Impulsivity And Obsessive Behaviors In Parkinsons Disease
Among the most startling changes for people with Parkinsons are impulse control disorders and obsessive behaviors. Some people start gambling or overspending, for example. One MyParkinsonsTeam member stayed up all night shopping and bought 10 surfboards in a short amount of time.
Many members of MyParkinsonsTeam have also found that their sex drive skyrocketed. One member said their increasing sexual needs were too much for their partner and strained their marriage. Another member, however, was happy with their wonderful postmenopausal sexual awakening.
Some behavioral changes are similar to obsessive-compulsive disorder symptoms and can cause real problems for people living with Parkinsons. For example, a member said their partner started taking things apart and putting them back together, which became a problem when it led to $3,500 in repair bills. Other times, the obsessive behaviors can be productive, like renewed artistic creativity. One member began making wooden flags to sell and donated some earnings to organizations for veterans.
Drug Reactions: Psychosis And Impulse Control Disorders
PD pharmacologic treatment emphasises dopamine replacement, dopamine receptor stimulation, or prevention of enzymatic breakdown of dopamine in the synaptic cleft.3 While these drugs have their effects on a variety of CNS neurotransmitter systems, they primarily affect dopamine transmission. Thus, it is not surprising that they often produce dramatic behavioural changes that cause significant difficulties for patients and their families and carers.5 There are convincing data that suggest that treatment with dopaminergic agents may be associated with the development of a variety of impulse control disorders in some patients.5 Impulse control disorders, including severe gambling and hyper-sexuality as well as shopping and binge eating, can be extremely disruptive to patients and families.
As with psychosis, impulse control disorders are more commonly associated with the dopamine agonists, pramipexole and ropinirole.11 Given the impact of impulse control disorders, clinicians need to educate patients and monitor them for the early signs of these disturbances.5
Delusions are uncommon in the first two years of PD therapy, but may also occur and, as with hallucinations, are often preceded by vivid dreams.5 These delusions are usually persecutory in nature, including fears of being injured, influenced, poisoned, filmed, and/or tape-recorded.5
What Are The Signs Of Depression
Depression can sometimes make your Parkinson’s symptoms worse. Get in touch with your doctor if you notice any of these things happening to you for longer than 2 weeks at a time.
- You have a depressed mood.
- You can’t find pleasure in things that you once enjoyed.
- You have trouble getting to sleep or you sleep too much.
- Your appetite changes.
- You have thoughts of death.
Also Check: Using Cbd For Parkinson’s Disease
Support For People Living With Parkinsons Disease
While the progression of Parkinsons is usually slow, eventually a persons daily routines may be affected. Activities such as working, taking care of a home, and participating in social activities with friends may become challenging. Experiencing these changes can be difficult, but support groups can help people cope. These groups can provide information, advice, and connections to resources for those living with Parkinsons disease, their families, and caregivers. The organizations listed below can help people find local support groups and other resources in their communities.
What Causes Hallucinations And Psychosis In Parkinsons
The source of psychosis isnt entirely understood. However, changes to important brain structures could be partially responsible. Some cases of psychosis may be caused by long-term treatment with dopaminergic medication. Deep brain stimulation surgery may also worsen existing psychotic symptoms in some people.
Also Check: Environmental Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
Serotonin Hypothesis Of Depression
Serotonin is mainly produced in the dorsal raphe nucleus . Serotonin transporters take up released serotonin from the synaptic cleft into serotonergic neurons in a manner that helps to modulate various functions in the brain including mood and emotion . The striatum, the amygdala, and the prefrontal cortex are regions of the brain that are innervated by serotonergic neurons . These brain regions including the dorsal raphe nucleus which is part of the brains serotonergic system, are activated during early maternal stress . Abnormal 5-HT levels in these brain areas have been associated with depression . Pre-clinical and clinical studies have demonstrated that early life stress affects 5-HT levels in the brain and this may lead to depression . Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors are a class of antidepressant drugs commonly used to treat depression . SSRIs work by blocking 5-HT re-uptake thus increasing the availability of 5-HT in the synaptic cleft as well as its chance to bind to receptors in the post-synaptic membrane . Therefore, by restoring the levels of monoamines and their transporters in the brain, SSRIs drugs are appropriate treatments to address early life stress dysfunction that predisposes to depression later in life.
