How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Autonomic Nervous System And The Heart
In PD, there are two major reasons why the automatic control of the cardiac system is impaired. First, areas of the brain that control this system often contain Lewy bodies and have undergone neurodegeneration. In addition, the autonomic nervous system itself is directly affected by Lewy body-like accumulations and neurodegeneration. This means, when the baroreceptors in the heart and carotid artery sense a drop in blood pressure and try to generate a signal to the heart and blood vessels to increase the blood pressure, the message may not get through. This results in neurogenic orthostatic hypotension , or drops in blood pressure upon standing due to autonomic nervous system dysfunction. There are no medications that can cure nOH by restoring the autonomic nervous system in PD. nOH however, can be treated. Read more about nOH and its treatments here.
Structural problems of the heart such as coronary artery disease or cardiomyopathy are not thought to be part of the pathology of PD, although of course, could co-exist with PD.
How To Manage Symptoms At The End Of Life
At the end of life, good practice is to plan for any potential symptoms that may arise. The most common symptoms anticipated are pain, dyspnoea, nausea and vomiting, agitation, anxiety, delirium and noisy respiratory secretions.18 For patients with PD particular considerations should be given to the more commonly used medicines, specifically anticholinergics and antidopaminergics. These are usually prescribed for treatment of respiratory secretions and nausea and vomiting. Alternatives are available for respiratory secretions, and include glycopyrronium, in preference to hyoscine hydrobromide. Although this is an anticholinergic, only a small proportion crosses the blood brain barrier.
For nausea and vomiting, ondansetron,19 cyclizine, domperidone have all been suggested in PD.20 However, ondansetron has been shown to be inferior to domperidone in the pre-treatment of apomorphine.21 Cyclizine has anticholinergic properties and may exacerbate confusion, especially when comorbid psychosis or cognitive impairment are present. Levomepromazine, although it has antidopaminergic effects, has been shown to be effective for nausea with rotigotine in a case report.22
Agitation, dyspnoea and pain can all be managed with the same anticipatory medications as recommended.20 Specifically relating to PD, several case reports have supported the intraoperative use of midazolam, during sedation, for tremor and dyskinesias,23,24 as well as for agitation at the end of life.20
Autonomic Dysfunction In Parkinsons Disease
Dysautonomia is a prominent non-motor complication of Parkinsons disease that may manifest many years prior to the onset of traditional motor symptoms. However, the nature of this dysfunction in PD remains poorly understood.
We are working with NYU Langones Dysautonomia Center to develop mechanistic understanding and develop biomarkers for these prodromal syndromes of synucleinopathies such as PD, dementia with Lewy bodies , and multiple system atrophy .
We also work with gastroenterologists to systematically study the physiological nature of constipation in PD patients. Using state-of-the-art methods to assess gastrointestinal function, we aim to determine whether PD constipation is unique in its etiology and requires specialized treatment modalities. We are also intensely interested in understanding the role of gut health in the pathogenesis of PD.
You May Like: Are There Support Groups For Parkinson’s Disease
Treatment Of Neurogenic Orthostatic Hypotension
The goal of nOH treatment in patients with synucleinopathies is not to normalize standing BP, but to reduce symptom burden, improve quality of life, and reduce morbidity and mortality associated with nOH.35 Consensus guidelines for the treatment of nOH are available.36, 37 The steps of nOH management include: a) correcting aggravating factors, b) implementing non-pharmacological measures and c) drug therapies. When OH is asymptomatic, treatment may not be required or may be limited to non-pharmacological measures. When nOH is symptomatic pharmacological treatment is usually required .
