Clinical Diagnosis Of Rigidity
A doctor will test for rigidity by flexing and extending the patients relaxed wrist and elbow joint, and look for sustained rigidity or intermittent rigidity if tremors are associated with it.
Clinically, Parkinsons rigidity is characterized by increased muscle tone during examination using passive movement of the affected body parts. Parkinsons rigidity is more marked in flexor muscles than extensor muscles . Rigidity may be enhanced by voluntary movement of other body parts and is more pronounced during slow stretching rather than fast stretching. These features help to differentiate Parkinsons rigidity from spasticity, which becomes worse during fast movements.
Beyond The Substantia Nigra
In Parkinsons, other areas of the brain beyond the substantia nigra are involved as the condition progresses. Changes in higher brain areas are linked to non-motor symptoms that can affect people with Parkinsons later on in the condition, and often have a significant impact on quality of life.
For instance, symptoms that affect memory and thinking can be linked to the presence of Lewy bodies in the largest area of the brain the cerebral cortex as well as the limbic system. The limbic system is also believed to be involved in symptoms involving mood and pain, and similar changes in the inferior temporal gyrus, an area of the brain involved in processing what we see, are thought to be the reason for hallucinations.
But research into the spread of Parkinsons through these areas, and how we can stop it , is just one side of the story. There is also ongoing research into where Parkinsons starts, and the effects it is having before it reaches these areas.
The presence of non-motor symptoms many months and maybe even years before the physical symptoms, such as tremor and slowness of movement, points towards the presence of other changes in the body long before the loss of dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra. These early symptoms could even help researchers predict those who will go on to be diagnosed with Parkinsons, which would help in the development of new and better treatments.
Further Information And Support
The Multiple System Atrophy Trust provides help and support to people with MSA, as well as their families, carers and the healthcare professionals treating them.
The charity also funds research to discover the cause of MSA and to try to find a cure.
Their helpline number is 0333 323 4591 . You can also email .
Page last reviewed: 15 July 2020 Next review due: 15 July 2023
You May Like: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Changes Inside The Brain
In Parkinson disease, nerve cells in part of the basal ganglia degenerate.
The basal ganglia are collections of nerve cells located deep within the brain. They help do the following:
-
Initiate and smooth out intended muscle movements
-
Suppress involuntary movements
-
Coordinate changes in posture
When the brain initiates an impulse to move a muscle , the impulse passes through the basal ganglia. Like all nerve cells, those in the basal ganglia release chemical messengers that trigger the next nerve cell in the pathway to send an impulse. A key neurotransmitter in the basal ganglia is dopamine. Its overall effect is to increase nerve impulses to muscles.
When nerve cells in the basal ganglia degenerate, they produce less dopamine, and the number of connections between nerve cells in the basal ganglia decreases. As a result, the basal ganglia cannot control muscle movement as they normally do, leading to tremor, slow movement , a tendency to move less , problems with posture and walking, and some loss of coordination.
How Parkinsons Disease Affects The Body
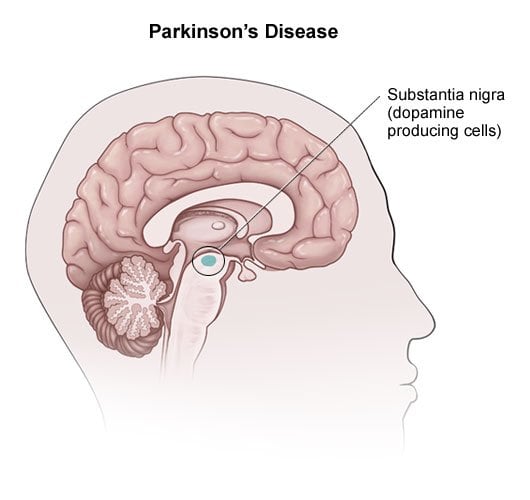
Life with Parkinsons is challenging, to say the least. This progressive disease starts slowly, and because theres currently no cure, it gradually worsens how you think and feel.
Giving up may seem like the only solution, but it certainly isnt. Thanks to advanced treatments, many people are able to continue living healthy, productive lives with Parkinsons.
Take a glance at this infographic to get a visual picture of how Parkinsons can affect everything from your memory to your movement.
Also Check: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Recommended Reading: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a nervous system disease that affects your ability to control movement. The disease usually starts out slowly and worsens over time. If you have Parkinsons disease, you may shake, have muscle stiffness, and have trouble walking and maintaining your balance and coordination. As the disease worsens, you may have trouble talking, sleeping, have mental and memory problems, experience behavioral changes and have other symptoms.
Treatment Of Muscle Diseases
Most diseases of the muscular system are incurable. The good news is, they can often be treated and managed.
Treatment goals may include relieving symptoms, delaying disease progression, and improving quality of life.
Treatment may include drug therapy. This may include immunosuppressants, drugs that reduce or prevent the overactivity of the immune system. These drugs may be used to treat some muscle and nerve diseases. They may also be used for conditions that affect both the nerves and muscles.