Read Also: Sleep Problems With Parkinsons Disease
The Effect Of Psychological Stress On The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Study Rationale:Many people with Parkinson’s disease experience chronic stress and associated disorders, such as depression, anxiety or both. Furthermore, many people with PD notice worsening of their motor symptoms during stress. In fact, stress might be a very important contributor to disability in Parkinson’s, and it is potentially amenable to treatment.
Hypothesis:We aim to: test the association between stress and motor and non-motor symptoms of PD, evaluate the association between dispositional mindfulness — the ability to be mindful in everyday life — and perceived stress, and evaluate experience with and/or interest in stress-reducing interventions such as meditation or mindfulness training in people with PD.
Study Design:In this study we will analyze data of people from the Fox Insight cohort at a given point in time. We will ask study participants to complete a questionnaire to assess stress levels, quality of life, personality traits associated with dispositional mindfulness, and the severity of motor and non-motor symptoms. Furthermore, we will also include questions focusing on participant’s experience with stress-reducing therapies.
Impact on Diagnosis/Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease:Stress is potentially an important modulator of motor and non-motor PD symptoms and could be amendable to treatment.
Read Also: Housing For Parkinson’s Patients
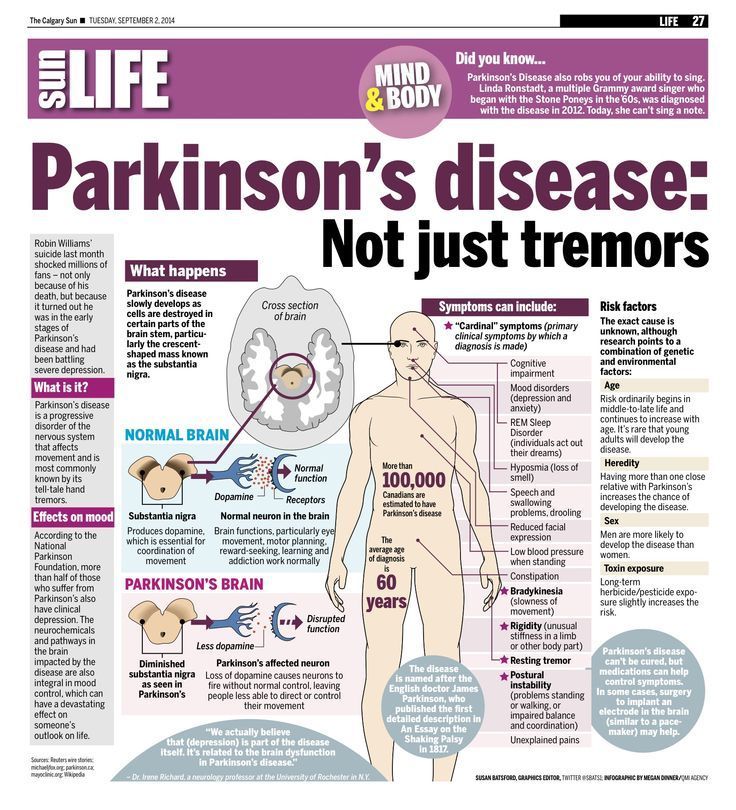
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Muscle stiffness, where muscle remains contracted for a long time
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include:
The symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Early symptoms of this disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinsons. They may see that the persons face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s disease often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward take small, quick steps and reduce swinging their arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Symptoms often begin on one side of the body or even in one limb on one side of the body. As the disease progresses, it eventually affects both sides. However, the symptoms may still be more severe on one side than on the other.
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
You May Like: Can You Be Tested For Parkinsons
Also Check: Ted Talk Parkinson’s Disease
Mood Disorders: Depression And Anxiety
Depression in PD has been the subject of study for a long time. The prevalence rates of depressive syndromes in PD reported in different studies vary widely, ranging from 2.7% to more than 90%, depending on the population studied, the way the diagnosis is established, and the type of prevalence reported . A recent systematic review of the prevalence rates of the different depressive disorders defined in DSM-IV depression in PD reported an average prevalence across studies of 17% for major depressive disorder, 22% for minor depression and 13% for dysthymia. In addition, 35% of patients showed a clinically relevant level of depressive symptoms without meeting the criteria for any specific depressive disorder . As expected, the prevalence of major depressive disorder in PD patients is lower in the general population than in outpatient and inpatient hospital settings . This is the same for the prevalence of clinically relevant depressive symptoms without a formal diagnosis of depressive disorder, which affects 10.8% in the general population versus 40.4 and 54.3% in hospital outpatients and inpatients, respectively .
