Recent Advances In Parkinson’s Disease
Brain neurotransmitters.
Parkinson.org
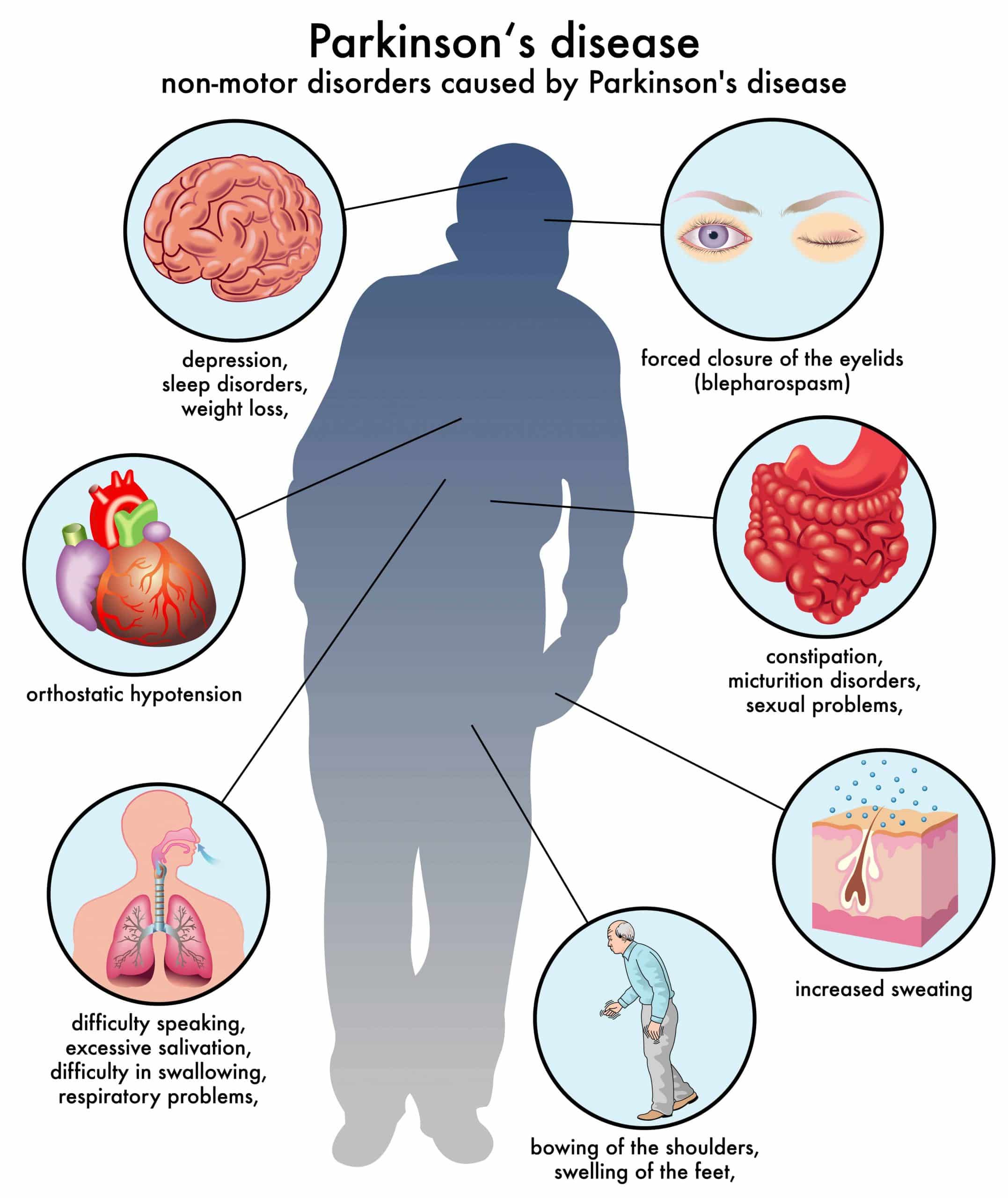
Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that induces symptoms of shaking, stiffness, uncontrollable movement, poor coordination, and balance. Development of Parkinsons disease occurs at the age of 60 onward. This brain disorder develops as early as 50 years old in 5-10% of cases. Parkinsons affects nerve cells deep in the brain called basal ganglia. These cells are responsible for producing dopamine and transmitting messages for bodily functions.