Corticosteroids and other medications may be given to reduce muscle spasms and cramping.
Your healthcare provider may also recommend physical and occupational therapy to manage symptoms and, if needed, surgery to correct muscle damage.
Recommended Reading: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
The Substantia Nigra And Movement
The reason that Parkinsons causes movement symptoms is that the substantia nigra makes up part of the circuitry, called the basal ganglia, that the brain uses to turn thought about movement into action.
The structures of the basal ganglia.
The substantia nigra is the master regulator of the circuit, it mainly communicates using the chemical dopamine, but other chemical transmitters are also used to communicate between other areas of the basal ganglia.
The balance of signals being sent between these structures allows us to control movement. But as Parkinsons progresses, and the dopamine-producing brain cells in the substantia nigra are lost, movement symptoms appear. Without enough dopamine, it becomes harder to start and maintain movements, which leads to symptoms such as slowness of movement, rigidity and freezing. And an imbalance of signals in the basal ganglia means people with Parkinsons can experience what is known as a resting tremor.
But while this is the description of Parkinsons you may find in most textbooks, it is now recognised that changes are not limited to the substantia nigra and basal ganglia.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Read Also: Judy Woodruff Health Problems
Locating The Basal Ganglia
|
The basal ganglia are collections of nerve cells located deep within the brain. They include the following:
The basal ganglia help initiate and smooth out muscle movements, suppress involuntary movements, and coordinate changes in posture. |
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed

Someone with the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease may be sent to see a neurologist, a doctor who specializes in the brain, nerves, and muscles. The neurologist may do some tests, including a brain scan and blood tests. These tests will not make the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease, but the doctor will want to make sure that there is no other problem causing the symptoms. To diagnose Parkinson’s disease, the doctor relies on a person’s medical history, symptoms, and a physical exam.
Don’t Miss: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
Causes Of Fatigue In Parkinsons Disease
Many of the symptoms of PD, including slow movement, muscle stiffness, depression, and changes to sleep quality can cause or worsen the symptom of fatigue.
- Akinesia Fatigue may be caused by akinesia . People experiencing akinesia find it challenging to accomplish simple tasks, requiring significantly more energy to get through the daily activities.
- Muscle fatigue Many of the symptoms of PD that affect the muscles, like stiffness, cramping, tremor, and difficulty starting movement, put extra stress on the muscles, causing fatigue. In addition, some people with PD experience muscle atrophy, in which the muscles shrink and weaken due to lack of use. Muscle atrophy decreases a persons stamina and endurance, contributing to the sense of fatigue.
- Depression Depression is another common non-motor symptom of PD, occurring in approximately 40% of people with PD. Depression can cause fatigue, adding to a sense of low energy or lack of motivation.
- Sleep disturbance PD often causes changes in sleep cycles, which can add to a sense of fatigue during the day.
- Medications Some of the medications used to treat PD, including dopamine agonists, can cause fatigue as a side effect. Others may cause insomnia as a side effect, leading to daytime fatigue.1,2
What Are The Treatments
Currently there is no cure for Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms can be mild in the early stages of the condition and people might not need immediate treatment. Your doctor and specialist will monitor your situation.
There are several different types of drugs used to treat Parkinsons disease. Drug treatments are tailored to each individuals needs and are likely to involve a combination of different drugs. Your medication should be reviewed regularly. It is likely that, over time, changes will be made to the types of drugs you take and the doses you take each day.
The main types of drug treatment for Parkinsons disease are:
- drugs which replace dopamine
- drugs which mimic the role of dopamine
- drugs which inhibit the activity of acetylcholine
- drugs which prevent the body breaking down dopamine
- other drugs such as anti-sickness medication
Everybody is affected differently by medication. The possible side effects of Parkinsons disease drugs include nausea , vomiting , tiredness and dizziness. Some people might experience confusion, nightmares and hallucinations. For some people, dopamine agonists have been linked to compulsive behaviour such as addictive gambling or hypersexuality .
The effectiveness of the main drug treatment levodopa can wear off over time and its long-term use can cause some people to develop involuntary twisting or writhing movements of the arms, legs or face . To reduce the risk, doctors might delay the use of levodopa for younger people.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Bike Therapy
Muscle Weakness And Rigidity
As his Parkinsons progresses, Dad complains that his stiffness is slowing him down. The frequency and intensity with which it occurs seem to be increasing. To better understand the disease and how it relates to the body, I decided to explore the research.
In an abstract of a literature review published by the American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, the authors stated that isokinetic muscle strength was decreased in patients with Parkinsons disease and that muscle weakness was not specifically related to tremor or rigidity.
Slowness Of Movement And Feeling Stiff
A person with MSA has much slower movements than normal . This can make it difficult to carry out everyday tasks. Movement is hard to initiate, and the person will often have a distinctive slow, shuffling walk with very small steps.
Some people may also have stiff and tense muscles. This can make it even more difficult to move around and cause painful muscle cramps .
