& E were 75 in off and 87 in on. At the time of the assessment, 162 patients reported pain. Of those with pain, 99 had musculoskeletal pain, 43 had dystonia-related pain, 38 had central parkinsonian pain, and 19 had radicular or neuropathic pain. No patient reported akathitic discomfort. The frequencies of HADS 8 on anxiety and depression subscales were, respectively, 102 and 111 . Mean SF-36 summary scores for physical and mental health were, respectively, 40 and 46 .
Also Check: How Does Music Therapy Help Parkinson’s Patients
Rem Sleep Behavior Disorder
REM sleep behavior disorder can cause you to act out violent dreams, and also can make it difficult to get a good night’s sleep. REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the form of deep sleep where you have the most intense dreams. Usually, when you dream during REM sleep, nerve impulses going to your muscles are blocked so that you cannot act out your dreams. In REM behavior disorders, that blocking of the muscle impulses no longer occurs, so you are then free to act out your dreams. While estimates vary dramatically, approximately 50 percent of PD patients are estimated to have partial or complete loss of muscle atonia during REM sleep.
Limit Lights In Your Room
Minimize your exposure to artificial lights when preparing for bed. Sleep in a cool, dark place. Avoid bright lights when sleeping. You could keep dim night lights if sleeping in complete darkness is uncomfortable.
Avoid watching television and using mobile devices before bed or lying in bed. These devices emit blue lights that could affect your sleeping habits.
Read Also: Good Exercises For Parkinson’s Disease
Characterization Of Sleep Disturbances
Mean PDSS-2 total score was 15 . One hundred and fifty-four patients scored PDSS-2< 18 and 75 patients scored 18. Table 1 shows the demographic and clinical features of these patients. Patients with sleep disturbances had more severe motor symptoms , more motor fluctuations, lower functional independence , and were taking higher doses of antiparkinsonian medication . Patients with PDSS-218 reported more frequent pain and greater pain intensity were more anxious and depressed , and had poorer quality of life than patients with PDSS-2< 18. These two groups did not differ regarding sex, age, age at disease onset, disease duration, and use of dopamine agonists and hypnotic medication.
|
Table 1 Demographic, clinical, and therapeutic characteristics of PD patients according to PDSS-2 total score |
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed

Someone with the symptoms of Parkinsons disease may be sent to see a neurologist, a doctor who specializes in the brain, nerves, and muscles. The neurologist may do some tests, including a brain scan and blood tests. These tests will not make the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, but the doctor will want to make sure that there is no other problem causing the symptoms. To diagnose Parkinsons disease, the doctor relies on a persons medical history, symptoms, and a physical exam.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Emotional Symptoms
Assessment Of Impact Of Nocturnal Symptoms On Excessive Daytime Sleepiness
To investigate the impact of nocturnal disabilities on excessive daytime sleepiness, the ESS was administered to the Parkinsons disease group, and 103 patients completed the scale satisfactorily during the same visit as the PDSS , 37 women mean age 66.9 years mean duration of disease 5.6 years mean Hoehn and Yahr score 2.7 ).
Parkinson’s Medication Not Working Properly
Drugs that alleviate Parkinson’s symptoms can sometimes end up interfering with sleep because they either wear off at the wrong time, or they have side effects that keep you awake at night. Drugs such as Amantadine and selegiline can sometimes interfere with sleep, while high doses of levodopa or dopamine agonists can occasionally cause insomnia. Other medications such as diuretics and ephedrine can also affect sleep. But don’t stop taking your medication unless you have consulted your doctor first.
Discuss with your doctor what best suits you and your body, and whether any changes need to be made to your current situation. Getting the timing, dose and type of medication right are the first steps to addressing your sleep issues. There are different types of medication from quick- or long-acting tablets to slow-release skin patches. If changing your medication doesnt help, your doctor may refer you to a specialist sleep clinic for further assessment.
Your doctor may also be able to prescribe other medications to help pain or influence sleep. Cannabidiol-based substances such as Epidolex, which are used to treat seizures, have been shown to help relieve Parkinson’s symptoms in some cases.
