The Muscarinic Receptors In The Striatum
In the striatum, every type of neuron expresses different subtypes of both mAChR and nAChRs . The mAChRs are metabotropic receptors that indirectly control the activity of membrane ion channels through heterotrimeric G-proteins . These G-proteins are composed of G and Gg subunits classified according to the type of subunit, which determines their association to specific G-protein coupled receptors .
In the CNS, the mAChRs are categorized into five subtypes groups . These receptors show significant differences in expression M1 > M2 > M4 > M3 and M5 .
A study using atropine to inhibit M2 and M3 mAChRs present on the glutamatergic terminals revealed a small but significant increase in corticostriatal transmission, suggesting the existence of tonic cholinergic presynaptic inhibition of this excitatory afferents inputs . At different, the M1 mAChR blocker pirenzepine decreased corticostriatal transmission .
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
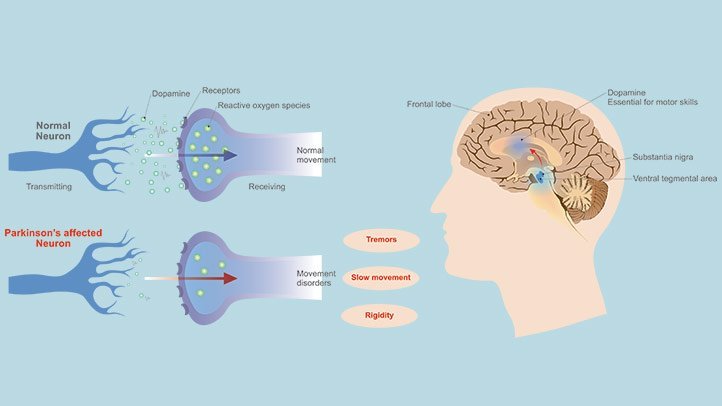
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra become impaired or die. These cells normally produce dopamine, a chemical that helps the cells of the brain communicate . When these nerve cells become impaired or die, they produce less dopamine. Dopamine is especially important for the operation of another area of the brain called the basal ganglia. This area of the brain is responsible for organizing the brains commands for body movement. The loss of dopamine causes the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinsons disease.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This chemical is needed for proper functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This system controls some of the bodys autonomic functions such as digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Loss of norepinephrine causes some of the non-movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists arent sure what causes the neurons that produce these neurotransmitter chemicals to die.
Read Also: Early Parkinson’s Symptoms Mayo Clinic
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosis is difficult at every stage of the disease, but particularly in the early stages. No single test can provide a diagnosis. A diagnosis will likely involve physical and neurological examinations, conducted over time to assess changes in reflexes, coordination, muscle strength, and mental function. Your doctor might also see how you respond to medicine.
You may need to have brain imaging tests to rule out other conditions that might be causing your symptoms. Such tests could include MRI and CT scans and possibly some other types of scans. Blood tests may also be done to exclude other illnesses.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Research Paper
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Structural Changes In The Cerebellum
With the deformation-based morphometry method, revealed significant contraction in the left cerebellum in patients with early-stage Parkinsons disease compared with control subjects. Using the voxel-based morphometry method, found that in patients with mild-to-moderate Parkinsons disease with and without resting tremor, grey matter volume is decreased in the right quadrangular lobe and declive of the cerebellum in Parkinsons disease with tremor compared with those without. Other studies also found cognitive- or olfactory-related structural changes in the cerebellum in patients with Parkinsons disease. Therefore, there are specific Parkinsons diseaserelated morphological changes in the cerebellum.
Also Check: Parkinson’s And Swollen Feet And Ankles
Motor Circuit In Parkinson Disease
The basal ganglia motor circuit modulates the cortical output necessary for normal movement .
Signals from the cerebral cortex are processed through the basal ganglia-thalamocortical motor circuit and return to the same area via a feedback pathway. Output from the motor circuit is directed through the internal segment of the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra pars reticulata . This inhibitory output is directed to the thalamocortical pathway and suppresses movement.
Two pathways exist within the basal ganglia circuit, the direct and indirect pathways, as follows:
-
In the direct pathway, outflow from the striatum directly inhibits the GPi and SNr striatal neurons containing D1 receptors constitute the direct pathway and project to the GPi/SNr
-
The indirect pathway contains inhibitory connections between the striatum and the external segment of the globus pallidus and between the GPe and the subthalamic nucleus striatal neurons with D2 receptors are part of the indirect pathway and project to the GPe
The STN exerts an excitatory influence on the GPi and SNr. The GPi/SNr sends inhibitory output to the ventral lateral nucleus of the thalamus. Dopamine is released from nigrostriatal neurons to activate the direct pathway and inhibit the indirect pathway. In Parkinson disease, decreased striatal dopamine causes increased inhibitory output from the GPi/SNr via both the direct and indirect pathways .
