How Commercial Stem Cell Clinics Work
A typical treatment at one of these clinics involves removing fat cells from the abdomen , treating the cells in various ways in order to isolate mesenchymal stem cells or stromal cells from the removed tissue, and finally injecting these cells back into the body. The cells are re-introduced into the body in different locations depending on which disease is being targeted. Such treatments are performed for a fee, sometimes a large one, and are not covered by insurance.
Fda Grants Fast Track Designation To Stem Cell Therapy For Parkinsons Disease
We were unable to process your request. Please try again later. If you continue to have this issue please contact .
The FDA granted fast track designation to DA01, a stem cell-based therapy, for the treatment of advanced Parkinsons disease.
DA01 is an allogeneic, gene-edited pluripotent stem cell-derived dopaminergic neuron therapy that is delivered locally through surgical implantation. Preclinical studies have suggested that dopaminergic neurons can restore motor function and increase dopamine release, according to the manufacturers website.
FDA fast track designation helps to expedite development, review and potential approval of treatments for serious or life-threatening diseases.
Receiving fast track designation from the FDA is an important step will help us further accelerate clinical development of our DA01 cell therapy approach for Parkinsons disease,Joachim Fruebis, PhD, chief development officer with BlueRock, said in a company-issued press release. This is another critical step in the BlueRock mission to create authentic cellular medicines to reverse devastating diseases, with the vision of improving the human condition.
Enrollment is underway for a phase 1 trial of DA01 for older patients with advanced Parkinsons disease.
The study is designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of DA01 for patients whose current medications are no longer effective and have not received previous neurosurgical treatment for Parkinsons disease.
World First Stem Cell Trial For Parkinsons Disease Starts
In a bid to cure Parkinsons disease, medical researchers at The Royal Melbourne Hospital have trialed a new revolutionary type of stem cell that is injected into the brain as part of a world-first clinical trial.
Specialist medical equipment for the study was purchased by the Royal Melbourne Hospital Neuroscience Foundation.
Recommended Reading: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
What Types Of Cells Are Used In Parkinsons Disease Stem Cell Treatment
TruStem Cell Therapy provides access to treatment that utilizes a patients stem cells isolated from their own bone marrow. There are multiple inherent benefits afforded by the utilization of bone marrow derived stem cells as Bone marrow and bone marrow components function in various diverse, innate therapeutic capacities.
Hematopoietic stem cells , found within BM, are the bodys source of most cells found in the peripheral or circulating blood. These include red blood cells and white blood cells . Evidence suggests that BM-derived monocytes may act to improve certain neurodegenerative conditions. In this disease environment exhausted microglia cannot efficiently clear A deposits, leading to peptide buildup and neurodegeneration. In this state, monocytes easily bypass the compromised blood-brain-barrier, adhere to A positive veins, then phagocytose and transport peptide from the brain microvasculature into the circulating blood.
In addition to HSCs, mesenchymal stem cells are also contained within BM. Evidence suggests MSCs can enter the circulating blood during injury and have been shown to readily home to areas of injury or inflammation. Once at these damaged tissue sites, MSCs can exert both protective cellular and immunomodulatory effects believed to be critical in many neurological conditions.
Stem Cell Therapy Is Regenerative Medicine
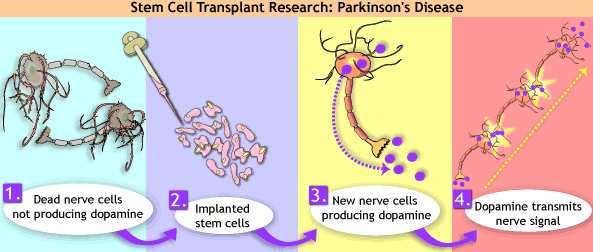
While regenerative medicine including stem cell therapy is still considered an alternative option, it is delivering promising results in the management of chronic symptoms. Stem cells are the building blocks of life, and they can replace damaged or dead cells in the brain.
A range of studies has provided clinicians with cause for optimism in relation to stem cell therapy as a Parkinsons treatment option. When delivered in a targeted way, stem cells may prevent the accumulation of inflammatory cells in the brain. If the rate at which dopamine reduces in the brain can be slowed down, so can the progression of the disease and some of the symptoms.
