S Rrna Gene Amplification And Sequencing
DNA extraction from thawed fecal samples was performed using the QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit following the manufacturers instructions. The V3V4 regions of 16S rRNA genes were amplified by polymerase chain reaction using the barcoded primers 341F 5-CCTACGGGRSGCAGCAG-3 and 806R 5-GGACTACVVGGGTATCTAATC-3. PCR reactions were performed in 30L mixtures containing 15L of 2 × KAPA Library Amplification ReadyMix, 1L of each primer , and 50ng of template DNA and ddH2O. The procedure of PCR was as follows: 95°C for 3min, followed by 30 cycles at 98°C for 20s, 58°C for 15s, and 72°C for 20s, then a final extension at 72°C for 5min. Amplicons were extracted from 2% agarose gels and purified using the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit according to the manufacturers instructions and were quantified using Qubit®2.0 . The pooled library was sequenced using an Illumina MiSeq system .
Levodopa Combined With Decarboxylase Inhibitors
Aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase is responsible for the enzymatic decarboxylation of levodopa to dopamine. Carbidopa is a commonly used decarboxylase inhibitor. The decarboxylase inhibitors do not penetrate the bloodbrain barrier and inhibit only the peripheral conversion of levodopa to dopamine, including the conversion that occurs in the intestinal lumen. Carbidopa allows an 80% decrease in the dosage of levodopa necessary to control parkinsonian symptoms . Carbidopa is relatively nontoxic but is inactive as an antiparkinson drug in the absence of levodopa.
The levodopa-carbidopa combination is not recommended in pregnancy or in patients younger than 18 years. Carbidopa is available as a single agent or formulated with levodopa in a fixed ratio of 10 mg/100 mg, 25 mg/100 mg, and 25 mg/250 mg and controlled-release preparations with fixed ratios of 25 mg/100 mg and 50 mg/200 mg . Packaged alone , carbidopa is useful for patients who require greater amounts of the drug than provided in the standard ratios.
Profiles Of Plasma Bcaas And Aaas And Their Correlations With Clinical Characteristics And The Gut Microbiota In Pd Patients
After correction for covariates, the plasma Leu , Ile , Val , and Tyr were significantly lower in PD patients compared with controls, while no differences were observed in Phe .
Table 2 Plasma levels of BCAAs and AAAs in controls and PD patients.
We performed Spearmans rank correlation analysis to explore the relationship of plasma BCAAs and AAAs with clinical characteristics . All of the AAAs and BCAAs negatively correlated with H& Y stage , including Phe , Tyr , Leu , Ile , and Val . Leu was negatively associated with MDS-UPDRS IV score , levodopa daily dose , and LEDD . Ile was negatively correlated with disease duration , levodopa daily dose , and LEDD . Val was negatively associated with MDS-UPDRS total score , MDS-UPDRS II score , MDS-UPDRS IV score , levodopa daily dose , and LEDD . Phe was negatively correlated with disease duration and levodopa daily dose . However, we found no significant difference in plasma BCAAs or AAAs in patients treated with or without other antiparkinsonian medications .
Fig. 1: Correlations between plasma BCAAs and AAAs and PD clinical characteristics.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Icd 10
Could Something As Simple As Targeted Amino Acid Supplementation Be The Missing Piece To Your Parkinsons Adhd Or Insomnia Healing Regimens
Neurologic issues are some of the most common and complex health challenges we face and the treatments are often worse than the disease itself! When it comes to medications for Parkinsons, ADHD, and insomnia, the side effects can be downright dangerous, ranging from balance issues all the way to suicidal depression. It may surprise you to know that there are safe, natural amino acid therapies that get to the root causes of these complicated illnesses to provide relief from the debilitating symptoms.
Effect Of Tyrosine On Orthostatic Hypotension In Parkinsons Disease

Objective/Rationale: Orthostatic hypotension is a sudden drop in blood pressure when an individual changes position. Individuals with Parkinsons disease commonly suffer from orthostatic hypotension and low BP due to reduced levels of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine. Medications used to treat PD reduce norepinephrine levels, thus further reducing BP. Tyrosine is a non-essential amino acid that is the building block for norepinephrine. Supplementing tyrosine may help to increase BP in individuals with PD.
Project Description: Forty subjects with PD, orthostatic hypotension and low blood pressure will keep a food diary detailing fluid and salt intake for seven days before testing. Subjects will be randomly assigned to a tyrosine supplementation group or to a placebo group. Both researchers and subjects will be blind to the treatment assignment. After an overnight fast, subjects will undergo an orthostatic hypotension test and an exercise test to induce stress at peak medication. Blood will be drawn before exercise testing and immediately post test. Heart rate and BP will be monitored every two minutes for the duration of the test. Subjects will then take seven days of tyrosine supplementation or placebo, and continue with the food diary. The same tests will be administered after seven days of tyrosine supplementation or placebo.