Anxiety And Parkinsons Disease
Anxiety is another common mood disorder of PD and is characterized by excessive nervousness or worry over several months. Patients with generalized anxiety disorder may experience symptoms such as:
- Restlessness, feeling wound-up or on edge
- Difficulty controlling the worry
- Sleep problems, such as difficulty falling or staying asleep, or restless or unsatisfying sleep1,3
Anxiety is not linked with disease progression of PD. It may develop before or after a PD diagnosis. It is often experienced along with depression in people with PD, as the disease process of PD changes the chemistry of the brain. Treatment for anxiety may include anti-anxiety medications, psychological counseling, exercise, relaxation techniques, and/or meditation.1
Also Check: On Off Phenomenon In Parkinsons Disease
Don’t Miss: Neuroplasticity And Parkinson’s Disease
Psychiatric Manifestations In Patients With Early Pd With Versus Without Mci
It has been previously shown that 27 of our patients with PD fulfilled the MDS Task Force level 2 criteria for MCI in PD, when the z cut-off scores were settled on 1.5 SD. Patients with MCI were more frequently depressed and anxious compared with patients with PD without MCI . PD-MCI patients also had higher SCOPA-S overall and SCOPA-NS scores compared with PD-nonMCI patients. A higher number of symptoms on the NPI , higher NPI scores for depression and sleep disturbances , as well as higher scores for depression distress and sleep distress were found in PD-MCI patients versus patients without MCI. However, no differences were seen for the AS, SCOPA-DS, and SCOPA-PC scores between these two groups of patients.
PD patients with MCI demonstrated a higher grade of altered dreams , sleep fragmentation , and movements during sleep that woke the patient , compared with patients with PD without MCI. There were 16 patients with PD-MCI and 17 patients with PD without MCI who had RBD .
Emotional And Spiritual Well Being

Page contents
Parkinsons is generally thought of as a physical condition but it commonly affects the mind and emotional wellbeing too.
Mood changes are thought to affect around 50% of people with Parkinsons, in particular anxiety and depression. There is increasing acceptance that your state of mind and how you feel will influence how Parkinsons affects you, including the severity of symptoms. Stress for example is directly related to tremor if you are stressed tremor tends to worsen whereas if you are relaxed it generally reduces.
Feeling down, anxious or depressed can certainly affect quality of life so keeping a positive attitude and finding ways to cope with such feelings will play a big part in how you live well with Parkinsons. Whilst it is easy to feel overwhelmed and simply accept the way you feel, there are lots of things you can do to take control of your feelings, look after your emotional wellbeing and influence how Parkinsons affects you.
Recommended Reading: How Does Parkinson’s Start
What Are The Symptoms Of End
In addition to needing help with daily tasks, symptoms of stage 5 Parkinsons include:
- Inability to rise from sitting or lying down without assistance
- Inability to walk or stand due to leg stiffness or freezing
- Possible hallucinations and/or delusions
People with end-stage Parkinsons can have a variety of severe motor and nonmotor symptoms including:
- Personality changes
Management Of Dual Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease And A Mental Health Disorder
Jasmine Carpenter, PharmD, BCPS
Adepeju Awodipe, PharmD Candidate 2015Howard University College of PharmacyWashington, DC
Washington, DC
US Pharm. 2015 40:34-38.
ABSTRACT: Mental health disorders are frequently seen in patients with Parkinsons disease , possibly as a result of the complex imbalance of neurotransmitters in both disease states. This imbalance poses various treatment challenges, such as the exacerbation of both disease states and drug interactions between the medications used to treat PD and mental health disorders. Owing to these challenges, mental health disturbances in PD patients often go untreated. By assisting with ruling out causative medications and underlying disease states, simplifying antiparkinsonian regimens, and recommending antipsychotics, the pharmacist can help ensure that both of these disease states are adequately treated.
Parkinsons disease , which impacts millions of people worldwide, is a neurodegenerative disorder involving the deterioration of motor, mental, and functional skills.1 This degenerative decline increases mortality rates and negatively affects patients quality of life. Motor movement disorders are heavily emphasized as cardinal signs of PD however, nonmotor manifestations such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis are major concerns that must be addressed in this patient population.
Recommended Reading: Ms Symptoms Vs Parkinson’s
Psychiatric Manifestations In Drug
A total of 40 patients with PD were drug naive at the time of assessment. Among treated patients, 19 and 26 were receiving dopamine agonists and levodopa monotherapy, respectively, and the remaining 26 patients were treated with the combination of levodopa and dopamine agonists. Compared with drug-naive patients with PD, treated patients had higher scores on the total SCOPA-S and more vivid dreams on the RBD-SQ . Treated patients did not differ in the frequency of MCI or in the mean ACE-R score compared with drug-naive patients.