Current treatments replace dopamine to the brain of a patient. Such treatments have been successful at reducing symptoms of nausea. At present, there is no cure for this brain disorder. It is important to manage Parkinsons early on, one new discovery that may help is the use of diagnostic tools.
Early detection of Parkinsons Disease
Biomarkers can be used as a diagnostic tool for identifying the stage of a disease in a patient with abnormal conditions. Researchers at Kobe and Hiroshima University developed a biomarker that detects early Parkinsons in patients’ blood serum samples such it is a quick and inexpensive process as outlined in figure 1.
Figure 1. Changes in P450 expression
https://neurosciencenews.com/parkinsons-biomarker-20673/
Figure 2. P450 inhibition assay process
https://neurosciencenews.com/parkinsons-biomarker-20673/
Model Analysis
Figure 3. Results of analysis using Parkinsons disease model rats and humans with Parkinsons … disease.
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapies For Neurodegenerative Diseases
While there have been significant advances in the symptomatic management of these diseases that improve quality of life and at times survival, the available medications likely only slow the progression of neuronal death by a few months. The idea of using cell therapy to treat neurodegenerative diseases has been around for decades, most notably in Parkinson’s Disease where a variety of cell transplant investigations have been performed with success.
According to a recent study conducted by Nathan P. Staff et al,
“The precise mechanism by which MSCs may exert beneficial effects in neurological disease is still being elucidated, but it appears that multiple different mechanisms may contribute. First, MSCs have been shown to secrete neurotrophic growth factors, including glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor , vascular endothelial growth factor, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor ,which can be further enhanced under specific culture conditions.Neurotrophic growth factors have been shown to improve neuronal survival in a number of preclinical models of neuron injury, including ALS, PD, and MSA transgenic animalsand nerve injury models. â Second, MSCs strongly modulate the immune system and can aid wound healing, and this mechanism has been exploited in disorders such as graft versus host disease and Crohnâs disease. From a neurodegenerative perspective, it has become increasingly recognized that neuroinflammation plays a significant pathomechanistic role.”
Parkinsons Breakthrough Can Diagnose Disease From Skin Swabs In 3 Minutes
A new method to detect Parkinsons disease has been determined by analysing sebum with mass spectrometry.
The study, published today in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, have found that there are lipids of high molecular weight that are substantially more active in people suffering from Parkinsons disease.
The researchers from The University of Manchester used cotton swabs to sample people and identify the compounds present with mass spectrometry. The method developed involves paper spray ionisation mass spectrometry combined with ion mobility separation and can be performed in as little as 3 mins from swab to results.
Professor Perdita Barran at The University of Manchester, who led the research said: We are tremendously excited by these results which take us closer to making a diagnostic test for Parkinson’s Disease that could be used in clinic.
The research used a sample group of 79 people with Parkinsons compared with a heathy control group of 71 people.
The study has arisen from the observation of Joy Milne, who discovered that she can distinguish PD in individuals from a distinct body odour before clinical symptoms occur.
Joy has hereditary Hyperosmia a heightened sensitivity to smells which has been exploited to find that Parkinsons has a distinct odour which is strongest where sebum collects on patients backs and is less often washed away.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Lewy Body Dementia Life Expectancy
Scientists Have Made A Breakthrough In The Development Of A Nasal Spray For Parkinsons Disease Treatment
Researchers from the University of York have developed a new gel that can adhere to tissue inside the nose alongside the drug levodopa, helping deliver Parkinsons disease treatment directly to the brain.