Macroscopic Pathologypd Msa Psp
PD is often unremarkable, with mild frontal atrophy in some cases. There is no significant atrophy of brainstem, and this can be useful in the differential diagnosis of PSP and MSA, in which there is midbrain atrophy in PSP and pontine atrophy in MSA. Sections of the brainstem usually reveal loss of the normally dark black pigment in the substantia nigra and locus ceruleus, but pigment loss in the substantia nigra is also characteristic of PSP and MSA. The loss of pigmentation correlates with neuronal loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and noradrenergic neurons in the locus ceruleus. Pigment loss in the locus ceruleus is consistent in PD, but less predictable in PSP and MSA.
MSA-P has atrophy and brownish discoloration of the posterolateral putamen , the brown color correlating with increased iron pigment. In cases with significant cerebellar signs, there is also atrophy of the pontine base and atrophy and gray discoloration of the cerebellar white matter. More subtle atrophy is noted in the medulla and the cerebellar cortex.
You May Like: What Causes Shaking In Parkinson’s Disease
Neurotransmitter Systems In The Striatum Altered By Pd
The striatum receives many synaptic inputs from all cortical regions and the thalamus providing excitatory glutamatergic afferents . At the same time, the nigrostriatal pathway delivers modulatory neurotransmitters such as DA, ACh, GABA, nitric oxide, and adenosine . All these neurotransmitter systems modulate the efficacy of the synaptic transmission in the striatum, which processes excitatory glutamatergic signals from cortical and thalamic afferents and modulates signals from dopaminergic neurons of the midbrain, aspiny GABAergic, and cholinergic interneurons . These signals are received and processed by the dorsal striatum MSN, which make up 9095% of the striatum neuron population . The remaining 510% of striatum neurons are interneurons, including the GABA and ACh interneuron populations, which are significant regulators of both MSN and striatal afferents . Among them, the most important are ChIs, which closely interact with DA afferents of the midbrain . The glutamatergic, serotonergic, cholinergic, GABAergic, noradrenergic systems are involved in modulating the striatums output signals . In addition, opioids, neuropeptides, steroids, and adenosine receptors families are present in the dorsal striatum . Due to the presence of such a variety of modulators, DA deficiency could be surmounted by modulating these receptors .
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Don’t Miss: How Close To A Cure For Parkinson’s
The Cerebellum And Non
Many non-motor symptoms, including sensory, autonomic, cognitive and behavioural problems, coexist with the motor signs in Parkinsons disease . Non-motor symptoms exist in up to 60% of patients , and can be primary complaints in Parkinsons disease . Cognitive impairment is common in patients with Parkinsons disease . Hypometabolism in the prefrontal, parietal, temporal and mesolimbic regions was correlated with cognitive impairment in Parkinsons disease . With fluorodeoxyglucose PET and spatial covariance analysis, identified a significant covariance pattern that correlated with cognitive performance, particularly involving executive functioning in Parkinsons disease. This Parkinsons diseaserelated cognitive pattern is characterized by metabolic reductions in frontal and parietal association areas, and increases in the cerebellar vermis and dentate nuclei . Parkinsons diseaserelated cognitive pattern expression increased with worsening of cognitive impairment , but is not correlated with the decline of striatal dopaminergic function . Therefore, the hypermetabolism in the cerebellum might also be a compensatory effort to maintain cognitive function in Parkinsons disease.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative, progressive disorder that affects nerve cells in deep parts of the brain called the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce the neurotransmitter dopamine and are responsible for relaying messages that plan and control body movement. For reasons not yet understood, the dopamine-producing nerve cells of the substantia nigra begin to die off in some individuals. When 80 percent of dopamine is lost, PD symptoms such as tremor, slowness of movement, stiffness, and balance problems occur.
Body movement is controlled by a complex chain of decisions involving inter-connected groups of nerve cells called ganglia. Information comes to a central area of the brain called the striatum, which works with the substantia nigra to send impulses back and forth from the spinal cord to the brain. The basal ganglia and cerebellum are responsible for ensuring that movement is carried out in a smooth, fluid manner .
