Analysis Of Flashback Phenomena
In a sub analysis concerning the original hypothesis that led to fx-DBS in AD, we carried out DBS fiber filtering by contrasting stimulation settings that did or did not induce flashback-like phenomena during the surgical procedure,. On a localized level, this effect had been studied before,, but not on a tract level. The sub-cohort in which this information was available included 39 patients in which different DBS parameters were probed, leading to a total of 2054 stimulation volumes, of which 66 resulted in experiential flash-back episodes. In contrast to clinical improvements, flashback-like phenomena were significantly associated with modulation of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure , which interconnects the middle and inferior gyri of the bilateral temporal lobes. Critically, electrical stimulation of these cortical regions has been associated with flashback-like phenomena in multiple historical and contemporary reports,.
Fig. 6: White matter bundle associated with occurrence of flashback-like phenomena.
What Are The Advantages Of Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation has many advantages:
- DBS does not cause permanent damage in any part of the brain, unlike thalamotomy and pallidotomy, which surgically destroy tiny areas of the brain and therefore is permanent and not reversible.
- The electrical stimulation is adjustable and reversible as the persons disease changes or his or her response to medications change.
- Because DBS is reversible and causes no permanent brain damage, use of innovative not-yet-available treatment options may be possible. Thalamotomy and pallidotomy result in small, but permanent changes in brain tissue. A persons potential to benefit from future therapies may be reduced if undergoing these procedures.
- The stimulator can also be turned off at any time if DBS is causing excessive side effects without any long-term consequences.
You May Like: Parkinsons Foundation Miami Florida
Will I Be Able To Resume My Normal Daily Activities
For the first few weeks after surgery, you should avoid strenuous activity, arm movements over your shoulder, and excessive stretching of your neck. You may gradually want to try activities that were difficult before your surgery. Talk about this with your doctor first, and make sure you follow all of your doctors instructions.
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Cause Hearing Loss
Am I A Good Candidate For Dbs
To determine if you are a good candidate, you:
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Clinical Assistant Professor and Dr. Amelia Heston, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Michigan.
Risks And Side Effects Of Deep Brain Stimulation
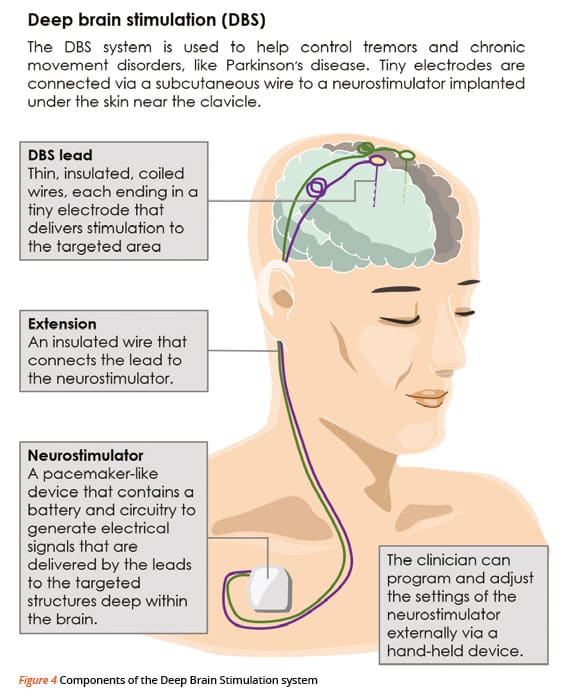
Like any surgery, deep brain stimulation can have side effects, and it carries potential risks. Its also important to consider the complications and side effects of medications you take since their dosages can often be reduced following surgery.
While DBS may cause side effects, it may also reduce side effects from medications.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Leg And Foot Pain
Surgery For Parkinsons Disease: Deep Brain Stimulation And Lesioning
When we refer to surgery in Parkinsons disease it usually refers to Deep Brain Stimulation .Deep Brain Stimulation involves placing a wire with electrodes at its tip into one of three target sites in the brain the thalamus, the globus pallidus or the subthalamic nucleus. A few days after they are connected to an implantable pulse generator . This small unit is inserted under the skin on the chest wall. When the IPG is turned on the electric pulses stimulate the target area and produce a change in the Parkinsonian symptoms..