Algorithm for the management of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in patients with synucleinopathies
Correction of aggravating factors
Drugs that reduce intravascular volume , induce vasodilatation , or block norepinephrine release/activity at the neurovascular junction worsen nOH and symptoms. Levodopa and dopamine agonists may also lower BP and a dose adjustment may be considered based on an individual risk-benefit assessment.38–41 Anemia should be investigated and treated.42 Erythropoietin in conjunction with iron supplements may be beneficial in patients with nOH and anemia.43
Non-pharmacological treatment and patient education
Pharmacological management
Sites of action and mechanism of therapeutic agents used for the treatment of neurogenic orthostatic hypotension
Treatment Of Dysphagia And Drooling
Patients with mild-moderate dysphagia may benefit from postural changes, behavioral changes , and modified meal consistencies .107 Expiratory muscle strength training and video-assisted swallowing therapy may be effective treatments for dysphagia in patients with PD and may also be helpful in patients with MSA.138 Botulinum toxin injections in the distal esophagus have shown some promise to improve esophageal dysphagia in patients with PD.139 Neuromuscular electrical stimulation of the suprahyoid muscles in patients with PD showed no benefits compared to behavioral/postural modifications.140 The role of dopaminergic drugs and deep-brain stimulation surgery is controversial.141–143 Some patients with MSA underwent tracheostomy and laryngeal closure surgery for the treatment of dysphagia with conflicting outcomes.144, 145 If dysphagia is severe, avoidance of the oral route with a gastrostomy tube placement to ensure adequate nutrition/hydration and reduce the risk of aspiration should be discussed with the patient.
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Disability For Parkinson’s
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome
POTS affects anywhere from 1 to 3 million people in the United States. Nearly five times as many women have this condition compared to men. It can affect children, teenagers and adults. It can be also associated with other clinical conditions such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, an inherited condition of abnormal connective tissue.
POTS symptoms can range from mild to severe. Up to one out of four people with POTS have significant limitations in activity and are unable to work due to their condition.
Correlation Between Scale For Outcomes In Parkinsons Disease For Autonomic Symptoms And Clinical Factors
The presence and severity of AutD can be affected by diverse clinical factors as some autonomic phenotypes may occur simultaneously with other clinical symptoms. To thoroughly investigate the correlation between SCOPA-AUT and other PD clinical manifestations, we employed partial correlation analysis investigating the SCOPA-AUT total score and its six subdomains . The total SCOPA-AUT score was significantly and positively associated with the motor severity scales and some of the non-motor symptoms, such as ESS and RBD. Meanwhile, the overall score of AutD and almost all the subdomains of AutD, except for the sexual domains, showed a significant correlation with the HAMD, fatigue scale, and PDQ-39, all of which were commonly used methods for the assessment of the quality of life. The gastrointestinal domain turned out to be the most significant contributor among all the domains of the SCOPA-AUT scale. The PDSS, MMSE, and HRS scores, in which lower scores indicate more severe symptoms, were also significantly and negatively correlated with the AutD total score and most of the subdomains. Details are shown in Figure 2. Together these results emphasize that autonomic dysfunctions are a key factor affecting the quality of life of patients with PD.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Lifestyle Changes
Research Is Underway To Further Understand The Cardiac Effects Of Parkinsons
It is possible to image the sympathetic nervous system of the human heart by injecting a radioactive tracer, meta-iodo-benzyl-guanidine, . Development of this technique, known as MIBG cardiac imaging, holds much promise as a test to confirm the diagnosis of PD , to identify those who are at risk of developing PD in the future, and to distinguish PD from related disorders. MIBG cardiac imaging is still considered an experimental procedure for detection of PD and is not yet in use as a clinical tool for this purpose.
A recent research study was conducted in monkeys in which the destruction of the sympathetic nerves of the heart was chemically induced to mimic the changes that are seen in PD. The cardiac system was then imaged using a number of new-generation radioactive tracers, which bind to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. This model system may help to shed light on the molecular changes that accompany the loss of the sympathetic nerves of the heart and can also be used to track the response of the cardiac system to therapeutic agents.
Also Check: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinsons
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth is associated with malabsorption due to a bacterial density above 105 colony-forming units/mL of small intestinal aspirate and/or the presence of colonic-type species . Recently, SIBO has been implicated as a gastrointestinal dysfunction in PD, and the prevalence of SIBO in PD ranged from 54% to 67% . SIBO in PD could be associated with worse onmedication motor scores and more severe motor fluctuations . The eradication of SIBO using rifaximin 400 mg 3 times a day for 7 days resulted in improvement in motor fluctuations without affecting the pharmacokinetics of levodopa . Therefore, it can be postulated that impaired gut motility in PD leads to SIBO, which may in turn induce a secondary inflammatory response in the gut mucosa and impair levodopa absorption.