These symptoms are typical of Parkinson’s disease but, unfortunately, the medicine used to relieve them in people with Parkinson’s disease is not very effective for people with MSA.
Also Check: Similar To Parkinsons
Causes And Symptoms Of Muscle Disorders
The causes of muscle disorders can be quite expansive, as their function relies on other processes in the body to be working optimally as well. Muscular disorders that result in the loss of function of a certain muscle group can lead to a condition called muscular atrophy, which is caused by wasting away of muscle tissue due to underutilization. Muscle atrophy is characterized by weakness and the shrinking of muscle mass. Pain may also be present in muscle disease and is primarily caused by defects in blood circulation, injury, or inflammation. Muscular pain may also result in additional symptoms of weakness and fatigue.
The following is a muscular system disease and disorders list outlining the intricacies of each condition.
How Does Parkinson Affect The Basal Ganglia
4.9/5Parkinson’saffectsbasal gangliafull answer
Conditions that cause injury to the brain can damage the basal ganglia. Such conditions include: Carbon monoxide poisoning. Drug overdose.
One may also ask, how does Parkinson’s affect the muscular system? Nerve cells use a brain chemical called dopamine to help control muscle movement. With Parkinson disease, the brain cells that make dopamine slowly die. Without dopamine, the cells that control movement can’t send proper messages to the muscles. This makes it hard to control the muscles.
In this regard, what is the function of the basal ganglia?
Basal ganglia are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion.
Who is affected by Parkinson’s?
However, the disease affects about 50 percent more men than women. One clear risk factor for Parkinson’s is age. Although most people with Parkinson’s first develop the disease at about age 60, about 5 to 10 percent of people with Parkinson’s have “early-onset” disease, which begins before the age of 50.
Read Also: Yopd Life Expectancy
How Does Pd Affect Muscle Activity
Table 4 Methodology and signal processing techniques for non-intervention studies.
Studies investigating the activity of MG muscle in individuals provided more conclusive results, with the majority reporting reduced activity in the PD group compared to HOA. As the MG muscle is important for forward propulsion of the body and vertical support, a decrease in activity may result in reduced gait speed and loss of postural balance along the vertical axis. Three studies reported prolonged increased activity of knee flexors and extensors,, in individuals with PD. Biomechanically, the enhanced proximal muscle activity may compensate for the reduced function of distal muscles. Greater contraction of the quadriceps during the stance phase will increase extension of the knee, leading to greater stability in this joint during single stance which may compensate for reduced stability at the ankle joint. Greater activity of hamstrings during swing will increase hip extension and knee flexion and may replace some of the foot placement and initial loading role of the distal muscles acting on the ankle joint. Increased muscle activity entails a larger metabolic demand which may limit walking speed and mobility. Differential compensatory changes in lower limb muscles during walking have been observed in other neurological pathologies such as post-polio syndrome and stroke,.
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
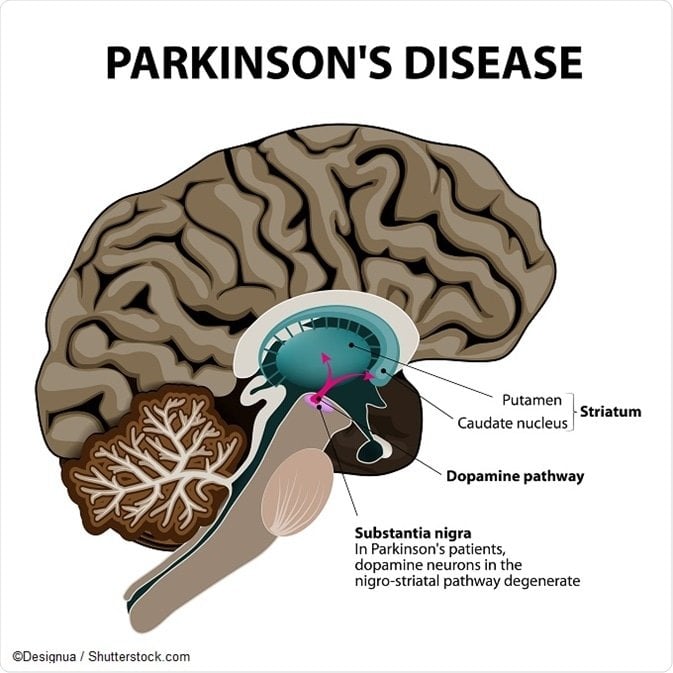
In the very deep parts of the brain, there is a collection of nerve cells that help control movement, known as the basal ganglia . In a person with Parkinson’s disease, these nerve cells are damaged and do not work as well as they should.
These nerve cells make and use a brain chemical called dopamine to send messages to other parts of the brain to coordinate body movements. When someone has Parkinson’s disease, dopamine levels are low. So, the body doesn’t get the right messages it needs to move normally.
Experts agree that low dopamine levels in the brain cause the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, but no one really knows why the nerve cells that produce dopamine get damaged and die.
p
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Double Vision