How Dopamine Agonists Are Used
Dopamine agonists are used at all stages of Parkinsons. You might take them alone when treatment is being started, or alongside levodopa to provide a more effective treatment with fewer side effects.
Treatment with dopamine agonists has to be started carefully to minimise the risk of side effects, with the dose gradually increasing until you and your specialist or Parkinsons nurse are happy that your symptoms are under control. Some dopamine agonists are available as one a day tablets. These can be a better option for the body and may help both movement and other symptoms of Parkinsons.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease Dementia
A chemical messenger in the brain called dopamine helps control and coordinate muscle movement. Over time, Parkinsons disease destroys the nerve cells that make dopamine.
Without this chemical messenger, the nerve cells cant properly relay instructions to the body. This causes a loss of muscle function and coordination. Researchers dont know why these brain cells disappear.
Parkinsons disease also causes dramatic changes in a part of your brain that controls movement.
Those with Parkinsons disease often experience motor symptoms as a preliminary sign of the condition. Tremors are one of the most common first symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
As the disease progresses and spreads in your brain, it can affect the parts of your brain responsible for mental functions, memory, and judgment.
Over time, your brain may not be able to use these areas as efficiently as it once did. As a result, you may begin experiencing symptoms of Parkinsons disease dementia.
You have an increased risk of developing Parkinsons disease dementia if:
Dont Miss: How Do Doctors Test For Parkinsons Disease
An Approach To The Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
No treatment can arrest or slow neurodegeneration in Parkinsons disease. The aim is to relieve symptoms and avoid the complications of therapy.
Early Parkinsons disease
Many studies have shown that early treatment with dopamine agonists reduces the incidence of dyskinesia.1Fewer motor fluctuations were shown in some but not all of the studies. We recommend a dopamine agonist as the first treatment in younger patients who have mild disease and no cognitive deficit. It is necessary to add levodopa within 1-5 years in most patients. In more severe disease, treatment begins with levodopa but a dopamine agonist may be added to keep the daily dose of levodopa in the lower range if there is no cognitive deficit. Dopamine agonists are used infrequently and with caution in patients more than 70 years old because of the risk of neuropsychiatric adverse effects and postural hypotension. They are contraindicated in the presence of dementia.
Isolated resting tremor is rarely disabling, but if it interferes with function it can usually be managed with levodopa. When this is ineffective at low to moderate doses, the addition of an anticholinergic can sometimes be useful.
Patients with motor fluctuations
Role of physical therapy and surgery
Read Also: Is Memory Loss A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Delayed Administration And Contraindicated Drugs Place Hospitalized Parkinsons Disease Patients At Risk
Problem: One-third of all patients with Parkinsons disease visit an emergency department or hospital each year, making it a surprisingly common occurrence.1 The disease affects about 1 million people and is currently the fourteenth leading cause of death in the US. Hospitalization can be risky for patients with Parkinsons disease when viewed from the perspective of pharmacological management.
Patients with Parkinsons disease require strict adherence to an individualized, timed medication regimen of antiparkinsonian agents. Dosing intervals are specific to each individual patient because of the complexity of the disease. It is not unusual for patients being treated with carbidopa/levodopa to require a dose every 1 to 2 hours. When medications are not administered on time, according to the patients unique schedule, patients may experience an immediate increase in symptoms.2,3 Delaying medications by more than 1 hour, for example, can cause patients with Parkinsons disease to experience worsening tremors, increased rigidity, loss of balance, confusion, agitation, and difficulty communicating.2 Studies show that three out of four hospitalized patients with Parkinsons disease do not receive their medications on time, or have had doses entirely omitted.4 According to the National Parkinson Foundation, 70% of neurologists report that their patients do not get the medications they need when hospitalized.2
Two case examples
References
Why Is When I Take Medications Important For Parkinson’s Disease

Parkinson’s disease symptoms can be very different for each person with the disease. You may have symptoms at different times of the day and in different amounts. It is important to take medications on a specific schedule and stick to that schedule. This is to help decrease symptoms and to stop the medication from wearing off too soon. Even changing your medications by one hour may make your symptoms worse and increase your chance of falling.
If a medication wears off too soon or is not working well, let your health care provider know. They may change the schedule, the dose, or the medication. You may take multiple medications to improve your symptoms.
Also Check: How To Help Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Coordinate Care With A Caring Team
Managing Parkinsons disease is a long-term process that involves multiple healthcare professionals. It is important for patients to have a caring and coordinated team of HCPs to ensure that their needs are met and that they receive the best possible care. HCPs should work together with patients to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to their individual needs and preferences.
Which One First: Levodopa Or Dopamine Agonists
Treatment is often started with just one medication. Levodopa and dopamine agonists are the most effective. Both have their own advantages and disadvantages that play an important role when deciding which one to take.
Dopamine agonists are usually recommended for people under the age of 60 to 70, in order to delay the onset of movement problems. Levodopa is usually recommended for older people because it’s better tolerated. Some people take a combination of levodopa and dopamine agonists from the beginning.
|
|
It is currently difficult to say which medication is best suited to the various age groups. There can be perfectly valid reasons for people under the age of 70 to start using levodopa first. Various factors other than age play a role here, such as the severity of the symptoms or concerns about particular side effects. Because of this, it’s important to discuss the pros and cons of the different medications with your doctor when deciding which would be most suitable for you.