Also Check: What Part Of The Brain Is Affected By Parkinson’s
C Elegans Strains And Maintenance
Worms were maintained at 20 °C on standard nematode growth medium plates or high growth medium plates seeded with OP50 E. coli or HT115 RNAi E. coli, as indicated. The following strains were used in this study: wild-type worms of the N2 Bristol strain, neuron-only RNAi strain CQ511 uIs69 , and the following neuronal RNAi-sensitive strains: CF512 , CQ434 baIn11 vIs69 , and TU3311 uIs60 .
Aromatic Amino Acid Decarboxylase Deficiency
Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase deficiency is an autosomal recessive disorder that combines serotonin and catecholamine deficiency. The gene locus is 7p11. Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase catalyzes the decarboxylation of L-DOPA and 5-hydroxytryptophan to dopamine and serotonin, respectively. Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase deficiency is characterized by a CSF profile of low homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, high L-DOPA, 5-hydroxytryptophan, and 3-O-methyldopa , and normal pterin levels. Clinical onset is typically by 6 months of age. The associated features are hypotonia and extrapyramidal movement disorders such as torticollis, dystonia, blepharospasm, athetosis, and myoclonus. Other manifestations are profound developmental delay, irritability, sleep disturbances, and autonomic manifestations such as temperature instability, impaired diaphoresis, hypersalivation, recurrent syncope, or cardiorespiratory arrest. Impaired sympathetic responses, with maintenance of systemic blood pressure following nitroprusside infusion, are demonstrable . The syndrome may present in the neonate with hypothermia, lethargy, poor sucking, ptosis, and hypotension . Typically, patients are initially diagnosed with cerebral palsy, epilepsy, suspected mitochondrial encephalopathies, myasthenia, or hyperekplexia. Neuroimaging is generally unremarkable but may reveal progressive cerebral atrophy.
James T. Boyd, Karen M. Lounsbury, in, 2017
Read Also: Virtual Reality Parkinson’s Disease
Dr Mary Hinz And Parkinsons Therapy
I began working with Dr. Hinz back in 2001. At that time, much of his focus was on managing appetite in order to facilitate long-term weight loss. Over time, however, it became apparent that amino acid therapy had a much larger application.
The first paper published by Dr. Hinz in relation to Parkinsons disease was a case study in 2011. This paper provided insight into a novel approach using the most effective therapy for Parkinsons disease which had the potential to help millions of people suffering from Parkinsons disease.
However, it was a couple landmark papers published in 2014 that really brought Dr. Hinzs approach to Parkinsons disease into the national spotlight. The first paper showed that the most popular medications used to treat Parkinsons disease could potentially cause a nutritional catastrophe in the body. This was shown to happen because of the adverse effect these drugs have on vitamin B6 and all the functions that vitamin B6 and B6-dependent enzymes have in the human body. The end result, according to this research, was that carbidopa may contribute to the worsening of Parkinsons disease and the increase in the Parkinsons disease death rate seen since the introduction of these medications.
Metformin Reduces Neurodegeneration And Restores Normal Levels Of Mitochondrial Respiration
While disease mechanisms in PD are thought to involve decreased mitochondrial function , our findings instead suggest that elevated mitochondrial respiration may also contribute to PD pathogenesis, potentially preceding an ultimate loss of mitochondrial function. Thus, strategies to restore mitochondrial homeostasis early in the disease may be efficacious. We recently identified the type 2 diabetes medication metformin as one of the top-performing candidates in a high-throughput screen for drugs that improve motor function in bcat-1 worms . Among several known targets, metformin can act as a complex I inhibitor , raising the possibility that reducing mitochondrial respiration may constitute a surprising new treatment avenue for PD.
To determine whether metformin rescues bcat-1associated toxicity in worms with -synuclein expression in dopaminergic neurons, we measured motor function and dopamine neuron degeneration. Worms treated with 50 M metformin as described above showed significantly reduced curling on day 8 . Remarkably, metformin also significantly rescued dopamine neuron viability. On day 8, the number of dopaminergic cell bodies and neurites with healthy morphologies was increased in metformin-treated bcat-1 worms compared with vehicle-treated worms . Neuroprotection was detected as early as day 6, after only 2 d of metformin treatment , with dopaminergic neurons showing significantly improved neurite morphologies .