Before DBS was introduced in the 1980s the only operation available for Parkinsons disease involved selectively damaging certain cells in the thalamus and the gobus pallidus called lesioning. While this sometimes relieved symptoms the damage was irreversible and the operation was risky. With DBS the insertion of the electrodes can be checked to confirm that they have been sited correctly and there are further opportunities for fine tuning through the IPG. The technical advances which have made this operation possible have been the development of CT and MRI scanning which allow the surgeon to locate the target site with great accuracy. While it is not essential, it is usual for the electrodes to be inserted with the patient awake so that they can provide evidence that the target has been reached.
Last reviewed May 2017.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Disease And Essential Tremor
Which Brain Targets Should Be Used To Implant The Dbs Lead
- There are three brain targets that the FDA has approved for use in Parkinsons: the subthalamic nucleus and the globus pallidus interna are the most common.
- The target choice should be tailored to a persons individual needs.
- There are many ongoing studies that will help refine target choice for individual people.
- Although the picture is not yet clear on the issue of target choice, the STN seems to provide more medication reduction, while GPi may be slightly safer for language and cognition.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Ketogenic Diet Pubmed
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
A team of experts, including a movement disorder specialist and a brain surgeon, conducts an extensive assessment when considering DBS for someone. They review your medications and symptoms, examine you when youre on and off Parkinsons medication, and take brain imaging scans. They also may do detailed memory/thinking testing to detect any problems that could worsen with DBS. If your doctors do recommend you for DBS and you are considering the surgery, discuss with your care team the potential benefits as each persons experience is unique. Its also critical to discuss the potential surgical risks, including bleeding, stroke and infection.
In DBS surgery, the surgeon places thin wires called electrodes into one or both sides of the brain, in specific areas that control movement. Usually you remain awake during surgery so you can answer questions and perform certain tasks to make sure the electrodes are positioned correctly. Some medical centers now use brain imaging to guide the electrodes to the right spot while a person is asleep. Each method has its pros and cons and may not be suitable for everyone or available everywhere.
Once the electrodes are in place, the surgeon connects them to a battery-operated device , which usually is placed under the skin below the collarbone. This device, called a neurostimulator, delivers continuous electrical pulses through the electrodes.
Dont Miss: What Are The Cardinal Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
Consult With A Neurologist And A Neuropsychologist
After learning more about DBS, the next step is to make an appointment at a center that specializes in the surgical treatment of Parkinson’s. It is important that anyone considering this surgery be evaluated by a neurologist who is familiar with the procedure, expected benefits and potential risks. If a neurologist thinks you are a good candidate for surgery, and you decide to proceed, meet the neurosurgeon to learn more and prepare for surgery.
Neuropsychological testing is also strongly recommended before proceeding with DBS. This test is often standard to ensure DBS is a good option and help determine how it could affect memory and thinking. DBS will not improve or worsen non-motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s.
Also Check: Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease In Adults
Tremors Persist After Surgery
Brezinski saw an improvement in his left side after his surgery, but his right-side tremors persisted, despite extensive DBS adjustments. In 2019, when Brezinski was transferred to Pope Army Airfield in North Carolina, he reached out to specialists at Duke.
When I first met Paul, what struck me was just how young he was, said Duke neurosurgeon Derek Southwell, MD. I could appreciate what an active person he had been before this condition took hold of him, and it was clear he had been doing all he could to minimize its impact on his life. Still, it was frustrating to think he had been through a surgery that had the potential to really help him, yet he wasnt really experiencing the benefits he had expected.
What Is Brain Surgery For Parkinsons Disease
Brain surgery for Parkinsons disease is done to balance the activity in certain areas of the brain that control physical movement. The surgery can involve placement of a stimulator device or creation of a surgical lesion in the brain.
The areas of the brain that are affected by Parkinsons disease are very small, and they are located deep within the brain. These procedures are done with precision and often with imaging guidance so your surgeon can see the structure of your brain with real-time pictures during the surgery.
Recommended Reading: Enfermedad De Parkinson En Español
What Happens During Surgery
For stage 1, implanting the electrodes in the brain, the entire process lasts 4 to 6 hours. The surgery generally lasts 3 to 4 hours.
Step 1: attach stereotactic frameThe procedure is performed stereotactically, which requires attaching a frame to your head. While you are seated, the frame is temporarily positioned on your head with Velcro straps. The four pin sites are injected with local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. You will feel some pressure as the pins are tightened .
Step 2: MRI or CT scanYou will then have an imaging scan, using either CT or MRI. A box-shaped localizing device is placed over the top of the frame. Markers in the box show up on the scan and help pinpoint the exact three-dimensional coordinates of the target area within the brain. The surgeon uses the MRI / CT scans and special computer software to plan the trajectory of the electrode.