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Affect Speech
Definition Of Autonomic Dysfunction
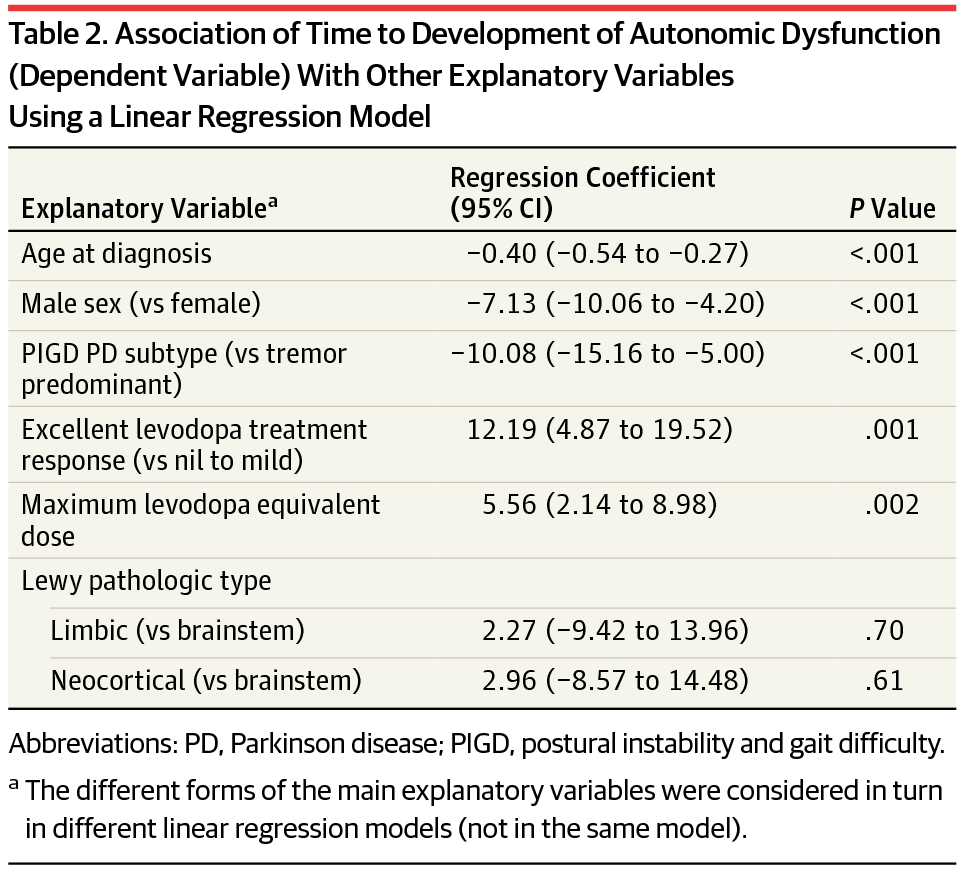
Autonomic dysfunction was defined as a score greater than or equal to one in SCOPA-AUT. A score of zero was regarded as normal autonomic function. Each of the six autonomic domains was categorized as impaired when at least one of the related items was rated. Referring to Merola, patients were further divided into three subgroups according to the number of affected domains: without AutD, with single-domain AutD, and with multiple-domain AutD .
Treatment Of Detrusor Underactivity
Incomplete bladder emptying as a consequence of detrusor underactivity is common in MSA and seldom reported in patients with PD, DLB or PAF. Estimation of the post-void residual bladder volume is a simple and useful test in patients with MSA even though their urinary complaints may be limited to urinary urgency or frequency, patients are usually unaware that their bladders do not empty completely. PVR can be measured by ultrasound echography or transurethral catheterization. If the patient has a PVR > 100 ml, clean intermittent self-catheterization must be recommended. Either the patient or the caregiver can usually perform this after education is provided. In patients with advanced disease and severe neurological disability, a permanent indwelling catheter, usually suprapubic, may be required. Antimuscarinic or 3-adrenergic treatment to reduce bladder overactivity should be added regardless of the PVR. The caveats are the same as with the treatment of overactive bladder. Replaceable remote-controlled intra-urethral prosthesis for women with underactive bladder have been recently approved by the U.S. FDA 209 these do not require surgery, increase quality of life, and reduce the risk of urinary complications, although the experience in patients with MSA is still limited .