But thats not all. There is also evidence that replenishing the bodys dopamine levels in this way may also help the body to replenish serotonin levels. Several studies into the use of regenerative medicine for Parkinsons patients point to an enhanced quality of life.
Its important to remember that stem cell therapy for the treatment of Parkinsons symptoms is still classified as an experimental option. And right now, the FDA has not approved it for use outside clinical trial settings. Patients who undergo this regenerative therapy must remain realistic when starting their treatment.
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent Getting Parkinson’s Disease
Box 1 Current Therapeutic Landscape For Parkinson Disease
Currently, the mainstay of treatment for Parkinson disease remains pharmacotherapy and, in some cases, surgery, with attention to patient education, lifestyle adjustments, occupational therapy, diet and exercise.
Pharmacotherapy
Pharmacotherapy to alleviate motor symptoms mostly aims to restore striatal dopaminergic tone, using DA agonists, monoamine oxidase B inhibitors and/or levodopa plus carbidopa,. Anticholinergic medications and amantadine are also useful in some patients. Moreover, pharmacotherapy is efficacious in treating some non-motor symptoms via a broad array of possible drug targets for example, antidepressant medications that manipulate the serotonergic system. However, off-target effects inherent to systemic administration and adverse on-target effects can be limiting, and complications can emerge in the intermediate and long term with levodopa therapy,. In particular, there is a progressive shortening of the duration of action of levodopa, and wearing off of the therapeutic effect occurs with emergence of poorly controlled PD signs and symptoms before the next scheduled levodopa dose.
Surgical treatments
The pipeline
An optimal cell-based therapy would avoid the hardware-associated problems of DBS and the adverse effects that limit dose delivery. It would also be advantageous over magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound ablation by providing a restorative rather than an ablative intervention.
Ipscs As Disease Model For Parkinsons Disease
The contribution of pharmacogenomics has been heightened through the use of patient-specific iPSC lines and genetic engineering technology to manipulate them. Ever since Yamanakas discovery in 2007 that a handful of transcription factors can reprogram cellular differentiation, iPSCs have been utilized extensively in the study of neurodegenerative disease to direct patient-specific cell fate . While still limited in scope, iPSCs are currently the most robust and phenotypically similar model for PD . Mutations of consequence can now be captured in iPSC lines and directed by small molecules to a DAn fate in PD modelsall within a dish. Displayed openly, the real-time cellular effects of mutation can be physically observed and studied in tandem with control lines to limit genetic background effects of the affected individual similarly, effects of oxidative stress common to PD can also be quantified with broad clinical applications for drug screening without human side-effects. Not surprisingly, it remains difficult to physically confirm the mechanisms of neurodegeneration and neuroprotection implicated by iPSC research as patients neurons are hidden deep within the brain. These effects similarly cannot be perfectly translated into the cellular environment of PD due to some epigenetic effects of aging eliminated in reprogramming protocols.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Cause Swelling
What Diseases And Conditions Resemble Parkinsons Disease
PD is the most common form of parkinsonism, in which disorders of other causes produce features and symptoms that closely resemble Parkinsons disease. Many disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of PD, including:
Several diseases, including MSA, CBD, and PSP, are sometimes referred to as Parkinsons-plus diseases because they have the symptoms of PD plus additional features.
In very rare cases, parkinsonian symptoms may appear in people before the age of 20. This condition is called juvenile parkinsonism. It often begins with dystonia and bradykinesia, and the symptoms often improve with levodopa medication.
Compelling Stem Cell Research In Japan About To Begin
On July 30, 2018, Kyoto University announced that a clinical trial using stem cells to treat Parkinsons disease is set to begin.
This trial will recruit seven patients and will use induced pluripotent stem cell-derived dopamine producing cells. These cells are created as follows: Adult skin or blood cells are taken from a donor and reprogrammed in a cell culture dish to revert to an embryonic state. Then, these cells, referred to as IPS cells, are further treated to become dopamine producing neurons. This trial will be the worlds first using IPS cells for the treatment of Parkinsons disease. The engineered IPS cells will be injected deep within the brain, in the basal ganglia, where the ends of the dopamine producing neurons live. Only patients who live in Japan are eligible for the trial.
