Tremor In Other Conditions
While tremor is a common symptom of Parkinsons, it can also be a symptom of other conditions, most notably essential tremor. The main difference between Parkinsons tremor and most other types of tremor is that in Parkinsons resting tremor is most common. Other conditions are usually characterized by action tremor, which tends to lessen at rest and increase when youre doing something, like trying to make a phone call or take a drink.
Tremors of the head and voice are also common in essential tremor but rare in Parkinsons.
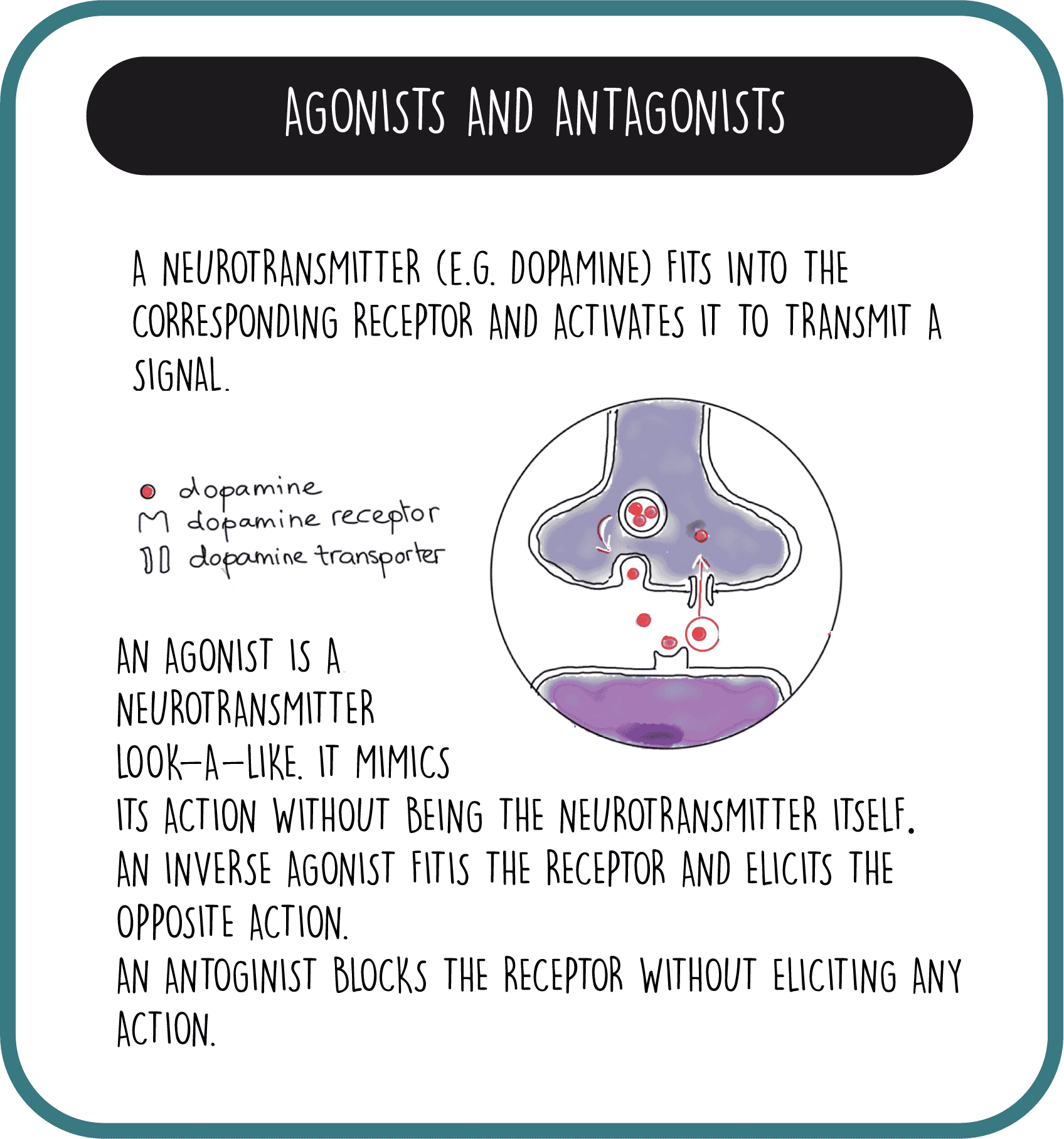
Medications Used For Treating Psychosis
Antipsychotic agents are designed to balance abnormal chemical levels in the brain. Up until the 1990s, the use of antipsychotics in PD was controversial because the drugs used until that time work by reducing excess dopamine. This alleviated psychosis but caused dramatic worsening of PD motor symptoms.Fortunately, medications that are better tolerated by people with PD are now available. Today, there are three antipsychotic medications considered relatively safe for people with PD. They cause limited worsening of PD while treating hallucinations and delusions.