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Affect Heart Rate
Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease
Treatment of PD requires a multifaceted approach comprising pharmacological and nonpharmacological efforts. Considerable evidence suggests that patients should be encouraged to adopt a regular program of exercise from the time of diagnosis.
There are numerous other medications available to treat PD. Anticholinergic drugs are primarily used to treat tremor. Amantadine is a modestly effective agent for a variety of motor symptoms and can also reduce levodopa-induced dyskinesias. MAO-B and COMT inhibitors, by extending the duration of action of individual doses of levodopa, may be useful for treating motor fluctuations. Patients who cannot be satisfactorily controlled with medications alone are often treated surgically. Deep brain stimulation surgery of the STN or globus pallidus pars interna is associated with marked motor benefit in a large proportion of correctly selected patients due to high-frequency electrical stimulation of the stereotactically targeted structure. Pallidotomy has not often been utilized since the advent of DBS.
Stanley Fahn MD, … Peter Jenner BPharm , PhD, DSc, FRPharms, in, 2007
Myth : Deep Brain Stimulation Is Experimental Therapy
Fact: Deep brain stimulation, or DBS, is a procedure in which doctors place electrodes in the brain at the point when medications are less effective in masking motor symptoms, such as tremor, stiffness and slowness of movement.
While it may sound frightening and futuristic, its been around and successfully used for decades. DBS works very similarly to a pacemaker, except the wire is in the brain, not in the heart. Its been a standard procedure for the past two decades.
These common symptoms of Parkinsons disease often begin gradually and progress over time:
- Shaking or tremor
- Slowing of body movements
As the disease continues to progress, additional symptoms can occur such as slurred or soft speech, trouble chewing and/or swallowing, memory loss, constipation, trouble sleeping, loss of bladder control, anxiety, depression, inability to regulate body temperature, sexual dysfunction, decreased ability to smell, restless legs and muscle cramps.
Recommended Reading: Judy Woodruff Parkinsons
Also Check: Can Acupuncture Help With Parkinson’s
Dopaminergic Features And Their Treatment
Patients with PD usually present with features indicative of degeneration of nigrostriatal pathways. A useful clinical definition for PD is asymmetric onset of an akinetic rigid syndrome with resting tremor and a good response to levodopa. When applied by neurologists with an interest in movement disorders, this definition has a pathological correlation exceeding 98%. When treatment is considered appropriate, and this is a topic discussed in detail below, a variety of options is available. The use of dopaminergic drugs improves motor function, significantly reduces both the morbidity and mortality of PD, and improves quality of life.
Levodopa remains the drug most commonly used in PD. It is very effective in improving bradykinesia and rigidity, and in practice remains the gold standard against which other drugs are judged. Some studies, predominantly in vitro, have suggested that levodopa may be toxic. However, such data are conflicting, and some laboratory studies have suggested a growth factor-like effect for levodopa. Overall, the pre-clinical evidence for levodopa toxicity is not convincing and there are no data to indicate that any toxic action is of clinical relevance.
Table 1
Percentage of patients remaining on dopamine agonist monotherapy at years 14 and years 15 during treatment trials
Side Effects And Problems With Dopamine Agonists
Common side effects of dopamine agonists include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hallucinations or delusions and confusion
- Existing dyskinesias becoming more troublesome initially
If you are taking Cabergoline , Pergolide or Bromocriptine your neurologist or GP will have to arrange a chest CT scan or ultrasound of your heart yearly as over time these medications may effect heart or lung tissue.
This precaution does not apply to the other dopamine agonists available in Australia.
Also Check: Is Thumb Twitching A Sign Of Parkinsons
You May Like: Exercises For Elderly With Parkinson’s Disease
Full List Of Medications Approved For The Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease In The Usa
Below is a full list of Parkinsons medications that have been approved to treat Parkinsons in the United States. This material is intended to provide you with information. It should not be used for treatment purposes, but rather as a source for discussion with the patients own physician. Work with your physician to determine which medications are best for you, and know the risks and benefits of each.
| Generic Name |
|---|
Common Drugs For Parkinson’s Disease
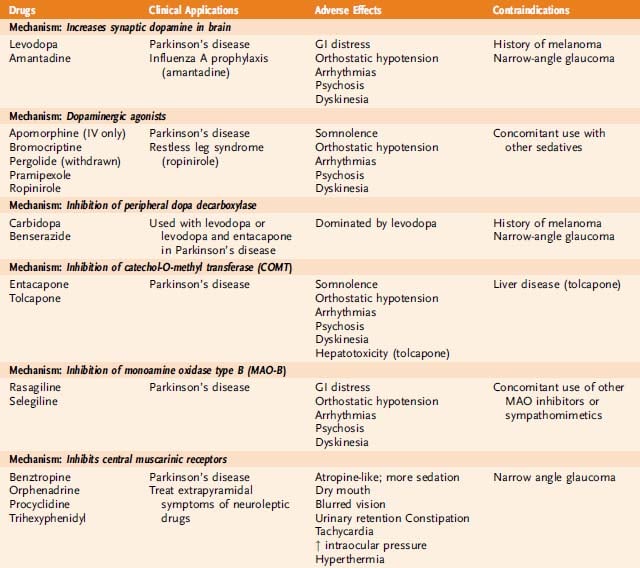
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole .
Read Also: Pump For Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons warning signs can be motor symptoms like slow movements, tremors or stiffness. However, they can also be non-motor symptoms. Many of the possible non-motor symptoms can appear years or even decades ahead of motor symptoms. However, non-motor symptoms can also be vague, making it difficult to connect them to Parkinsons disease.
Non-motor symptoms that might be early warning signs include:
Also Check: Keto Diet For Parkinson’s
Focused Ultrasound Therapy To Treat Tremor
Focused Ultrasound is used to treat Parkinsons patients experiencing tremor that does not respond to medication.
In medical terms this procedure is known as a non-invasive thalamotomy.
During the Focused Ultrasound procedure, the patient is awake. No general anaesthesia or surgical incisions are required.
A frame is placed on the patients head with local anaesthetic and the patient lies in a Magnetic Resonance Imaging scanner. If required some sedation can be given to help maximise comfort and relaxation during the procedure.
Doctors then use brain scans to direct ultrasound beams to the target location in the thalamus region of the brain.
The thalamus is a small structure within the brain located just above the brain stem. It has nerve connections with both cerebral cortex and the midbrain. The main function of the thalamus is to relay motor and sensory signals to the cerebral cortex.
The focused ultrasound sends 1024 individual ultrasound beams through the brain that intersect at a single target point in the thalamus to destroy the tremor-causing cells without damaging the surrounding normal tissue.
This is all monitored in real time on the MRI and by repeatedly checking the patient and until the tremor has been treated.
When the treatment is over there is an immediate and significant reduction in tremor.
In Australia, Focused Ultrasound therapy is administered by St Vincents Hospital where it is known as the Neuravive Procedure.
Also Check: My Dad Died From Parkinsons
Your Parkinsons Drug Treatment
Dopamine is a chemical messenger made in the brain. The symptoms of Parkinsons appear when dopamine levels become too low. This is because many of the cells in your brain that produce dopamine have died or are dying. Taking dopamine as a drug doesnt work because it cannot cross the blood brain barrier. To get around this, doctors use other medication that can act in a similar way.
Don’t Miss: Weight Loss In Late Stage Parkinson’s
Signs You May Have Parkinsons Including Stiffness And When To Seek Help
Parkinsons disease is a neurological disorder that can cause uncontrolled movements like shaking, hand tremors and loss of balance. According to the Parkinsons Foundation, Nearly one million people in the U.S. are living with Parkinsons disease . This number is expected to rise to 1.2 million by 2030. Parkinsons is the second-most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimers disease. In addition, Nearly 90,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with PD each year. More than 10 million people worldwide are living with PD, the foundations site states, and that includes actor Michael J. Fox who uses his celebrity platform to raise awareness and over 1 billion dollars for research so far.
Theres currently no cure for the condition, but according to Parham Yashar, MD FACS FAANS, Board-Certified in General, Spinal, Cranial Neurosurgery, Board-Certified in CNS Endovascular Neurosurgery, President, Yashar Neurosurgery, Stroke Medical Director, Dignity Health Northridge Hospital there are ways to lower the chance of getting Parkinsons. There are suggestions for ways to potentially help reduce your risk of developing Parkinsons Disease. In some studies, caffeine has been associated with a lower risk of developing PD. Exercise, such as aerobic or physical activity may be protective according to some meta-analysis studies performed.
Also Check: What Part Of The Brain Does Parkinsons Affect
Antipsychotic Use In The Elderly
Antipsychotic agents are frequently used in facilities for the elderly and in general hospitals to treat older patients with behavioral problems, which are not uncommon. In nursing home facilities, behavioral disturbances are seen in as many as 40% to 95% of residents40% to 80% with dementia, 5% to 25% with depression, and 2% to 5% with schizophrenia. However, although approximately 50% to 75% of all nursing home residents take antipsychotic medications, only a relatively small proportion of residents actually see a mental health professional. In a study of the availability of mental health services in nursing homes, data indicated that 65% of nearly 2000 nursing home residents were found to have some type of mental disorder yet, the 1-month rate of contact with mental health professionals for this group was only 4.5%. Additionally, only 2% with a diagnosis of dementia and 17% of residents diagnosed with chronic schizophrenia had seen a mental health specialist.
Educational programs designed for primary care physicians and specialists such as nurses, psychologists, and social workers, as well as patients and their families, are clearly needed to achieve safer and more efficacious care for elderly patients. Learning to identify, distinguish, and manage drug-induced movement disorders associated with conventional, and sometimes atypical, antipsychotic agents can aid primary care physicians and others in achieving that end.
Don’t Miss: Lift Chair For Parkinson’s Patients