The adult cells to be reprogrammed will be taken from donors, and not from the trial patients, which means that at least initially, an immunosuppressant medication will be administered to those in the trial to prevent rejection of the cells.
One concern of using IPS cell-derived dopamine producing neurons in humans was that the cells, once injected into the brain would not engraft correctly into the brain and could even cause tumors. To address this concern, the Kyoto group tested these cells in monkeys and last August. The cells that were injected survived and functioned as dopamine neurons. In addition, after two years of observing the monkeys, no tumors were seen.
You May Like: Parkinson’s And Swollen Feet And Ankles
Extranigral Pathology In Pd
Over time, most individuals with PD develop pathology at various CNS and non-CNS sites, leading to levodopa-unresponsive motor symptoms as well as non-motor symptoms. Frequent falls and freezing of gait are motor symptoms that often do not respond to levodopa, and thus are not likely to be ameliorated by DA neuron replacement. Non-motor symptoms such as dementia, psychosis and some sleep disturbances are also not likely to be substantially ameliorated by replacing DA neurons, as these phenomena are thought to relate, at least in part, to damage to neuronal networks besides those traditionally studied in PD, such as the cholinergic and noradrenergic systems,.
Recent advances in our understanding of the networks affected in PD have highlighted their complexity, but compared with the DAergic pathways, the networks involved in non-levodopa-responsive systems are poorly described. It is therefore likely that an optimal effect requires greater characterization of the precise networks affected in each patient and a tailored combination of cells delivered to the relevant locations.
Pure Substantia Nigra Mda Neuron
Recently, single cell gene profiling has been used to define subtype compositions during mouse and human midbrain development . Such technology extended the previous molecular definition of mDA neurons and enabled to further divide SN and VTA region into seven distinct molecular clusters . However, to what extent these molecular findings can be translated into hPSC-derived mDA neuron development remains unexplored. This is illustrated when profiling of hPSC-derived mDA neurons in La Manno et al., which seem to recapitulate key stages of in vivo ventral midbrain development. However, those cell preparations expressed many poorly defined radial glial and neuroblast markers and differed from the in vivo phenotypes in gene expression . Additionally, ALDH1A1 was not expressed in any of those PSC-derived mDA cells. This result may be due to the in vitro culture environment that does not fully support mDA neuron development or lack of proper induction of certain subtype-specific genes. In either case, those results indicate that there is considerable room for further improvements in mDA neuron derivation and maturation strategies.
Don’t Miss: Development Of Parkinson’s Disease
Early Clinical Trial Expectations
In 2018, a groundbreaking clinical trial of surgical transplantation of allogeneic human iPSC -derived DAergic neuron precursors into the putamen of individuals with PD launched in Japan,. Further clinical trials of cell transplants in PD are expected to start soon,,. The first trials of hPSC-derived transplants in PD will have a primary focus on evaluating feasibility, safety and tolerability. If successful, these trials will be followed by efficacy trials. The current trials conducted by academic groups are summarized and compared with the TRANSEURO clinical trial in Table . In addition to these trials, several companies have announced that they are developing commercial cell preparations which, if the trials are successful, will ensure widely available therapies in the future.