What Are The Symptoms Of Psychosis
Two of the most prominent symptoms are hallucinations and delusions.7 Hallucinations involve seeing, hearing, experiencing or sensing things that are not really there. Delusions are false beliefs that are not based in reality. In describing symptoms of Parkinsons disease psychosis, patients may use such common terms as: seeing things, paranoia, flashbacks, nightmares, false beliefs, or not being in touch with reality.8
Recommended Reading: End Stage Parkinson’s Dementia
Parkinsons Disease Psychosis: Hallucinations Delusions And Paranoia
As part of Parkinsons Disease and its treatment, hallucinations, illusions, delusions, suspiciousness and paranoid behaviors occur in over 50% of patients. In this 1-hour webinar Dr. Christopher Goetz suggests lifestyle changes, medication adjustments and a recently FDA approved drug to specifically treat psychosis in Parkinsons Disease.
Also Check: Early Onset Parkinsons Tremor
What Are Parkinsons Hallucinations
Symptoms of psychosis occur in up to 50% of people with Parkinsons disease.
Parkinsons disease psychosis is considered a neuropsychiatric condition. This means it involves neurology and psychiatry . While the psychosis involves mental health symptoms, they are caused by Parkinsons disease, which is a disease of the nervous system.
Psychosis in Parkinsons disease comes in two forms:
- Hallucinations: Sensory experiences that are not really happening
- Delusions: False beliefs not based on reality
These symptoms can be debilitating and scary for the people experiencing them. They can interfere with a persons ability to care for themselves and to relate to other people.
Psychotic symptoms in Parkinsons disease are associated with increased caregiver distress, risk of hospitalization and nursing home placement, and healthcare costs.
A study suggests the presence of hallucinations and delusions in people with Parkinsons disease is a predictor of mortality .
Don’t Miss: Does Dennis Quaid Have Parkinsons
Hallucinations Delusions And Parkinson’s
It is estimated that about 50% of people with Parkinsons will, at some point, experience hallucinations. They can affect younger people but are more often associated with those who are older and have had Parkinsons for some time.
Hallucinations experienced early in Parkinsons may also be a symptom of the condition dementia with Lewy bodies so it is important to let your doctor know if hallucinations begin at an early stage.
Parkinsons itself can be a cause of hallucinations and delusions, but very often they are a side effect of certain medications used to treat the condition. Not everyone who takes Parkinsons medications will experience hallucinations and delusions though. This varies from person to person and is often related to the particular type of medication and dosage.
Other factors may also be involved such as underlying illness, memory problems, sleep difficulties and poor eyesight.
How Commonly Do Parkinsons Disease Patients Develop Psychosis
Psychosis in Parkinsons disease generally comes in two forms: hallucinations or delusions . When hallucinations occur, they are mostly visual . Sometimes, they can be threatening, but this is less common. Auditory hallucinations are rare in Parkinsons disease and if they do occur, they are usually accompanied by visual hallucinations.
Delusions are usually of a common theme, typically of spousal infidelity. Other themes are often paranoid in nature Because they are paranoid in nature, they can be more threatening and more immediate action is often necessary, compared to visual hallucinations . It is not uncommon that patients actually call 9-1-1 or the police to report a burglary or a plot to hurt them.