Parkinsons disease is a condition in which parts of the brain become progressively damaged over many years. This leads to a reduction in dopamine in the brain, which plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. The main symptoms include involuntary shaking, slow movement, and stiff and inflexible muscles.
Radical New Therapy For Parkinsons Will Use Stem Cell Transplants
Lab-grown nerve cells will replace those destroyed by disease scientists hope treatment may be available in five years
Early next year, a radical new treatment for Parkinsons disease involving tissue transplants will receive its first trial with patients including a group from the UK.
Stem cells grown in the laboratory and transformed into nerve cells will be used to replace those destroyed by the disease. It is hoped that these will stop the spread of debilitating symptoms.
It has taken a long time to get to this stage but hopefully results from these trials will mean that, in a few years, we might be able to offer tissue transplants as standard treatments for Parkinsons, said Prof Roger Barker, of Cambridge University. It is certainly a promising approach.
In the UK, about 145,000 people live with Parkinsons and about 18,000 new cases are diagnosed every year. The disease is triggered when nerve cells that supply dopamine to the brain start to die due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Dopamine helps a person control movement. When supplies drop, the result is shaking, stiffness, depression and other symptoms that can end with patients using a wheelchair or being bed-ridden. The diseases progress can be slowed by the drug L-dopa, which replaces some of the lost function of dopamine cells. Treatments become less effective over the years. Scientists have been searching for years for new approaches.
Read Also: What Is The Va Rating For Parkinson’s
How Can I Tell The Difference Between Long
Long-COVID is defined as the persistence of symptoms greater than 12 weeks after COVID-19 infection that are not explained by an alternative diagnosis. This phenomenon has been well described in the general population and the more common neurologic symptoms reported are brain fog, or a decrease in concentration and/or memory issues, fatigue, decreased mobility, and sleep disturbances. All of these symptoms are also common in people with PD , so it can be difficult to sort out if these symptoms are occurring as part of long-COVID or not.
This study looked at people with PD who had COVID-19 infection and found a high prevalence of long-COVID symptoms. The study acknowledges that although long-COVID is likely playing a role in the persistence of symptoms, other factors are also relevant including baseline PD symptoms, decreased access to PD healthcare, and decreased rehab efforts during the infection period.
What Are Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Stem cells are the body’s raw materials â cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are created. Mesenchymal stem cells are adult stem cells that have self-renewal, immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, signaling, and differentiation properties. Mesenchymal stem cells , self renewal capacity is characterized by their ability to divide and develop into multiple specialized cell types present in a specific tissue or organ.
Mesenchymal stem cells can be sourced from a variety of tissue including adipose tissue , bone marrow, umbilical cord tissue, blood, liver, dental pulp, and skin.
MSCs are widely used in the treatment of various diseases due to their self-renewable, differentiation, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties. In-vitro and in-vivo studies have supported the understanding mechanisms, safety, and efficacy of MSC therapy in clinical applications.
Recommended Reading: Cbd And Parkinson’s Video
Important Points About The New Medications
With multiple new medications available for the treatment of PD, there is more hope than ever that Parkinsons symptoms can be successfully managed for many years. A few things to consider:
- For people whose symptoms are difficult to control, these new treatments are welcome additions to what was previously available and many people with PD have been using these new medications with significant benefit.
- On the other hand, many of the newly-approved medications have the same mechanisms of action as older medications so they are not breaking new ground in treating symptoms.
- In addition, for some people, the effect on symptoms may be mild or not substantial.
These caveats may mean that your physician has not suggested a medication change for you. It is also important to note that despite all the new medications, carbidopa/levodopa remains the most potent medication to treat the motor symptoms of PD.
If your doctor does choose to try one of the new options, there may be multiple paths that your doctor can take when contemplating a medication adjustment. Often trial and error is the only way to determine the best medication regimen for you, so you may need to practice some patience as you work together with your doctor to determine what works or doesnt work.