Step 3: skin and skull incisionYou will be taken to the operating room. You will lie on the table and the stereotactic head frame will be secured. This prevents any small movements of your head while inserting the electrodes. You will remain awake during surgery. Light sedation is given to make you more comfortable during the initial skin incision, but then stopped so that you can talk to the doctors and perform tasks.
What Is Parkinsons Disease Surgery
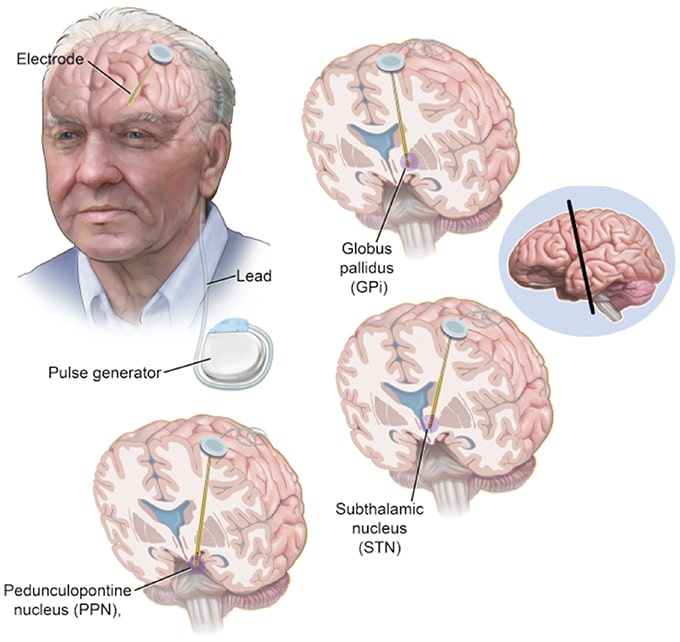
Parkinson’s disease surgery is a brain operation called deep brain stimulation . The surgery is also used to treat epilepsy, obsessive-compulsive disorder and a condition called “essential tremor.” DBS is widely considered one of the most significant neurological breakthroughs in recent history, posing a potential treatment for major depressive disorder, stroke recovery and addiction. Parkinson’s disease brain surgery aims to interrupt problematic electrical signals from targeted areas in the brain and reduce PD symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Huntington’s And Parkinson’s Symptoms
Tracts Associated With Optimal Dbs Response
As the core analysis of this study, we determined the stimulation of which fiber tracts was associated with maximal clinical improvement. This analysis should be seen as the main analysis of the present work since the fornix constitutes a network target aiming to modulate distributed network activity within the circuit of Papez, the target is a white-matter structure readily identifiable by structural imaging and tractography, and tractography could be used to define tract-targets in prospective clinical trials, as has been done previously. We applied the DBS fiber filtering approach, introduced in and methodologically generalized for use with E-fields in. While the method has led to robust results that were predictive across DBS cohorts and surgeons in multiple reports and indications,,, it should still be considered an experimental approach and fiber filtering results hence warrant multiple levels of validations. To do so, patients were first pseudorandomly split into a training and hold-out cohort. We then performed DBS fiber filtering on the training set using an ultra-high resolution normative connectome calculated from a 760µm resolution whole-brain diffusion scan to identify a set of white matter streamlines connected to the stimulation volume of each patient and correlated degrees of overlap with clinical outcome improvements .
Fig. 2: Validation of tract models predictive of clinical improvements as evaluated using ADAS-cog 11.
Effect On Motor Symptoms
Before surgery, the motor symptoms were significantly reduced by 52% by medication . STNDBS significantly reduced UPDRS III by 61% when comparing the OFF/off and the ON/off conditions 1 year after surgery and significantly by 39% at the longterm followup 8 to 15years after surgery .
Medicine significantly reduced motor symptoms further when added to the DBS treatment. The effect of both STNDBS and medicine was a reduction of motor symptoms by 69% 1 year after surgery , and by 51% at the longterm followup compared with the OFF/off condition .
Read Also: What Is The Difference Between Parkinsons And Huntingtons Disease
Read Also: What Leads To Parkinson’s Disease
How Does Dbs Surgery Work
Deep brain stimulation involves electrodes being inserted into the brain through a small opening in the skull. These electrodes have an extension of insulated wire that passes under the skin of the head, neck and shoulder, before connecting the lead to a neurotransmitter or the size of a stopwatch. The neurotransmitter is implanted under the skin, usually near the collarbone. The role of the neurotransmitter is to deliver electrical stimulation to the parts of the brain affected by Parkinson’s disease to block PD symptoms. The device will be turned on a few weeks after the surgery and will be adjusted to find the right setting for you.