Unfortunately, psychosis occurs in up to 40% of Parkinsons disease patients . In the early stage of Parkinsons disease psychosis, the patient often still has a clear understanding and retains their insight, but this tends to worsen over time and insight may eventually be lost. At later stages, patients may be confused and have impaired reality testing that is, they are unable to distinguish personal, subjective experiences from the reality of the external world. Psychosis in Parkinsons disease patients frequently occurs initially in the evening, then later on spills into the rest of the day.
Recommended Reading: Medicine For Parkinsons Hallucinations
You May Like: Parkinson’s And Sugar Cravings
Other Types Of Hallucinations
In addition to persistent or repeated visual hallucinations, a Parkinsons Disease patient might also see a fleeting image out of the corner of their eyes, like a cat or a shadow passing by, but when they turn to look, there isnt anything there. Sometimes they see slight flashes of light, which are very much like reflections off their eyeglasses. A presence hallucination, is another type of experience which is not really a hallucination. With a presence hallucination, patients have a strong feeling of another person, or an animal, being behind them or to the side, but when they turn around, there isnt anything there. This is a strong feeling something most people have experienced on occasion but in this case, its experienced more frequently and more strongly.
Demystifying Hallucinations Night Terrors And Dementia In Parkinsons
This two-hour webinar includes extensive discussion about hallucinations, delusions, illusions and other examples of Parkinsons psychosis in Parkinson’s. Presenters: Rohit Dhall, MD, MSPH and Vergilio Gerald H. Evidente, Director, Movement Disorders Center of Arizona in Scottsdale. Pay particular attention to Dr. Rohit Dhalls description of the causes of PD psychosis as well as treatment options and what to discuss with your movement disorder specialist. Dr. Evidente gives a clear description on differences in PD dementia, Alzheimer’s and other dementias.
Also Check: Non Tremor Parkinson’s Disease
Pathophysiology Of Pd Psychosis
The precise pathophysiology of visual hallucinations in PD remains unclear however, neuropathological and structural imaging studies have provided some insight regarding the type and distribution of pathologic change associated with these phenomena. Neuronal loss in multiple brain regions, with associated LBs containing alpha-synuclein, is the principle pathological finding in Parkinsons disease . However, characteristic Alzheimers disease pathology can be found in the brains of patients with PD and is associated with earlier onset of dementia . Cognitive impairment is a risk factor for visual hallucinations, and concomitant AD pathology has been linked with the phenomena .
Dopamine cell loss in the substantia nigra is a required feature for the pathological confirmation of PD, but this is not the earliest affected area . According to Braaks hypothesis, LBD pathology begins in the olfactory regions and lower brain stem , progresses to the midbrain substantia nigra , and then to the basal forebrain, hypothalamus, thalamus, and hippocampus before spreading to higher-order cortical association areas . The evolution of visual hallucinations in PD has been conceptualized to mirror this spreading pathology with minor experiences indicating brainstem pathology, formed visual hallucinations with insight indicating basal forebrain involvement, and multimodality hallucinations with associated loss of insight and delusions indicating widespread cortical LBD pathology .
What Treatments Are Available For Parkinsons Psychosis
Your doctor may first reduce or change the PD medication youre taking to see whether that reduces psychosis symptoms. This is about finding a balance.
People with PD may need higher doses of dopamine medication to help manage motor symptoms. But dopamine activity shouldnt be increased so much that it results in hallucinations and delusions. Your doctor will work with you to find that balance.
You May Like: Does Weed Help With Parkinson’s
Address Possible Underlying Causes
Sometimes underlying health problems, from acute infections to metabolic changes, can be linked with psychosis, says Dr. Espay. When people develop unexpected psychotic symptoms, Espay says he sometimes orders blood tests to check for infections or changes in kidney or liver function in his patients that may contribute to a change in symptoms.