Also Check: How To Tell Difference Between Parkinson’s And Essential Tremor
Curling And Other Motor Assays
Manual quantification of individual worms curling level was performed as described previously . In brief, worms were picked into a drop of M9 buffer on a microscope slide, and 30-s videos were obtained. The percentage of time spent curling was quantified for each individual worm using a standard stopwatch. Automated curling analysis was performed as described previously . In brief, on the day of analysis, worms were rapidly washed twice with M9 buffer and dispensed into 96-well plates, and 30-s videos or a series of snapshots were obtained for individual wells containing 3 to 30 worms each. Our curling detection software quantified the number of worms in a curled position divided by the total number of worms detected, which was defined as the percentage of worms in a curled position. For body wave number and activity index, 30-s videos were obtained and analyzed by CeleST software as described previously .
Amino Acid Therapy And Your Brain
Amino acid therapy may be used to treat a variety of conditions, including from anxiety, depression, Parkinsons disease , attention deficit disorder, migraines, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue, and even addictions. Amino acids are basic building blocks used to make proteins in our body that build tissues and muscle, but they also synthesize neurotransmitters in the brain. What does all of this mean? Let me explain.
You May Like: Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Dementia
Add Medication For A Winning Combo
Diet and exercise are important for managing PD, but dont forget about medications. Take them regularly and exactly as your doctor prescribes.
If you tend to forget your medication, set an alarm to remind you. You can also use a pillbox thats labeled with days and times of day. Take your meds on a set schedule, dont skip doses and dont double dose, says Dr. Gostkowski. When youre diligent about taking your medications and following a healthy lifestyle, youll feel your best.
Dietary Protein And Parkinsons
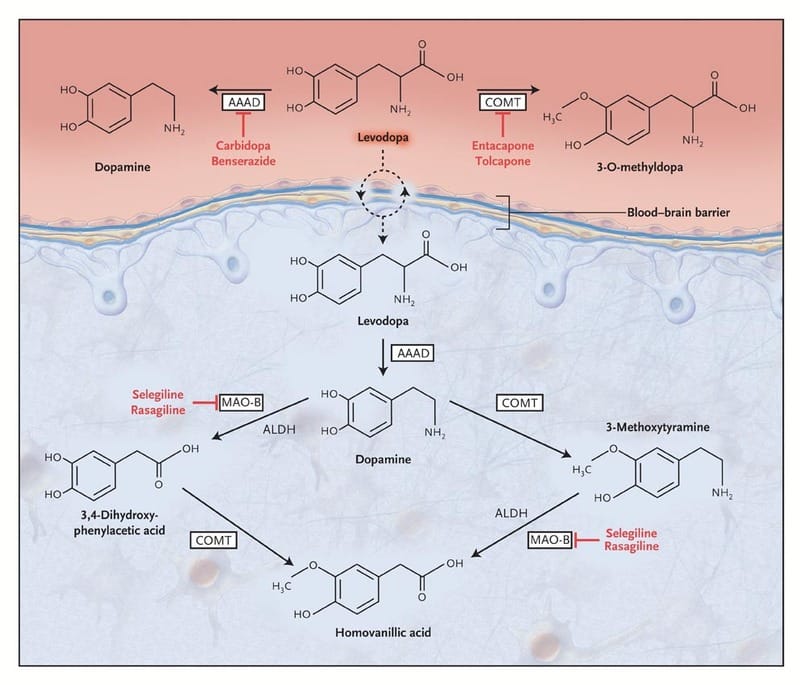
This known interaction between levodopa and amino acids in the gut means that people with Parkinsons need to be careful about their protein consumption around the time of taking their medication.
When you have a large amount of protein, they get broken down in the stomach into amino acids. And once these amino acids enter the small intestine, they start competing with levodopa to use the transporter system out into the blood. This competition can cause a reduction in the amount of levodopa reaching the brain, in turn reducing the effectiveness of the dose.
Read Also: Is Constipation A Symptom Of Parkinsons
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Vs Ms
Dyskinesia Uncontrolled Involuntary Movement
This is the most unpleasant side effect that appears within 2 years of using levodopa therapy, although in some patients, it may appear after 5 years.
It refers to the abnormal uncontrolled involuntary movements that mostly affect the arms, legs, and face. In this condition, the tremor becomes more aggressive and results in the wiggly movement.
You May Like: Alcohol And Parkinsons Disease
Neurotransmitters And Amino Acid Therapy Getting To The Heart Of The Matter
by admin | Aug 13, 2013 | Amino Acid Therapy, Natural Remedies, Naturopathic health, Naturopathic medicine |
Neurotransmitter imbalances are associated with an incredibly wide array of diseases and disorders. Typically, 90+% of the people we see have three or more neurotransmitter related disorders active simultaneously they just dont know that they are related. The standard medical approach in these cases is to treat each disorder in a vacuum this usually means giving specific drugs for specific disorders without looking for the root cause that may connect them. Amino acid therapy provides an extremely effective and efficient solution that addresses the root of the problem.
The goal with amino acid therapy in these cases is to get both serotonin and dopamine levels into their optimal ranges. This really has two parts: the first is the get serotonin and dopamine into what is often referred to as the Phase 3 therapeutic range the second part is to get serotonin and dopamine balanced with one another.
This process requires the skills of a practitioner trained in the proper use of amino acid therapy and may involve specialized testing to determine each persons exact amino acid needs. However, optimizing neurotransmitter status is absolutely vital for a long term solution, so the time and effort required is well worth it.
To find a provider near you, visit . If a local provider is not available, please contact us.
Read Also: Everything You Need To Know About Caregiving For Parkinson’s Disease
Safety And Clinical Outcomes
The primary outcome measure was the safety and tolerability of AADC gene transfer as assessed by frequency of adverse events and serious AEs and their relationship to VY-AADC01 or the trial procedure. Secondary outcome measures included changes from baseline in PD medications measured as daily levodopa equivalent dose , and motor function as assessed by PD diary good âonâ time and âoffâ time, Unified Dyskinesia Rating Scale total scores, Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Part III âoffâ-medication and âonâ-medication scores, and mH& Y scale âoffâ-medication scores. Changes to PD medications were made at the discretion of the investigator. Patient Global Impression of Improvement and Clinical Global Impression of Improvement were assessed throughout follow-up. Changes in quality of life were assessed using the 39-item Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire . The âoffâ medication state was defined as â¥12 hours after stopping PD medications the âonâ medication state was defined as 30â120 minutes after taking the first daily dose of PD medications when participants and investigators both agreed that benefits of PD medications had occurred. If the participant was not fully âonâ as judged by the participant and investigator, an additional ½ to 1 carbidopa/levodopa 25/100 mg tablet was administered.
Side Effects Of Protein
A modulation of levodopa dosage is the major method to control dyskinesia on a protein-restricted diet. In two studies of Pincus et al., respectively, 75 and 73% of the subjects required a reduction in levodopa dosage to avoid chorea . In addition, there were two outpatients who noticed that a reduced dosage of Sinemet helped to improve their dyskinesia without shortening their on time . Beside a smaller medication dosage, a pro re nata protein supplement was also reported to reverse dyskinesia on PRD by two patients . Compared with a low protein-high carbohydrate diet, Berry et al. indicated that a diet with a carbohydrate: protein ratio of 5:1 was less likely to cause dyskinesia as well as fluctuations in levodopa concentrations . However, the effectiveness of these approaches to relieve dyskinesia on protein-restricted diets has only been reported in small numbers of patients without any statistical analysis. Additional large-sample studies or double-blinded trails are still required.
Recommended Reading: What Systems Are Affected By Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: Stage 3 Parkinson’s Disease
Demographics And Clinical Characteristics Of Study Participants
Demographics and clinical characteristics of study participants are summarized in Table . A total of 106 PD patients and 114 controls were enrolled in this study. Age, sex, and body mass index were indistinguishable between PD patients and controls. PD patients had an average Hoehn and Yahr stage of 2.5±0.9, disease duration of 6.5±4.6 years, and Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale total score of 61.9±21.8 points. All PD patients were using antiparkinsonian medications. Dopamine agonists were used by 70 patients, including pramipexole , piribedil , and ropinirole . Monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors, including selegiline and rasagiline , were used by 36 patients. There were no significant differences in age, sex, or BMI between patients with early and advanced PD . The disease duration was longer MDS-UPDRS total and part II, III, and IV scores were higher and levodopa daily dose and levodopa equivalent daily dose was larger in patients with advanced stage. More patients were treated with levodopa in the advanced stage.
Table 1 Demographics and clinical characteristics of study participants.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is currently no cure for Parkinsons disease, which always gets worse over time. Death is usually because of complications, including pneumonia or falling-related injuries.
Parkinsons disease changes the quality of life for patients and their families. In order to make the most worthwhile treatment decisions, education is imperative. Some prescription drugs and surgical procedures may drastically improve symptoms.
Treatment plans for Parkinsons depend on symptoms, other health issues and medications used to treat them, metabolism, and age. Because most Parkinsons symptoms result from a lack of dopamine in the brain, many drugs attempt to replenish proper levels of dopamine or mimic the action of dopamine. Termed dopaminergic medications, these treatments target muscle rigidity, speed and coordination of movement, and tremors.
Though these medications can decrease symptoms for some Parkinsons patients, they do come with side effects, some of which can be severe. The list of reported side effects for top Parkinsons drugs includes:
| Confusion |
Dont Miss: How Does General Anesthesia Affect Parkinsons
You May Like: Is Drooling A Symptom Of Parkinson’s Disease