Table 1 Academic clinical cell transplantation trials in Parkinson disease
Parkinsons Disease Diagnosis And Prognosis
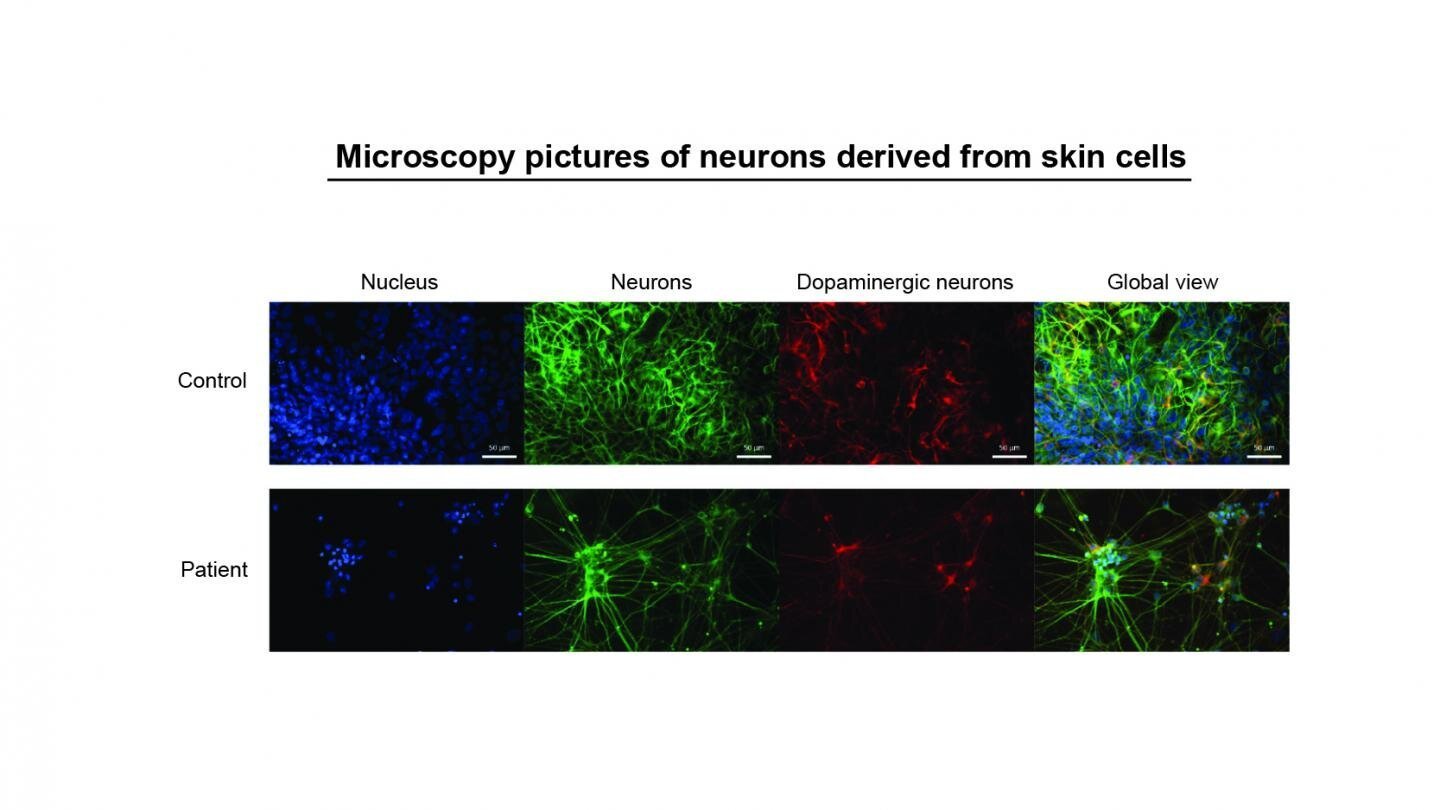
A Parkinsons disease diagnosis cannot be determined by a single test but is rather assigned based on a patients medical history, symptoms, and a series of neurological and physical exams. Each patients Parkinsons disease prognosis is different, as the disease is unique to each person. While all patients will experience some degree of motor dysfunction, the severity and course that the disease takes may differ from person to person.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Regimen
From Cell Replacement To Circuits
A key requirement for cell-replacement therapy to work is that engrafted neurons connect to resident neuronal networks, thereby reconstructing damaged circuits or establishing alternative circuitries that can compensate for the functional deficits elicited by neurodegeneration.