Diet And Lifestyle Changes
Additional therapies for Parkinsons disease treatment include eating a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise.
Some individuals may benefit from participating in physical and occupational therapy. These therapies often focus on balance, improving your gait, or tactics to allow you to complete your work.
Other alternative options center on promoting holistic well-being while living with Parkinsons disease. These are not shown to stop the diseases progression but can help you manage symptoms and stay hopeful:
Also Check: Parkinson’s Stem Cell Clinical Trials
Can Having Been Infected With Covid
There have been some articles in the medical literature, suggesting that COVID-19 may be a risk factor for developing PD. This paper reviewed the medical literature and found 20 cases of people who developed parkinsonism in the setting of severe COVID-19 infection . It must be emphasized however, that since COVID-19 remains a new illness, and PD is known to be a disease that develops slowly over years, the relationship between COVID-19 and PD may yet unfold over time. This review article nicely explains many of the issues to consider when thinking about the relationship between COVID-19 and PD.
New research has shed some light on whether COVID-19 can increase the risk of PD. It is well established that the pathologic hallmark of PD is the abnormal aggregation of alpha-synuclein which can be found in the cerebrospinal fluid of people with PD, even very early on in the disease course. The laboratory of Un Kang was not able to isolate any abnormally aggregated alpha-synuclein from the cerebrospinal fluid of patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Although this research is reassuring, the relationship between COVID-19 and Parkinsons disease may yet evolve over time as we learn more.
Editorial Note On The Review Process
F1000 Faculty Reviews are commissioned from members of the prestigiousF1000 Faculty and are edited as a service to readers. In order to make these reviews as comprehensive and accessible as possible, the referees provide input before publication and only the final, revised version is published. The referees who approved the final version are listed with their names and affiliations but without their reports on earlier versions .
The referees who approved this article are:
- Fredric P. Manfredsson, Parkinson’s Disease Research Unit, Department of Neurobiology, Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, Arizona, USANo competing interests were disclosed.
- Tipu Z. Aziz, Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford, Oxford, UKNo competing interests were disclosed.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Affect Swallowing
The Primary Series Of Vaccination Consists Of One Of The Following:
- Two Pfizer-BioNTech vaccines given 3-8 weeks apart
- Two Moderna vaccines, given 4-8 weeks apart
- One Johnson & Johnson vaccine
- Two Novavax vaccines, given 3-8 weeks apart
At least two months after the primary series, a booster is recommended. Currently, the recommendation is to receive the newly introduced Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna bivalent boosters meaning the vaccines have been adjusted to protect against two strains the original virus as well as Omicron variants. If you have had a recent COVID-19 infection, you may delay receiving your next vaccine or booster dose by three months, but this is not necessary.
If you already received a booster, but it was before Sept 2022, the booster was likely not a bivalent booster. You may benefit from receiving a fourth vaccination with the newest type of booster. Talk with your primary care physician about whether this is best for you.
Although this has not yet been determined by the CDC, moving forward it is possible that there will be a recommendation that people receive an annual COVID vaccination, similar to an annual flu shot, that has been adjusted for whatever the prevalent current strain of the virus is. We will update you if and when any official guidelines are publicized.
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention is a great resource for COVID-19-related vaccination information.
Breakthrough In Parkinsons Disease: Israeli Scientists Discover New Therapeutics
Ben-Gurion University Researchers are focusing on bringing their discovery closer to clinical application
Scientists at the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev have discovered that a promising therapeutics protein called BMP5/7 could slow down or even halt the progression of Parkinsons disease .
The findings were published in clinical neurology journal, Brain.
Parkinsons disease affects 1 percent of the population over the age of 60 which is 10 million worldwide or over one million Americans. Approximately 60,000 people are diagnosed with PD each year in the U.S.