Depression May Be An Early Symptom Of Parkinsons
Depression is one of the most common, and most disabling, non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease. As many as 50 per cent of people with Parkinsons experience the symptoms of clinical depression at some stage of the disease. Some people experience depression up to a decade or more before experiencing any motor symptoms of Parkinsons.
Clinical depression and anxiety are underdiagnosed symptoms of Parkinsons. Researchers believe that depression and anxiety in Parkinsons disease may be due to chemical and physical changes in the area of the brain that affect mood as well as movement. These changes are caused by the disease itself.
Here are some suggestions to help identify depression in Parkinsons:
- Mention changes in mood to your physician if they do not ask you about these conditions.
- Complete our Geriatric Depression Scale-15 to record your feelings so you can discuss symptoms with your doctor. Download the answer key and compare your responses.
- delusions and impulse control disorders
Read Also: Grants For Parkinson’s Patients
Tips For Managing Behavioral Changes In Parkinsons
Guidance from medical professionals is crucial, but advice from other people with Parkinsons can make the difference between living and thriving. Following are suggestions from MyParkinsonsTeam members to manage the behavioral changes in Parkinsons disease.
- Find healthy outlets to channel obsessive behaviors, such as art, woodworking, music, or video games.
- Educate yourself and your loved ones so that others can help you identify and manage behavioral symptoms and mood changes.
- Take your medications on time and with a meal or snack if advised. Make sure you take your medication as prescribed, and tell your medical team if you have any side effects.
- If youre a caregiver or loved one of a person with Parkinsons, be patient and pick your battles. Step away, if possible, to clear your head before engaging.
- If behavioral or personality changes make living arrangements with your spouse too tricky, consider separate living arrangements.
- If you have Parkinsons, be kind to yourself. If your loved one has it, give them grace while also taking care of your needs and well-being.
- Its tough to go it alone, so find in-person and online support groups. MyParkinsonsTeam is an excellent place to start.
Take the quiz: Is Your Parkinsons Causing Behavioral Changes?
Tips For Coping With Depression
Caring for your mental well-being is key to living well with Parkinson’s. These strategies can help you manage depression:
- Empower yourself with knowledge about PD and its symptoms, including depression.
- Ask for help it takes courage, but it also puts you in control of finding a way to feel better and overcome feelings of helplessness.
- Keep an open mind. Depression is not a personal failing or a sign of weakness, it is a chemical imbalance in the brain.
- Plan short-term goals that you can achieve daily. Makes plans to walk, do a chore or talk to a friend. Small accomplishments contribute to a feeling of self-worth.
- Maintain social ties. Plan to connect with a friend once a week or take on volunteer work.
- Plan something to look forward to. Think about things you can do to enhance your quality of life and plan how to achieve them in small steps.
- If you have stopped or cut back on leisure activities because of Parkinson’s, try to resume one that you enjoyed or find a new one.
- Connect with the PD community. Compare notes on coping with depression with members of a support group.
Page reviewed by Dr. Kathryn P Moore, Movement Disorders neurologist at Duke Health, a Parkinson’s Foundation Center of Excellence.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Electrical Stimulation Suit
Mimicking Human Conditions In Animal Models
With the advance of the medical research, it is possible to mimic certain human conditions in selected animals, such as mouse or rat, to study the development of a disease and search for treatment. In addition to being very close to the human physiology, these animal models are reliable and critical to develop new treatment strategy and to understand the pathophysiology of a disease.
In the laboratory of Professor Musa V. Mabandla, we have by exposing pups to early maternal separation once daily, from post-natal day 1 to 14. We thereafter injected these rat models with depressive-like behaviors with a preclinical dose of 6-hydroxydopamine stereotaxically into the medial forebrain bundle to mimic Parkinsonism. This has resulted to a rat model of PD associated with depressive-like behaviors.
We also injected these animal models with Fluvoxamine maleate , an antidepressant widely used for the treatment of psychiatric disorders, to investigate the neuroprotective effects of the drug on a parkinsonian rat model of neurodegeneration.
Our findings show that early maternal separation exacerbated the effects of 6-hydroxydopamine, but FM treatment attenuated neurodegeneration associated with 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity.
Liked the blog? Now read the research:
Recommended Reading: Pre Parkinsons Disease Symptoms