The action of dopamine is opposed by another neurotransmitter called acetylcholine. In PD the nerve cells that produce dopamine are dying. The PD symptoms of tremor and stiffness occur when the nerve cells fire and there isn’t enough dopamine to transmit messages. High levels of glutamate, another neurotransmitter, also appear in PD as the body tries to compensate for the lack of dopamine.
Read Also: What Is The Difference Between Alzheimer’s And Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
Pathogenesis Of Parkinsons Disease
A number of mechanisms have been implicated in PD pathogenesis, with -synuclein aggregation central to the development of the disease. Multiple other processes are thought to be involved, with several studies suggesting that abnormal protein clearance, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuroinflammation play a role in the onset and progression of PD. However, the relationship between these pathways remains unclear.
You May Like: Drugs Prescribed For Parkinson’s Disease
What Treatments Are Available
Many Parkinson’s patients enjoy an active lifestyle and a normal life expectancy. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet and staying physically active contributes to overall health and well-being. Parkinson’s disease can be managed with self-care, medication, and surgery.
Self careExercise is as important as medication in the treatment of PD. It helps maintain flexibility and improves balance and range of motion. Patients may want to join a support group and continue enjoyable activities to improve their quality of life. Equally important is the health and well being of the family and caregivers who are also coping with PD. For additional pointers, see Coping With Parkinsons Disease.
These are some practical tips patients can use:
Medications There are several types of medications used to manage Parkinson’s. These medications may be used alone or in combination with each other, depending if your symptoms are mild or advanced.
After a time on medication, patients may notice that each dose wears off before the next dose can be taken or erratic fluctuations in dose effect . Anti-Parkinsons drugs can cause dyskinesia, which are involuntary jerking or swaying movements that typically occur at peak dosage and are caused by an overload of dopamine medication. Sometimes dyskinesia can be more troublesome than the Parkinsons symptoms.
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of PD vary from person to person, as does the rate of progression. A person who has Parkinson’s may experience some of these more common “hallmark” symptoms:
- Bradykinesia – slowness of movement, impaired dexterity, decreased blinking, drooling, expressionless face.
- Tremor at rest – involuntary shaking that decreases with purposeful movement. Typically starts on one side of the body, usually the hand.
- Rigidity – stiffness caused by involuntary increase in muscle tone.
- Postural instability – sense of imbalance. Patients often compensate by lowering their center of gravity, which results in a stooped posture.
Other symptoms that may or may not occur:
Freezing or being stuck in place Shuffling gait or dragging of one foot Stooped posture Cognitive impairment
You May Like: Insomnia And Parkinson’s Disease
The Development Of An Imbalance Between Different Systems In The Striatum As The Main Contributing Factor In Pd
Dopamine deficiency in the striatum causes an imbalance of activity between two MSN populations, each expressing only one type of receptor . Each of both MSN groups has a unique path to the GPi/SNpr neurons. MSNs expressing D1R form a direct pathway, while those expressing D2R form an indirect pathway via the GPe and the subthalamic nucleus . DA deficiency causes a decrease in the activity of MSN expressing D1R and increases the activity of neurons expressing D2R, thereby causing motor and cognitive dysfunctions . The balance between the dopaminergic and cholinergic systems is vital for the correct functioning of the striatum . PD symptoms such as tremor and rigidity are ameliorated by L-DOPA and anticholinergic drugs, suggesting that PD is a hypercholinergic disorder induced by a dysbalance between Dopaminergic and cholinergic systems .
How Is A Diagnosis Made
Because other conditions and medications mimic the symptoms of PD, getting an accurate diagnosis from a physician is important. No single test can confirm a diagnosis of PD, because the symptoms vary from person to person. A thorough history and physical exam should be enough for a diagnosis to be made. Other conditions that have Parkinsons-like symptoms include Parkinsons plus, essential tremor, progressive supranuclear palsy, multi-system atrophy, dystonia, and normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Read Also: 1st Sign Of Parkinson’s
Differential Diagnosis Of Parkinson Disease
Perhaps expression analysis of genes in brains of patients with various neurodegenerative and recognizing disease-specific patterns will in the future assist in differentiating PD from other parkinsonian disorders. For example, using microarray technology in SN samples from six patients with PD, two with PSP, one with FTDP, and five controls, Hauser and colleagues found 142 genes that were differentially expressed in PD cases and controls, 96 in the combination of PSP-FTDP, and 12 that were common to all three disorders. Further studies are needed to confirm this intriguing finding.
Claudia Trenkwalder, in, 2005