Deep brain stimulation cannot cure Parkinson’s disease, nor will it slow down the progression of symptoms. However, most people notice a marked reduction in symptoms after DBS, although many continue to take medication in small doses. The surgery may help you manage the effects of Parkinson’s disease so that you can lead a more comfortable life with the condition.
Am I Eligible for Parkinson’s Disease Surgery?
Before surgery, you will have a series of tests to make sure deep brain stimulation is the right option for you. You’ll also be given a brain imaging scan to map the areas of your brain where the electrodes will be inserted.
According to The Parkinsons Foundation, you may be eligible for DBS if you meet the following criteria:
Parkinsons Disease Surgery: Deep Brain Stimulation
Like all existing therapies for Parkinsons disease, deep brain stimulation has no effect on the progression of the disease. However, it can help you better manage your tremors, slow movements, OFF periods and dyskinesias.
Surgery for Parkinsons disease is limited to certain patients. If you are considering deep brain stimulation surgery, you should have realistic expectations about the results. This technique does not result in a complete cure and results vary from person to person
A multidisciplinary team consisting of a specialized neurologist, neurosurgeon, psychiatrist and other health care professionals can assess your eligibility and explain the benefits and risks of this procedure.
Read Also: Parkinson Symptoms Caused By Medication
Management Of Depression In The Preoperative And Postoperative Phases
The existence of depressive symptoms is not per se a contraindication to DBS surgery. However, ongoing severe depression, psychotic symptoms, and suicidal ideation should be considered absolute contraindications as they might worsen and increase suicidal risk, particularly in the first year after surgery . Less evidence is available regarding severe depressive patients who were eventually stabilized by psychotherapy and medication, months or years prior to undergoing DBS: a trend toward a slightly worse motor and mood outcome has been described, but this certainly does not constitute an absolute contraindication to surgery . In any case, most groups and guidelines support the recommendation of a thorough psychiatric assessment before DBS surgery, and of a careful post-operative follow-up. Of note, the post-operative psychiatric assessment should not be limited to the immediate post-operative period, as the occurrence of apathy, for instance, peaks at around 4 months after surgery, often accompanied by depressive symptoms . Particularly after STN-DBS, which allows for a steeper reduction of dopaminergic medication, dopamine withdrawal symptoms should be prevented, when possible favoring the continued treatment with dopamine agonists .
You May Like: Parkinsons And Heavy Legs
Am I A Candidate For Surgery
If you have PD, you should consider surgery when your medicine becomes insufficient in controlling your symptoms, if you experience severe ups and downs , or if your tolerability of the medication is poor and you develop side effects, including dyskinesias . You should not consider surgery if you have severe depression, advanced dementia, or an unstable medical condition, or if you have symptoms that are atypical for PD and that may represent atypical parkinsonism or Parkinsons plus, such as progressive supranuclear palsy or multiple system atrophy. It is important to understand that surgery will not eliminate your need for medication it will help make your symptoms less severe so that lower doses may be used.
Before determining whether surgery is an option, your condition will be thoroughly evaluated and assessed. A neuropsychologist will assess your thinking and memory and a neurologist will review your current medication regimen and evaluate your physical condition using the Hoehn and Yahr scale and the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale , which examine:
mentation, mood, and behavior motor complications
Recommended Reading: University Of Michigan Parkinson’s Clinic
Deep Brain Stimulation Could Help Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
by Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia, but it is not easily treatable. One potential therapy is deep brain stimulation delivered by a kind of pacemaker. A team of researchers at CharitéUniversitätsmedizin Berlin has found that stimulating a specific network in the brain of Alzheimer’s patients reduces their symptoms. The researchers hope the findings, which appear in Nature Communications, will pave the way for further studies.
Deep brain stimulation is a form of therapy that is already approved in Germany for treating neurological movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and dystonia, and neuropsychiatric diseases such as obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Very thin electrodes are implanted in the patient’s brain and constantly deliver mild electrical pulses to a specific region. The electrodes remain in the brain permanently and are connected via wires that run under the skin to a pacemaker-like device implanted in the chest area. The device is used to adjust the strength and frequency of the electrical stimulation.
“DBS works very well in patients with Parkinson’s,” he says. “It improves their quality of life significantly.” Since Alzheimer’s is also a neurodegenerative disease, it seems likely that DBS could be used to treat this condition, too. But safe, effective treatment is only possible if the precise brain regions that require stimulation are known.”
abcNNature CommunicationsMore information: