What Are Other Parkinsons Disease Risk Factors
- Age: Parkinsons disease mainly affects people over 60 years of age and the risk of developing the disease increases over the years.
- Population: Parkinsons disease is more common among people with white skin.
- Sex: More men have Parkinsons disease than women.
- Career: Some occupations, such as farmers or factory workers, may be more exposed to certain chemicals or toxins that increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
- Serious head injuries: Different types of serious head and brain injuries, such as concussions, increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Location: The number of people living with the disease in rural areas is higher. This seems to be related to agricultural pesticide exposure.
Recommended Reading: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
What Are The Major Challenges In Searching For Environmental Causes Of Pd
The fact that late-onset sporadic PD takes decades to develop and the lack of understanding of this prolonged prodromal phase present a major challenge to understand environmental contributions to PD. In this disease development paradigm, causative exposures that initiate PD pathological process may have to occur and be documented decades before disease clinical diagnosis, which is often infeasible in epidemiological studies. Further, once neurodegeneration is initiated, many environmental and genetic factors may come into play to modify PD progression during the decades of prodromal disease development. As a consequence, even the most robust epidemiological findings, including those from longitudinal cohorts, are subject to alternative explanations. For instance, smokers have a robust and substantially lower risk for PD than non-smokers in all types of epidemiologic studies . While a causal interpretation that cigarette smoking reduces PD risk is appealing, alternative hypotheses such as reverse causation and confounding by personality and other unknown risk factors are equally possible . Similar analogies can be easily extended to most, if not all, of the presumed protective modifiable risk factors afore-mentioned.
Environmental Factors In Parkinsons Disease
Here are environmental factors that may play a role in the development of Parkinsons disease:
Although environmental exposure to these and other toxins is of continued research interest, its hard to determine if any one substance is a culprit. Most often, individual cases of Parkinsons disease result from a complex interplay between genetics and environmental and other factors.
Targeting Parkinsons-Linked Protein Could Neutralize 2 of the Diseases Causes
Researchers report they have discovered how two problem proteins known to cause Parkinsons disease are chemically linked, suggesting that someday, both could be neutralized by a single drug designed to target the link.
Read Also: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Recommended Reading: How Do I Know If I Have Parkinson’s
Leading Possible Risk Factors For Parkinsons
Genetic factors
Scientists estimate that less than 10% of cases of Parkinsons disease are primarily due to genetic causes. The most common genetic effect that triggers Parkinsons disease is mutation in a gene called LRRK2. The LRRK2 defect is particularly frequent in families of North African or Jewish descent. Mutations in alpha-synuclein have also been found to trigger Parkinsons, but these are quite rare. In most cases, no primary genetic cause can be found.
Other risk factors
There are other things that put an individual at higher risk for developing Parkinsons. The main risk factor is age, because Parkinsons disease is most commonly found in adults over the age of 50 . Men also have a higher risk of Parkinsons disease than women. The actual links between any of these factors and Parkinsons disease are not completely understood.
How Do Genetics Contribute To The Development Of Parkinsons Disease
Genes are like an instruction manual. They code the synthesis of molecules that make up the body. A change in these instructions can lead to different effects and potentially to diseases.
Some of these modifications or mutations have been identified in people living with Parkinsons disease. They increase the risk of developing the disease but are not common. Moreover, they do not always lead to the development of the disease.
Also Check: Is Numbness A Sign Of Parkinson’s
Metagenomic And Metabolomic Evidence Of Gastrointestinal Involvement In Pd
Trillions of bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi residing in the gastrointestinal tract comprise a vast, dynamic ecosystem that interacts with the host . They participate in maintaining homeostasis of the intestinal barrier, immune maturation, nutrition absorption, and metabolism . Recent evidence indicates that the gut microbiota communicates with the brain and is associated with several neurodegenerative disorders, including PD . Alterations in the composition of bacteria, fungi, and viruses and their related metabolites have been described in PD patients, with most studies focusing on bacteria . Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth compared to unaffected controls is a common presentation in PD patients, with an estimated prevalence of 46% in a meta-analysis and this associates with worse motor function and complications . 16S rRNA gene amplicon surveys to study the bacterial and archaeal community structures and shotgun metagenomic sequencing to carry out non-targeted sequencing of the gut microbiota community are widely used techniques for investigating the associations between changes in the gut microbiota and the development of PD.
Environmental Factors: Etiological And Disease
From 1817 when Dr. James Parkinson first described 6 patients with the condition that would later bear his name , much progress was made in the following 150years. It became known that the SN was the site affected by PD pathology together with the presence of cytoplasmic inclusions, and levodopa became available as the first effective symptomatic drug treatment of PD in 1960s . However, the etiology of PD remained elusive.
Table 1 Examples of environmental factors and their biologic correlates
The most robust beneficial environmental factor associated with PD is cigarette smoking which has been seen in early case-control studies and then confirmed in more recent large prospective cohorts. Active smokers have 50% lower risk of PD compared to never smokers . There is a strong dose-response relationship including duration, intensity, pack-years and years since last smoking: PD risk decreases with increasing duration of smoking and increases again with time since quitting . Preliminary reports also support an inverse relationship between passive smoking, smokeless tobacco use and PD .
Recommended Reading: Is Parkinson’s A Prion Disease
Genetic Profile Environmental Exposure And Their Interaction In Parkinsons Disease
Letizia Polito
1Golgi Cenci Foundation, Abbiategrasso, 20081 Milan, Italy
2Geriatric Unit and Gerontology-Geriatrics Research Laboratory, Department of Medical Sciences, IRCCS Casa Sollievo della Sofferenza, San Giovanni Rotondo, 71013 Foggia, Italy
Academic Editor:
Abstract
1. Introduction
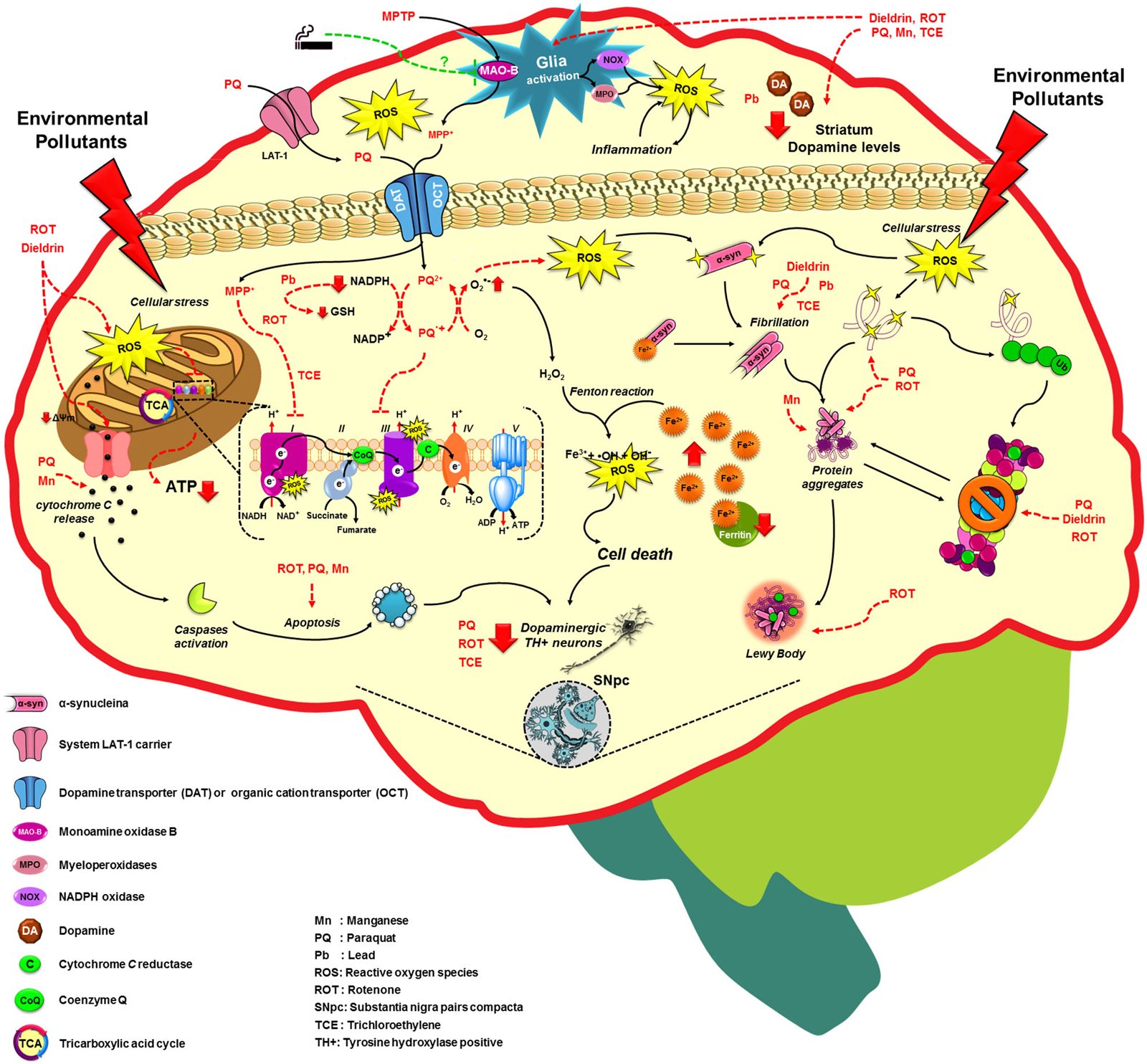
Exploring the contribution of environmental exposure markedly advanced our understanding of the mechanisms involved in the development of PD. Initial evidence came from findings that subjects exposed to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine developed PD-like symptoms . Since then, environmental exposure to pesticides , polychlorinated biphenyls , organic solvents , metals , and air pollutants has been proposed to increase risk for PD. However, results concerning the contribution of environmental factors in PD are still inconsistent.
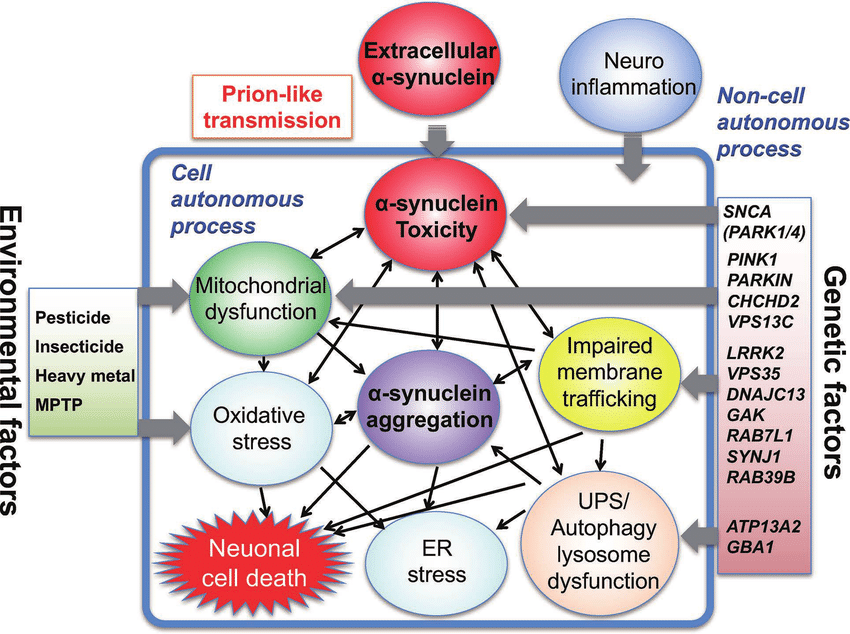
Altogether, although genes are likely to play a role, the vast majority of PD cases cannot be ascribed exclusively to genetic factors. PD is probably caused by a complex interplay of many genetic variants interacting with many nongenetic risk factors.
2. Monogenic Forms of PD
Recently, mutations in three novel genes, that is, the vacuolar protein sorting 35 homolog , eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 gamma 1 , and dnaJ homolog subfamily C member 13 , were proposed to cause late onset autosomal dominant inheritance and need further replication to be confirmed .
3. Genetic Variants Associated with PD
4. Environment Factors Related to PD
The Search For Environmental Causes Of Parkinsons Disease: Moving Forward
Issue title: The Times They Are a-Changin: Parkinsons Disease 20 Years from Now
Guest editors: Patrik Brundin, J. William Langston and Bastiaan R. Bloem
Article type: Review Article
Authors: Chen, Hongleia* | Ritz, Beateb
Affiliations: Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, College of Human Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA | Department of Epidemiology and Environmental Health Sciences, Fielding School of Public Health, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, CA, USA
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Honglei Chen, MD, PhD, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, College of Human Medicine, Michigan State University, 909 Wilson Rd, East Lansing, MI 48824, USA. Tel.: +1 517 884 3990 E-mail: .
Keywords: Parkinsons disease, etiology, progression, environmental risk factors, prodromal symptoms
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-181493
Journal: Journal of Parkinsons Disease, vol. 8, no. s1, pp. S9-S17, 2018
Abstract
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Similar Diseases
We Know Age And Genetics Play A Role In Parkinsons But How Does The World We Live In Impact On Our Risk Of Developing The Condition
Parkinsons is a neurodegenerative condition affecting around 145,000 people in the UK. It develops when dopamine-producing cells in the brain stop working properly and, over time, are lost.
This much we know. But what we dont know is what actually causes Parkinsons. Its often referred to as idiopathic Parkinsons, which translates from the original Greek as a disease of its own kind the cause is unknown.
Age is the biggest risk factor most people who get Parkinsons are aged 50 or over. As we age, damaging molecules called free radicals build up inside our bodies, causing the cells to become stressed. Energy-producing mitochondria may stop working properly, damaged proteins may accumulate, and, over time the cells may die. Research has shown that dopamine-producing brain cells seem to be particularly vulnerable to these changes seen with ageing, increasing the risk of Parkinsons as we get older.
But, age isnt the only player at the table. People under the age of 50 can get Parkinsons too. This early onset Parkinsons is often linked to very rare changes in certain genes, such as those involved in removing damaged proteins and helping mitochondria to work properly.
In this blog, well specifically investigate environmental factors in more detail.
Environmental Risk Factors For Parkinsons
When we talk about the environment, we mean the world around us, and the pathogens , toxic chemicals, and heavy metals that occupy it.
The idea that the environment could play a role in Parkinsons first arose from an unusual medical case in the early 1980s. A group of heroin users in California took drugs from a batch contaminated with a substance called MPTP. Almost overnight, they experienced a type of parkinsonism that could be treated with L-dopa. The case hit the headlines, and sparked an interest in how chemicals and other environmental exposures could play a role in Parkinsons.
Over the years, several more environmental factors have been suggested to influence the risk of developing Parkinsons. While some associations remain unproven, other factors have repeatedly been found to either increase or decrease risk.
1. Pesticide use
Over the years, studies have linked Parkinsons with rural living, farming, and well-water consumption. The common denominator in these studies is thought to be exposure to certain pesticides, including herbicides, insecticides, fungicides, and rodenticides.
2. Other chemicals
Trichloroethylene
Manganese
One study looking in welders in the US reported that exposure to manganese, found in welding fumes, increased the risk of developing manganism. And recent research suggests that this condition is caused by manganese triggering the misfolding of a protein in the brain cells, causing them to die.
3. Heavy metal exposure
Recommended Reading: Arthritis And Parkinson’s Disease
Environmental Factors And Parkinsons
Researchers believe that a combination of genetic and environmental factors can cause Parkinsons. Chemicals, viruses, bacteria and heavy metals have all been linked to the condition this could be because they may cause neurons that produce dopamine to die. Scientists have also suggested a connection between herbicides and pesticides, and Parkinsons.
To find out more about the causes of Parkinsons, please visit the EPDA website.
Read more:
Potential Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
The causes of Parkinsons disease are still unknown, although there is some evidence for the role of genetics, environmental factors, or a combination of both. It is also possible that there may be more than one cause of the disease. Scientists generally believe that both genetics and environment interact to cause Parkinsons disease in most people who have it.
Currently, there is an enormous amount of research directed at producing more answers about what causes Parkinsons disease and how it might be prevented or cured. When physicians diagnose Parkinsons, they often describe it as idiopathic . This simply means that the cause of the disease is not known.
Also Check: Parkinson Bicycle Cleveland Clinic
You May Like: Can Parkinsons Be Passed Down
Interplay Between Genetic Predisposition And Gut Microenvironmental Changes In Pd
Fig. 2
Genetic predisposition and gut microenvironmental changes collaboratively contribute to PD pathogenesis. Genetic susceptibility to PD leads to vulnerable neurons related to aberrant immune responses, abnormal protein aggregation, autophagolysosomal impairment, and mitochondrial dysfunction that together with gut microenvironmental changes attributed to intestinal stimuli contribute to PD pathogenesis
Genetic And Environmental Factors Affect Gut Microbiota
The gut microbiota is a dynamic microbial system, and it can be modified by genetic and environmental factors. Previous studies have reported that the gut microbiota is constantly challenged by environmental factors such as exercise, diet, stress, altitude, temperature, toxicants/pollutants, and noise,. Environmental contaminants can affect the composition of the gut microbiota, leading to physiological disorders in the host and causing certain diseases. The gut microbiota has become a new toxicological target for some environmental pollutants. A decreasing diversity of gut microbiota is often observed after exposure to heavy metals. In our previous studies, Mn exposure led to decreased abundances of Prevotellaceae, Fusobacteriaceae, and Lactobacillaceae,. In addition, Nasuti et al. showed that changes in gut microbiota may be one of the reasons for the neurotoxicity of permethrin. Many studies have shown that antibiotic administration leads to disturbances in the microbial diversity and metabolism of the gut microbiome that might be linked to a multitude of diseases.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Early Symptoms For Parkinson Disease
Altered Gut Microbiota In Pd
Notably, emerging evidence indicates that protein nucleation and aggregation may be influenced by an extracellular amyloid protein called curli, which is secreted by Escherichia coli, inducing neuronal deposition of alpha-synuclein in the gut and promoting neurodegeneration . The abundance of E. coli at the colonic mucosa correlates with enteric alpha-synuclein deposition in PD patients . Curli is an amyloid protein that bacteria secrete for surface adherence and biofilm formation . Induction of abnormal alpha-synuclein aggregation by curli has been demonstrated in vitro, and ingestion of curli and curli-producing bacteria accelerates enteric and central alpha-synucleinopathy, as well as neuroinflammation, dopaminergic neuronal degeneration, and motor dysfunction, in transgenic rodent models of PD . Therefore, distinct gut microbiota species result in a pro-inflammatory status in the intestinal tract or promote enteric alpha-synuclein aggregation to facilitate the occurrence and progression of PD.