Algorithm for the management of underactive bladder in patients with synucleinopathies
Read Also: Music Therapy For Parkinson’s
Subdomains Of Autonomic Dysfunction
To determine which autonomic symptoms drove the associations, post hoc analyses were performed with subdomains of the SCOPA-AUT. These results showed that the reported associations with the total SCOPA-AUT were mainly driven by cardiovascular and gastrointestinal symptoms . Also here, adding UPDRS-III scores to adjust for the influence of disease severity, only FP-CIT binding in the right caudate nucleus was significantly associated with autonomic symptoms .
Stages Of Parkinsons Disease: Progression Of Parkinsons
The Parkinsons disease stages are well-known among doctors. If you are diagnosed with Parkinsons, its important to be aware of these stages so you can prepare yourself and your family for the future. As the disease progresses, you may develop further needs or require full-time care. Find out everything you need to know about the five stages of Parkinsons disease and the progression of Parkinsons symptoms.
Also Check: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Parkinson’s Disease
Involvement Of The Autonomic Nervous System In Pd
PD is characterised by deposition of abnormally phosphorylated -synuclein. The aggregates are typically found in neurons as Lewy bodies. Alongside the hallmark degeneration of the substantia nigra in PD, Lewy bodies and cell loss are detected in: autonomic regulatory areas such as the hypothalamus, parabrachial nucleus, intermediate reticular zone of the medulla, locus coeruleus and raphe preganglionic parasympathetic regions, such as the EdingerWestphal nucleus and dorsal vagal motor nuclei preganglionic sympathetic neurons in the intermediolateral cell column and neurons in paravertebral and paravertebral autonomic ganglia. Histological loss of neurons and Lewy body accumulation in sympathetic ganglia, and cardiac sympathetic denervation in several studies are also evident. In addition, -synuclein pathology has been reported to be shown in the ventrolateral medulla and the enteric plexus in PD patients. The lesions in autonomic regulatory areas could be key causes of cardiovascular, sudomotor, bladder and bowel dysfunction. Evidence suggests that urinary dysfunction is also a process of degeneration in the substantia nigra as urinary dysfunction in PD appears to correlate with PD severity.
