Coordinates Of Active Electrode Contacts
Retrospective analysis of the stereotactic position of the active electrode contacts was done in 25 patients for whom postoperative T1 weighted MRI of sufficient quality or stereotactic radiographic examinations were available. Such analyses could not be undertaken in other patients implanted with subthalamic nucleus electrodes during the same period because of motion artefacts in the postoperative MRI, missing postoperative T1 weighted MRI, or missing postoperative stereotactic x rays. For the 25 patients evaluated, the mean and median coordinates of all active contacts are summarised in table 3. The mean laterality of all active electrode contacts mm median 12.7 mm) correlated well with the laterality of the subthalamic nucleus, as determined 3 mm ventral to the intercommissural plane in T2 weighted MRI of 35 patients mm). However, in the dorso-ventral direction the mean and median z coordinate of all active contacts do not project within the subthalamic nucleus proper, but suggest an area between the dorsal margin of the subthalamic nucleus and the subthalamic region according to different stereotactic brain atlases. Moreover, 12 of 49 active contacts were located within 0.5 mm of the intercommissural plane or further dorsal they were thus most probably in the subthalamic area.
Active electrode contacts relative to the mid-commissural point
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of The Stn
Before the MRI era, localization of the STN was performed indirectly, on the basis of an averaged distance from an internal reference that was visualized on a stereotactically acquired ventriculography . The most commonly used reference was the line between the anterior and posterior commissures . Standard human brain atlases were used to determine the position of the subthalamic nucleus, relative to the ACPC midpoint, in each direction of a Cartesian coordinate system superimposed on the brain by a stereotactic frame. In 1995, Benabid was the first to target the STN using direct visualization on a T2-weighted 1.5-T MRI . In recent years, new MRI sequences such as susceptibility-weighted imaging have been introduced and magnetic field strengths have increased up to 7 T, all leading to improved STN visualization . On coronal 7-T T2-weighted imaging, the STN can be distuingished from surrounding white matter and the more ventrally located substantia nigra pars reticulata . Direct targeting of the dorsolateral part of the STN on MRI is now feasible, together with visualization of the motor fibers in the nearby internal capsule through the use of diffusion tensor imaging .
Fig. 2
Neuronal Activity Of The Snpr
Neuronal activity of the SNpr was recorded 0.53 mm below the STN. Eighty neurones were recorded `on-line’. The action potentials during the recording were biphasic, with high frequency and brief duration , and a predominant tonic pattern of discharge. Of the 80 neurones recorded, 27 were adequately isolated for `off-line’ analysis. These neurones showed a tonic pattern of discharge characterized by a mean firing rate of 71.59 ± 28.33 Hz with a mean ISI of 16.44 ± 7.01 ms and a mean CV of the ISI of 0.85 ± 0.29 . In only three neurones was there a response to sensorimotor stimulation. Comparing SNpr neurones with the group of STN neurones with a tonic firing pattern, the SNpr had a significantly higher firing discharge rate however, there was no difference in the CV of the ISI, indicating that both neuronal groups discharged with a similar pattern.
Also Check: Mucuna Plants For Parkinson’s Disease
Analysis Of Neuronal Activity And Statistics
Neuronal action potentials were discriminated using the AlphaSort program . Well-isolated neurones were digitized for analysis with the Labview program. This program provides quantitative information about the activity of a single neurone during a 12 s period. Statistics derived from the analysis included the interspike interval histogram and instant frequency histogram with a temporal basis of 50 ms, mean firing rate, the minimum and maximum ISI and the burst index. A one-way analysis of variance with post hoc exploratory evaluation was used for differences in firing rate and the coefficient of variation of the ISI for each neuronal type.
In patients in whom tremor was a prominent feature, microrecording of the neuronal activity in the STN, and electromyographic study of the muscles involved in the tremor were performed simultaneously. The signals were analysed on the basis of linear spectral methods . The autopower spectrum was derived after 4 s analysis of the neuronal and EMG signals independently. It provided the intensity of the signal as a function of frequency. Calculation of the spectral cross-power determined the extent to which power in the two signals has the same predominant frequency. Phase relationships were not analysed by this method.