Please help us out : Will you offer us a hand? Every gift, regardless of size, fuels our future.Your critical contribution enables us to maintain our independence from shareholders or wealthy owners, allowing us to keep up reporting without bias. It means we can continue to make Jewish Business News available to everyone. You can support us for as little as $1 via PayPal at [email protected]. Thank you.
This disease causes tremors and severe movement impairment due to progressive degeneration of dopamine-producing brain cells. It is believed that the protein alpha-synuclein, present in all human brains, misfolds and forms toxic clumps in these cells, which causes the disease.
While current Parkinsons disease therapies improve symptoms, they are not effective in advanced illness stages and, unfortunately, do not slow or cure the disease.
Also Check: Nad Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons Breakthrough: Scientists Have Identified A Key Molecule
Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement and can cause tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination. It is caused by a loss of cells that produce dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in the bodys movement and reward systems.
Why Scientists Believe Theyve Made New Breakthrough In Parkinsons Disease Treatment By Building On Gdnf Research
The Finnish researchers are now working to improve the properties of BT13 to make it more effective as a potential treatment that could benefit many people living with the disease.
The study, which was published online yesterday in the journal Movement Disorders, builds on previous research on another molecule that targets the same receptors in the brain.
GDNF or glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor is an experimental treatment for Parkinsons discovered in 1993 that has been shown to bring dying brain cells back to life and particularly effective in dopamine neurons.
It was the subject of a BBC documentary in February 2019 that followed a phase two trial in Bristol involving 42 patients. While the results werent clear cut, GDNF has shown promise to restore damaged cells in people with Parkinsons.
However, the GDNF protein requires complex robot-assisted surgery to deliver the treatment to the brain because its a large molecule that cant cross the blood-brain barrier a protective wall that prevents some drugs from getting into the brain.
BT13 is a smaller molecule that is able to cross the blood-brain barrier and therefore could be more easily administered as a treatment if shown to be beneficial in further clinical trials.
Dr Yulia Sidorova, lead researcher on the study, said: We are constantly working on improving the effectiveness of BT13.
Our ultimate goal is to progress these compounds to clinical trials in a few coming years.
Related Article
Also Check: Is Parkinson’s A Prion Disease
Exploring Seven Recently Approved Parkinsons Treatments
Remarkably, in the last five years, seven new medications have been approved for the treatment of the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease , with two approved in 2020. Thats exciting progress! And while it is great to have so many choices, the various options can be confusing so today I will describe these new medications and their uses.
Stem Cells For Parkinson’s Disease Are Safe And Effective
According the Venkataraman and colleagues, “A subjective improvement was found in symptoms like facial expression, gait, and freezing episodes 2 patients have significantly reduced the dosages of PD medicine. These results indicate that our protocol seems to be safe, and no serious adverse events occurred after stem-cell transplantation in PD patients.”
As stated in a 2005 study held by Brian Snyder,
Stem cells offer the potential to provide a virtually unlimited supply of optimized dopaminergic neurons that can provide enhanced benefits in comparison to fetal mesencephalic transplants. Stem cells have now been shown to be capable of differentiating into dopamine neurons that provide benefits following transplantation in animal models of Parkinson’s disease.
Don’t Miss: How To Treat Tremors In Parkinson’s
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in the brain. This loss of nerve cells within the brain results in a reduced amount of dopamine being created which acts as a messenger between the parts of your brain that control voluntary and involuntary movement. Therefore without that vital connection, your brain starts losing the ability to effectively control movement. Currently, it is unknown what causes the deterioration of nerve cells associated with Parkinson’s Disease . Currently, it is believed that both environmental factors, as well as genetic factors, may play a role in the loss of nerve cells.
Parkinson’s Disease is a lifelong condition that can greatly impair the ability of one’s daily functions. Traditional treatments only address the symptoms of the condition, but researchers are excited about the possibilities of certain gene therapies and stem cell therapy, which may have the ability to reverse damage and halt the progression of the disease.