How Is Psychosis Managed
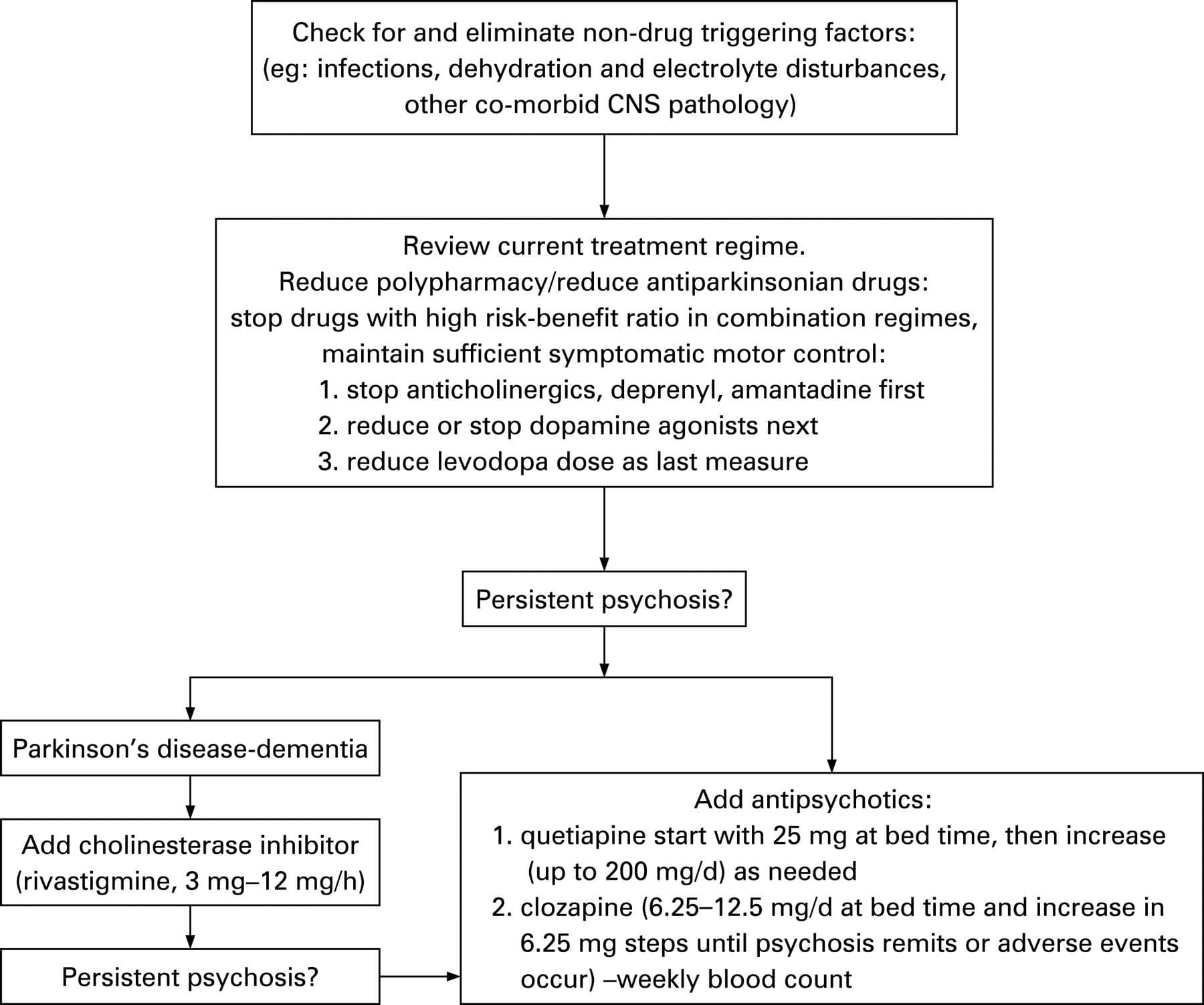
The urgency of treatment will depend on the type and characteristics of psychosis. Sometimes, when the hallucinations are mild and benign, and insight is retained, it is best that the Parkinson regimen be kept as is. However, when a patient is experiencing more threatening paranoid delusions, then more aggressive treatment is warranted .
The management of psychosis includes:
- Follow us on or on .
Dont Miss: What Does Parkinsons Disease Mean
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s Disease A Death Sentence
How Long Does It Take To Work
Nuplazid takes a while to begin working in your body. You may start to notice youre having fewer hallucinations or delusions about 4 weeks after starting the drug. However, in some people, it may take 6 weeks for Nuplazid to work.