What Are The Risks
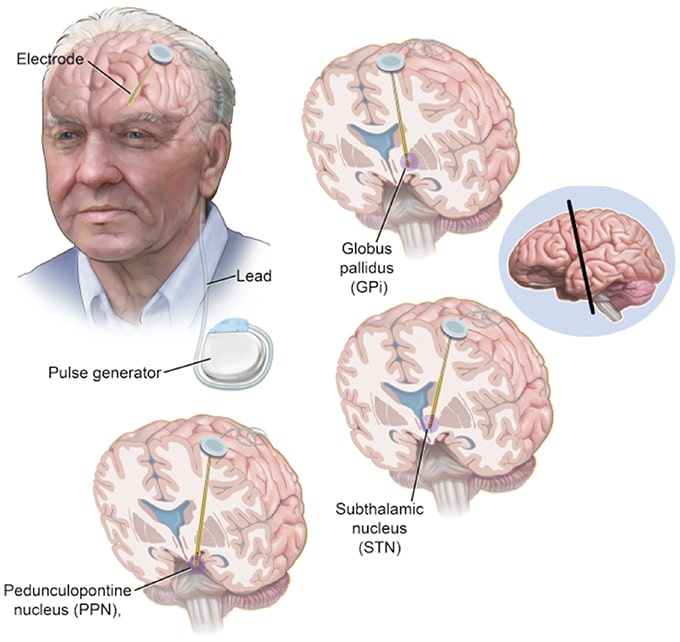
No surgery is without risks. General complications of any surgery include bleeding, infection, blood clots, and reactions to anesthesia. Complications related to placement of the DBS lead include seizures, infection, and a 1% chance of bleeding in the brain.
Reasons for which you might need additional surgery include breakage of the extension wire in the neck parts may wear through the skin and removal of the device due to infection or mechanical failure. If you have a non-rechargeable DBS system, the battery will need to be replaced every 3 to 5 years. Rechargeable DBS systems have a battery that lasts 10 to 15 years.
DBS may also cause worsening of some symptoms such as speech and balance impairments. In some patients with Parkinson’s, DBS may cause or worsen depression. If you develop any side effects from a stimulation adjustment, you need to return to the office for further programming.
Also Check: What To Do For Parkinson Tremors
Research To Improve Deep Brain Stimulation
Researchers are working to improve upon existing DBS devices and methods to help treat more symptoms and more people. Some researchers are putting electrodes in a different area of the brain the pedunculopontine nucleus to treat walking and balance problems that don’t typically improve with present-day DBS. Others are developing a “smart” DBS device that can record a person’s unique brain signals and deliver electrical stimulation only when needed, such as when symptoms return, rather than continuously, as the current systems do. This could help reduce side effects such as numbness and weakness and lengthen the battery life of the neurostimulator, which would result in a longer time between battery replacement procedures.
Scientists also are planning to test deep brain stimulation in the first years after a Parkinson’s diagnosis to see if the therapy may slow or stop disease progression. Testing in Parkinson’s models showed the therapy may help protect brain cells, and a small human trial showed motor symptoms improved after early-stage DBS.
Open Access License / Drug Dosage / Disclaimer
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License . Usage and distribution for commercial purposes requires written permission. Drug Dosage: The authors and the publisher have exerted every effort to ensure that drug selection and dosage set forth in this text are in accord with current recommendations and practice at the time of publication. However, in view of ongoing research, changes in government regulations, and the constant flow of information relating to drug therapy and drug reactions, the reader is urged to check the package insert for each drug for any changes in indications and dosage and for added warnings and precautions. This is particularly important when the recommended agent is a new and/or infrequently employed drug. Disclaimer: The statements, opinions and data contained in this publication are solely those of the individual authors and contributors and not of the publishers and the editor. The appearance of advertisements or/and product references in the publication is not a warranty, endorsement, or approval of the products or services advertised or of their effectiveness, quality or safety. The publisher and the editor disclaim responsibility for any injury to persons or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content or advertisements.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Disease Cause Personality Changes
Unilateral Vs Bilateral Dbs
Another important factor to consider when interpreting the effects of STN-DBS on reward seeking is whether the stimulation is applied unilaterally or bilaterally. One set of studies performed under matched conditions from the same group reported that chronic unilateral STN-DBS during a FR1 task did not recapitulate the sustained reward seeking deficit that occurred with chronic, bilateral stimulation . With the unilateral STN-DBS, the effect was only transient and lasted no more than 5 days. Overall, the few studies using unilateral STN-DBS do not report robust reward seeking deficits, or report deficits that are only transient . In the clinic, bilateral STN-DBS is generally associated with superior reduction in motor symptoms relative to unilateral stimulation , but may also induce more non-motor side-effects . Notably, a study within the same clinical center observed apathy following bilateral but not unilateral STN-DBS . These observations suggest that preserving function of one STN by applying DBS unilaterally protects against a reward seeking deficits in patients or in animal models. It is also possible that DBS may drive compensatory metabolic or neural circuit changes in the un-stimulated hemisphere that may mitigate reward-seeking deficits induced by STN-DBS. Thus, whether STN-DBS is applied uni- or bilaterally is an important factor to consider when interpreting STN-DBS effects in animal models and its relevance to clinical populations.
Surgical Procedure And Clinical Results
The intraoperative results of microrecording and microstimulation were used to direct macroelectrode implantation into one of the five tracks investigated. The central track was chosen more often than the anterior , medial , lateral , or posterior tracks .