Parkinson Causes: What Adds Up To Trigger The Disease
Researchers say that Parkinson causes are multifactorial. 1
Risk factors that add up as Parkinson Disease causes, are exposure to:
- pesticides
- injury in a specific location of the brain , resulting in neurologicdysfunction
Some or all factors combine in the brain and nervous system and cause:
- neuro-toxicity
- oxidative stress
A combination of factors can converge over a lifetime as Parkinson causes:
- For instance, when researchers fed extra metal iron and the pesticide rotenone to experimental animals, this led to Parkinsons Disease in the substantia nigra part of the brain.
- However, when they gave only one of these, or each separately just iron or rotenone alone this did not happen.2
Is Parkinsons a Syndrome rather than a specific Disease?
There is evidence that instead of long term chronic exposure, there was likely a more specific environmental or toxic event or exposure.
This would have killed some nigraldopaminergic cells, and damaging others. 3
Recommended Reading: What Are The Initial Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Read Also: What Drugs Cause Parkinson Like Symptoms
Characteristic Structural Features And Function Of
-syn consists of 140 amino acids and is divided into three regions: a positively charged N-terminal region , a central hydrophobic region with the non-amyloid-beta component, and a highly acidic C-terminal domain . Under physiological conditions, -syn exists mainly in the substantia nigra, cortex, and hippocampus, and plays an important role in synaptic function and plasticity . Except for the brain, -syn is also expressed in the heart, muscle, and other tissues, where it maintains calcium homeostasis in mitochondria through the modulation of the endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondrial membranes . Although -syn is also found in biological fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid, blood, and plasma, there is an ongoing debate about the use of -syn as a biomarker for diagnosis, and the quantification of -syn in cerebrospinal fluid and blood has failed to produce consistent results .
In addition, the other synuclein members – and -synuclein are two isomers of -syn, which also belong to the small molecular non-structural protein family . According to previous studies, although – and -synuclein proteins are not found in LBs, both of them are related to the hippocampal axonal pathology of PD and dementia with Lewy bodies . Besides, a change in the expression of -synuclein has also been specifically observed in enhanced metastasis and cancer drug resistance .
No One Definitive Cause Of Parkinsons
There are no biomarkers or objective screening tests that indicate one has Parkinsons. That said, medical experts have shown that a constellation of factors are linked to it.
Parkinsons causes are likely a blend of genetics and environmental or other unknown factors. About 10 to 20 percent of Parkinsons disease cases are linked to a genetic cause, says Ted Dawson, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Institute for Cell Engineering at Johns Hopkins. The types are either autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive .
But that leaves the majority of Parkinsons cases as idiopathic, which means unknown. We think its probably a combination of environmental exposure to toxins or pesticides and your genetic makeup, says Dawson.
Age. The biggest risk factor for developing Parkinsons is advancing age. The average age of onset is 60.
Gender. Men are more likely to develop Parkinsons disease than women.
Genetics. Individuals with a parent or sibling who is affected have approximately two times the chance of developing Parkinsons. Theres been an enormous amount of new information about genetics and new genes identified over the past 10 or 15 years that have opened up a greater understanding of the disease, says Dawson.
Recommended Reading: What Kind Of Pain Is Associated With Parkinson’s