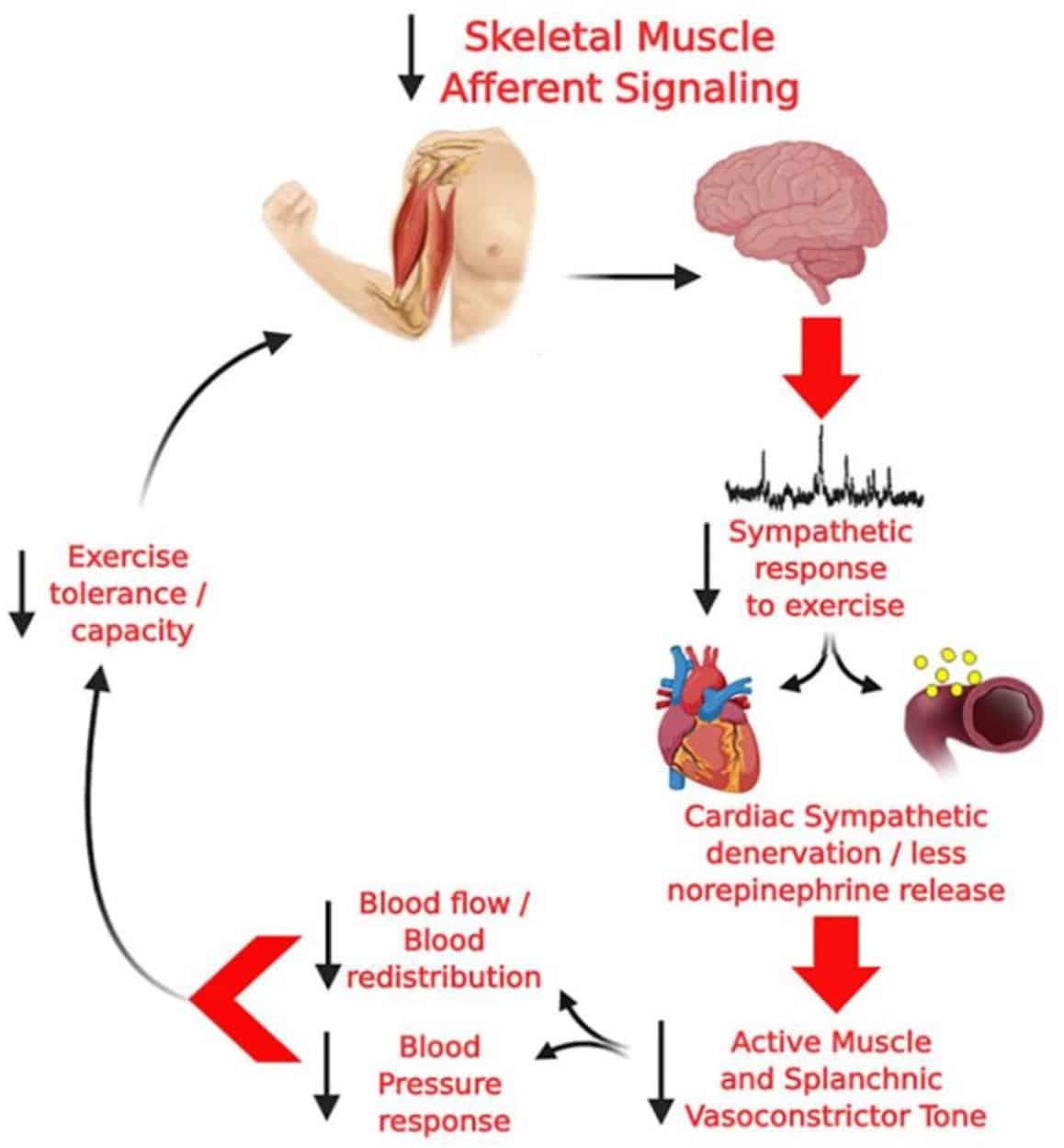
Autonomic Function In Patients With Parkinsons Disease: From Rest To Exercise
- 1NeuroVASQ Integrative Physiology Laboratory, Faculty of Physical Education, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil
- 2Manaaki Mnawa The Centre for Heart Research, Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, The University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand
- 3Graduate Program in Medical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, University of Brasília, Brasília, Brazil
Parkinsons disease is a common neurodegenerative disorder classically characterized by symptoms of motor impairment , but also presenting with important non-motor impairments. There is evidence for the reduced activity of both the parasympathetic and sympathetic limbs of the autonomic nervous system at rest in PD. Moreover, inappropriate autonomic adjustments accompany exercise, which can lead to inadequate hemodynamic responses, the failure to match the metabolic demands of working skeletal muscle and exercise intolerance. The underlying mechanisms remain unclear, but relevant alterations in several discrete central regions have been identified. Herein, we critically evaluate the clinically significant and complex associations between the autonomic dysfunction, fatigue and exercise capacity in PD.
Recommended Reading: Words Of Encouragement For Someone With Parkinson’s
Clinical Trials For Msa
Participation in clinical trials may be an option for certain patients and can be a way for people with MSA to collaborate with the research community to advance potential new treatments. A number of clinical trials for MSA are currently underway and you can learn more about them to help decide if getting involved is right for you.
Autonomic Dysfunctions In Parkinsons Disease: Prevalence Clinical Characteristics Potential Diagnostic Markers And Treatment
Abstract
Parkinsons disease is a common neurodegenerative disease in the middle-aged and the elderly. Symptoms of autonomic dysfunctions are frequently seen in PD patients, severely affecting the quality of life. This review summarizes the epidemiology, clinical manifestations, and treatment options of autonomic dysfunctions. The clinical significance of autonomic dysfunctions in PD early diagnosis and differential diagnosis is also discussed.