Studies in rodents using allografted fetal VM demonstrate synapse formation from host to graft and from graft to host,. Novel technologies have made the assessment of synaptic integration of hPSC-derived neurons more accessible. For example, retrograde tracing based on modified rabies virus has allowed monosynaptic connections of afferent neurons to and from the graft to be mapped in the 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of PD, and revealed that the host circuitry, specifically nuclei of the intact mesDA system, formed appropriate synaptic contacts with grafted hPSC-derived neurons,. Using the same experimental design, another study demonstrated that grafted neurons also formed synaptic contacts with host circuitry, namely with surrounding striatal medium spiny neurons and neurons of the medial prefrontal cortex that are normally targeted by A10 DA neurons. These studies demonstrate that synaptic integration between host and transplanted neurons is a dynamic process, starting as early as 6 weeks after transplantation and maintained for at least 6 months, that occurs between reconstructed physiologically relevant circuits.
Do Symptoms Get Worse
PD does not affect everyone the same way. The rate of progression and the particular symptoms differ among individuals.
PD symptoms typically begin on one side of the body. However, the disease eventually affects both sides, although symptoms are often less severe on one side than on the other.
Early symptoms of PD may be subtle and occur gradually. Affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. Activities may take longer to complete than in the past. Muscles stiffen and movement may be slower. The persons face may lack expression and animation . People may notice that they speak too softly or with hesitation, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. This very early period may last a long time before the more classical and obvious motor symptoms appear.
As the disease progresses, symptoms may begin to interfere with daily activities. Affected individuals may not be able to hold utensils steady or they may find that the shaking makes reading a newspaper difficult.
People with PD often develop a so-called parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, taking small quick steps as if hurrying , and reduced swinging in one or both arms. They may have trouble initiating movement , and they may stop suddenly as they walk .
You May Like: What Causes Shaking In Parkinson’s Disease
Where Do Stem Cells Come From
Various types of stem cells are found at different stages of human development and in different parts of the body, all of which are of interest to researchers.
Embryonic stem cells: these stem cells are found in fertilised eggs that are only a few days old. These are the only cells that can develop into any type of cell within the body. The abundance of stem cells decreases as the embryo grows and stem cells become specialised cell types that form parts of our body.
Whilst embryonic stem cells are very promising as a treatment for Parkinsons, they also have the risk of uncontrolled growth in the body which could lead to the formation of tumours. Much more research is needed in order for scientists to understand how stem cells work and how they may be used to produce treatments for Parkinsons and many other medical conditions.
Adult stem cells: although adult stem cells exist, they are found in quite small numbers in certain parts of the body and do not multiply quickly. Adult stem cells have been used to treat some conditions for example bone marrow transplants to treat leukaemia. However, it is not currently possible to change adult stem cells into nerve cells suitable as a treatment for Parkinsons.
Bone marrow: these stem cells are found in our bone marrow and bones.
What Are The Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
- Parkinson Stage 1: Only mild symptoms occur in facial expressions or slight tremor. However, the daily life is only minimally affected and only one sided.
- Parkinson Stage 2: At this stage symptoms are getting worse and affect both sides. The tremor and waling problems are getting worse. Often this is the stage where L-Dopamine is employed.
- Parkinson Stage 3: Loss of balance and slowed movements characterize this stage. Living independently is still possible but symptoms significantly impair daily activities.
- Parkinson Stage 4: The Symptoms are severely limiting every activity, especially walking. Movements are still possible but may require aid. Usually living alone is not possible at this stage any more.
- Parkinson Stage 5: The final and most debilitating stage, where stiffness in legs makes movement impossible. The person requires full time nursing and is bound to the wheelchair. Usually many non-motoric symptoms set like delusions, hallucinations and depressions.
You May Like: Can Lead Poisoning Cause Parkinson’s
What Are Stem Cells
Stem cells are a class of immature cells that are able to differentiate, or mature, into specialised cell types. They are found in many parts of the body. In nature, stem cells come from two main sources: embryos , and adult tissue , and are generally characterised by their potential to differentiate into particular cell types, such as skin, muscle or bone. In recent years, stem cells have also generated mature, specialised cells such as skin cells.
As well as the ability to differentiate into another cell type with a specialised function, stem cells are also characterised by the fact that they are able to divide and multiply to form copies of themselves.
These two distinct properties mean stem cells can serve as an internal repair system, dividing without limit to replenish other cells.