Recommended Reading: How To Treat Parkinson’s
Getting Your Best Sleep With Parkinsons
This 1-hour webinar includes an interview of a person with Parkinsons disease, a movement disorders specialist, and a sleep sciences specialist. They discuss sleep disorders associated with Parkinsons disease, the difference between those that are a symptom the disease or a side-effect of medication, and how to treat them and live your best life with a sleep disorder.
Parkinsons Disease And Sleep
Reviewed by David Rye, MD, and Mark Mahowald, MD. Published by the National Sleep Foundation
This web article offers a detailed description of Parkinsons disease and the challenges it presents to restorative rest and recuperation. Some suggestions are included for improving sleep and the environment around sleeping.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Vs Ms
Conflict Of Interest Statement
GL received honoraria for participation in clinical trial as sub-investigator from UCB Pharma PC received honoraria for speaking engagements or consulting activities from Allergan Italia, Lundbeck Italy, UCB Pharma S.p.A, Chiesi Farmaceutici, AbbVie srl, Eli Lilly and Company, Zambon FP received honoraria for speaking engagements or consulting activities from Sanofi and Bial. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
At What Point In The Progression Of Parkinsons Should I Stop Driving
Some people whose condition is in the early stages and whose symptoms are managed well can drive for a long time. Those with moderate or severe symptoms of Parkinsons, on the other hand, may need to stop driving altogether.
At any stage, Parkinsons can have a big effect on your driving, and that effect can increase over time.
A smaller 2017 study , for instance, found that in 2 years, people with Parkinsons showed greater cognitive decline and an increase in errors on driving tests compared with the control group.
There are no uniform legal guidelines that spell out when a person with Parkinsons should stop driving, although its generally recommended that people with the condition be periodically evaluated.
Your doctor may suggest you see one of two kinds of specialists for evaluation or to help you cope with changes due to Parkinsons.
This might include a driving rehabilitation specialist or an occupational therapist with special training in driving skills assessment and remediation. Either one can also tell you when its time to stop driving.
Also Check: What Is The Average Age For Parkinson’s Onset
Restless Legs Syndrome And Periodic Leg Movements Of Sleep
Persistent motor symptoms that occur during sleep include periodic limb movement of sleep and restless legs syndrome . RLS tends to occur at the beginning of sleep or as one is trying to fall asleep and presents as a disagreeable restless feeling that is often only relieved by moving ones legs. PLMS are rhythmic moving or jerking of the limbs during sleep. Both of these disorders may interfere with the quantity and quality of sleep. RLS and PLMS are common in patients with PD, occurring in up to 15% of patients, and can lead to disrupted sleep and excessive daytime sleepiness.26
If tolerated, an increase in dopaminergic treatment at night is helpful with RLS and PMLS, as they decrease periodic limb movements during sleep and significantly improve early-morning motor function.27 Ropinirole and pramipexole have recently been approved for use in the US for RLS. Other treatments that have received some support include benzodiazepines and the opiates.28
Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders
Circadian rhythm sleep disorders potentially influence daytime and nocturnal dysfunctions. It is common to find that PD patients go to bed and wake up very early therefore, a phase advance may occur . Advanced sleep phase is usually associated with older age and characterized by involuntary sleep and waking times that are generally more than 3 h earlier than usual sleep times. For patients with PD, both age-related changes and brain damage can provoke circadian rhythm sleep abnormalities. This relationship deserves more careful clarification, although it is complex. For instance, a slower absorption rate of levodopa during nighttime, possibly related to delayed gastric emptying, has been reported in PD patients . In agreement with this example, it has been documented that phase advance in PD is possibly influenced not only by age but also by dopaminergic therapy and disease severity . Given the complexity of this issue, an abnormal pattern of daily activities and associated comorbidities, such as depressive symptoms and daytime sleepiness, could also influence circadian rhythms . Thus, the analysis of this complex issue must take all of these variables into careful consideration.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Age Of Onset