1. Introduction
In this review, we will discuss the prevalence, clinical manifestations, and treatment of autonomic dysfunctions in PD, as well as the clinical significance of autonomic dysfunctions in early diagnosis and differential diagnosis of PD.
2. Prevalence of Autonomic Dysfunctions in PD
About 27% to 39% PD patients had symptoms of urinary system dysfunctions, which could be categorized into irritative and obstructive symptoms . The incidence of detrusor hyperreflexia was as high as 45 to 100%, while the incidence of obstructive symptoms was 27% .
3. Clinical Manifestations of Autonomic Dysfunctions in PD
Autonomic dysfunctions in PD can involve the sympathetic noradrenergic system , the sympathetic cholinergic system , the sympathetic adrenomedullary system , the parasympathetic nervous system , and the enteric nervous system manifested as symptoms and signs of cardiovascular system, digestive system, urinary system, reproductive system and skin, and other systems .
3.1. Autonomic Dysfunctions of Cardiovascular System
Read Also: Parkinson’s Leaning To One Side
Autonomic Dysfunction And Parkinson’s
Autonomic dysfunction often occurs in Parkinsons due to the loss of dopamine-producing cells and the presence of microscopic protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain. As a result, a number of non-motor symptoms may be experienced. Research suggests that the peripheral nervous system may be affected long before such symptoms appear.
If autonomic dysfunction is severe, atypical parkinsonism, such as multiple system atrophy , should be suspected.
Please click on the links below for information on individual symptoms related to ANS dysfunction:
- bladder problems including urgency, frequency, incontinence and night time urination
- constipation and weight loss
- swallowing difficulties .
Scientists now recognise that many medications used to treat Parkinsons can affect the ANS and so make symptoms worse. It is important to monitor your medications and symptoms so that you can discuss these with your doctor. He or she may then be able to adjust medications to reduce the impact on the ANS and so improve symptom control. See Keeping a diary for more information on this and how it can help.
Research suggests that about 90% of people with Parkinsons experience autonomic dysfunction which may considerably reduce quality of life.
Content last reviewed: January 2020
The Impact Of Autonomic Dysfunction On Survival In Patients With Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinsons Disease With Dementia
-
Affiliation Clinical Memory Research Unit, Department of Clinical Sciences, Malmö, Lund University, Sweden
-
Affiliations Center for Age-Related Medicine, Stavanger University Hospital, Stavanger, Norway, Department of Neurobiology, Ward and Society, Alzheimers Disease Research Center, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden
-
Affiliation Clinical Memory Research Unit, Department of Clinical Sciences, Malmö, Lund University, Sweden
Also Check: Bike Riding And Parkinson’s Disease
Autonomic Problems In Parkinsons Disease
There have been current advances as well as the experience of doctors, the healthcare team, and family members when taking care of patients with Parkinsons disease. They have revealed that autonomic problems play a crucial role in the evaluation of patients and that the signs and symptoms that present are sometimes the cause of disability. Symptoms seen in Parkinsons disease include cardiovascular dysfunction, sweating, and gastrointestinal failure, among others.
What Is Orthostatic Hypotension?
The American Autonomic Society describes orthostatic hypotension as a change in orthostatic blood pressure, with its systolic value dropping to 20 points and the diastolic dropping to 10 points. It is measured in the standing position and within three minutes. Heart rate also increases to over 130 beats per minute, which is known as postural tachycardia. However, it is important to note that the effects of medication, dehydration, and intravascular volume depletion may also affect the changes seen in PD patients.
We are ashamed that we are ill and so we dont speak about it this silence surrounding illness feeds back into our shame, reinforcing our seeming inability to speak. Katie Willard Virant MSW, JD, LCSW
Are There Non-specific Symptoms Suggesting Hemodynamic Or Cardiovascular Autonomic Dysfunction?
What Other Dysautonomias Can Be Seen In PD Patients?
Which Gender Is More Affected?
How Is Erectile Dysfunction Seen In PD Patients?
How Can Sexual Issues Be Treated?