Talk with your doctor if you have questions about when you should start seeing results from Nuplazid.
You should take Nuplazid according to your doctors or healthcare providers instructions.
The drug comes as a capsule or a tablet thats taken by mouth.
Examples Of Delusions In Pd
- Belief: Your partner is being unfaithful.
- Behavior: Paranoia, agitation, suspiciousness, aggression.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Multiple System Atrophy
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Disease Shorten Your Life
Hallucinations And Delusions In Pd
Hallucinations and delusions are collectively referred to as psychosis.
Visual hallucinations are the most common type of hallucination. In a visual hallucination, someone sees things that are not actually there. There can also be auditory and olfactory hallucinations. Often hallucinations are not alarming to the person experiencing them.
Delusions are when there is an alternative view of reality: an entire irrational story is created. Paranoia is a common type of delusion. Capgras delusions are a specific type of delusion where the person believes that a spouse, adult child, or other family member has been replaced by an imposter.
Dont Miss: Hip Pain And Parkinsons
Visual Hallucinations: Differential Diagnosis And Treatment
Have you ever encountered a patient who reported isolated visual hallucinations but did not have any other symptoms of delirium or psychosis? Have you wondered which medical and neurologic illnesses may present with visual hallucinations? Have you deliberated about how best to work up and treat patients with visual hallucinations?
If you have, then the following questions and answers should serve to frame the differential diagnosis of visual hallucinations and to explore the available options for diagnostic testing and treatment.
Recommended Reading: Long Term Care For Parkinson’s Patients
Psychosis: A Mind Guide To Parkinsons
Can be downloaded as a PDF or ordered the Parkinsons Foundation online store. This 40-page booklet is a thorough guide to all aspects of Parkinsons psychosis, including symptoms, causes, treatment options, coping strategies for both the family and person experiencing the psychosis, and a chapter on tips for caregivers.
The Cause Of Parkinsons Delusions And Hallucinations
Some risk factors associated with the development of psychosis in Parkinsons disease include:
- Age: Parkinsons disease usually occurs in people over age 60.
- Duration and severity of Parkinsons disease: Psychosis is more common in advanced or late-stage Parkinsons disease.
- Later onset: Occurring later in life
- Hyposmia: A decreased sense of smell
- Cognitive impairment: Problems with thinking, including trouble remembering, difficulty learning new things, difficulty concentrating, problems making decisions that affect everyday life
- Depression: People who have both depression and Parkinsons disease are at a greater risk of developing psychosis.
- Diurnal somnolence: Daytime sleepiness
- REM sleep behavior disorder: A sleep disorder in which you physically act out dreams involves making vocal sounds and sudden, often extreme, arm and leg movements during REM sleep
- Visual disorders: Impaired vision
- Severe axial impairment: Speech, swallowing, balance, freezing of gait
- Autonomic dysfunction: Impairment of the autonomic nervous system , which controls involuntary or unconscious actions such as heart rate, breathing, body temperature, blood pressure, digestion, and sexual function
- High medical comorbidity: The existence of more than one condition or illness in the same person at the same time with Parkinsons disease, may include conditions such as dementia, depression, and sleep disorders
Recommended Reading: Neupro Patch For Parkinson’s
How Delusions May Affect You
When delusions are mild, the person with Parkinsons may know what is happening and can be helped to overcome their false beliefs. A GP or specialist may just monitor the situation.
However, when delusions make people suspicious and distrusting, they can cause problems in relationships, medications and treatments.
With a serious delusion, there is a chance the person could accuse your partner or a family member of something they havent done. They may no longer be able to tell whether things are real or not, which can make them feel very anxious or irritable.
Some people with Parkinsons experience a mixture of hallucinations and delusions. This could lead them to feeling confused and can have an impact on day-to-day life.
Dont Miss: Assisted Living For Parkinsons Patients
What Are Hallucinations And Delusions
Hallucinations are not dreams. They occur when a person is awake. Sometimes people are aware of their hallucinations this is called insight. Hallucinations are categorized by the five senses:
- Visual hallucinations occur when a person sees something that isnt actually there. These types of hallucinations are the most common among people with Parkinsons.
- Auditory hallucinations are sounds that are not there.
- Olfactory hallucinations occur when a person smells a smell that isnt present.
- Tactile hallucinations are experiences of feeling something that isnt there.
- Gustatory hallucinations occur when a person experiences a taste that has no source.
Delusions are false beliefs that are often irrational. They are less common than hallucinations about 8 percent of people with Parkinsons disease experience delusions, according to the Parkinsons Foundation. Often people who have delusions believe they are being mistreated and can become angry or paranoid as a result.
People frequently experience jealousy delusions usually a belief that a spouse is being unfaithful. Persecutory delusions, a belief that someone is conspiring against you or trying to hurt you, are also common. These types of delusions usually involve a spouse, family member, or caregiver.
The delusions make it hard to handle. They are directed at me and are very hurtful, said a MyParkinsonsTeam member caring for a spouse with Parkinsons.
Risk factors for hallucinations and delusions include:
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Non Motor Symptoms
What Is A Hallucination
A hallucination is a perception of something that does not actually exist. This may be visualised, heard, felt, smelled or tasted. Hallucinations are sometimes confused with illusions, which are distortions of a reality rather than something that is purely imagined as with hallucinations.
Visual hallucinations: In Parkinsons, hallucinations are most commonly visual and may be in black and white, in colour, still or moving. Often the images involve small animals and children. They may disappear quickly or may last for some time.
Auditory hallucinations: auditory hallucinations are less common. These generally involve hearing voices or other familiar sounds. Auditory hallucinations can also be part of a depressive symptomatology.
Tactile hallucinations: hallucinations may be tactile, that is, you may feel a sensation, like something touching you.
Smell and taste hallucinations: less commonly you may feel that you can taste something you havent eaten, or you may smell something that is not present, such as food cooking or smoke.
Usually hallucinations are not threatening or distressing. If you hallucinate you may be unaware that your perceptions are not real, and sometimes imagined images or sensations can be comforting. But hallucinations can also be distressing and you may feel threatened or frightened and may need reassurance and comfort from those around you.
Practical Tips For Caregivers Of People With Parkinson’s Psychosis
This 2-page tip sheet has bullet point suggestions for what to do if the person you care for experiences hallucination, delusions or confusion, or becomes agitated or aggressive. In addition, there are tips for how to best be prepared for a doctors appointment when you bring this behavior to the attention of your medical team.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Age Of Onset
Conflict Of Interest Statement
All of the authors were involved in a randomized controlled trial of quetiapine in Parkinsons disease psychosis, which is now complete. This was a noncommercial trial funded by the Parkinsons Disease Society. Dr Michael Samuel has received honoraria for lectures/educational material from UCB, GSK, Medtronic and Orion. He has received unrestricted educational grants from Britannia, Solvay, GSK, Teva, Ipsen, Boehringer-Ingelheim and Medtronic. He has received funding for educational trips from Teva, Ipsen, Pfizer, Medtronic, UCB and Boehringer-Ingelheim.
Recommended Reading: Common Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Whats The Treatment For Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
The single most important thing to do when it comes to Parkinsons disease psychosis is to tell your care providers and partners the minute you notice changes in your vision, hearing, thinking and behavior. The earlier they know whats going on, the sooner they can begin interventions to help you feel better.
Once you bring your concerns up to your doctor, they will typically do a clinical evaluation, review your medications and dosage, assess your lifestyle and determine the severity of your symptoms. Depending upon what they find, they may refer you to counseling or therapy, adjust your medication, change your medication, eliminate medication or do all of the above. If none of those strategies work, they may try antipsychotic drug therapy to see if they can adjust chemical levels in the brain. This can bring with it an entirely different set of problems so its important to be invested every step along the way and be sure youre well-informed before you move in that direction.
Recommended Reading: How Does L Dopa Work In Parkinsons Disease
Also Check: What Are The Stages Of Parkinson Dementia