Table 1
Tracks chosen for permanent electrode implantation
Following implantation of the quadrupolar electrode , contacts resulting in the best alleviation of rigidity with the lowest voltage and without side effects were considered optimal and selected for permanent stimulation. As shown in table 2, contact 2 was chosen most often for permanent stimulation. Contacts 1 and 3 were also often selected, whereas contact 0 was rarely chosen . Only one of 25 patients required unilateral stimulation in a bipolar mode.
Table 2
Electrode contacts chosen for permanent stimulation
Figure 1
Unified Parkinsons disease rating scale motor score determined preoperatively and three and 12 months after surgery. MED, suprathreshold dose of levodopa DBS, stimulation with optimal contacts and stimulation parameters.
Read Also: Lewy Body Dementia Vs Parkinson
Surgical Procedure And Stimulation Programming
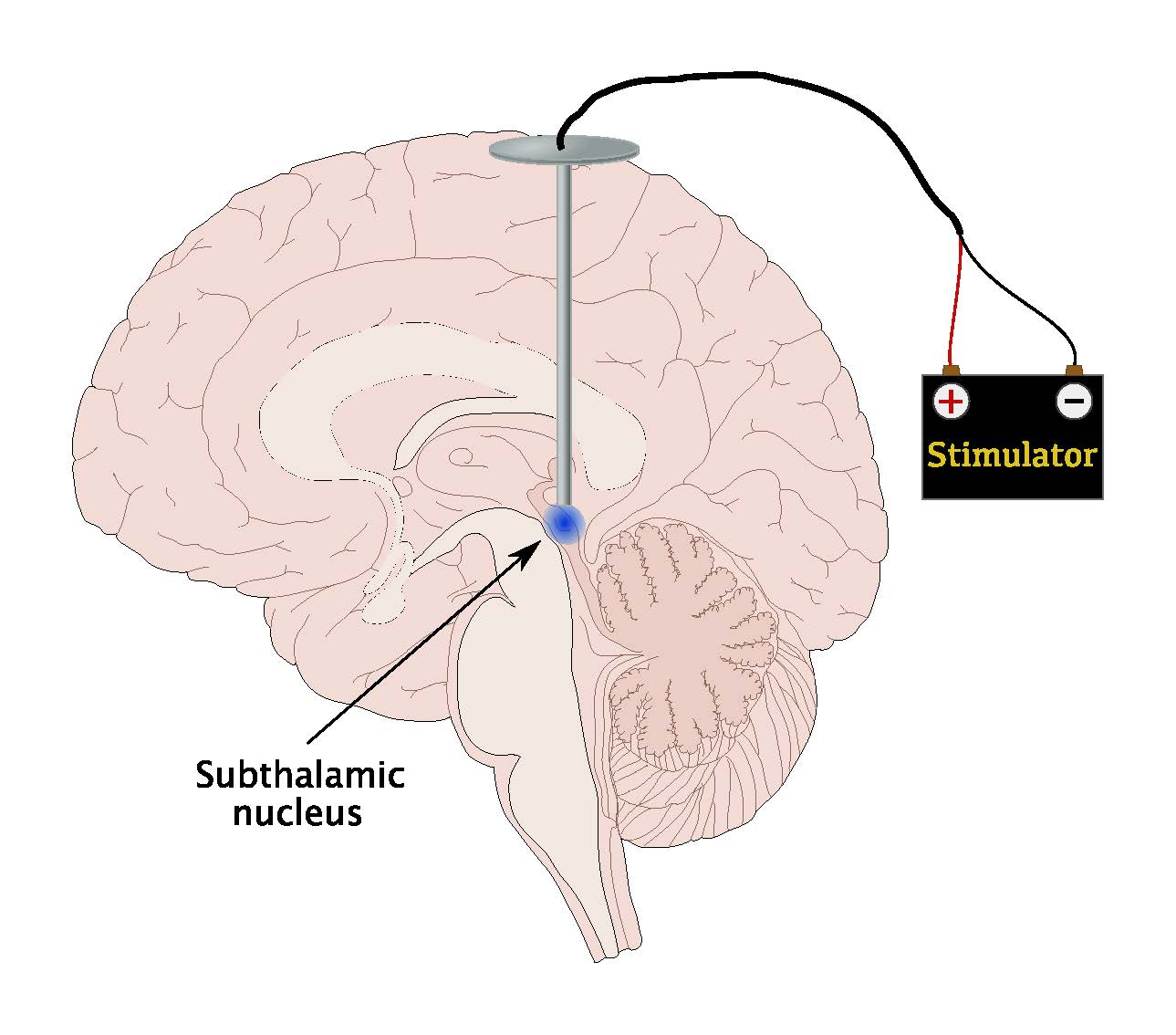
Details of our neurosurgical procedure, using an MRI-guided and MRI-verified technique, have been previously described., Briefly, implantation of bilateral quadripolar DBS electrodes was performed under local anaesthesia, in the off-medication condition to allow clinical evaluations during electrode placement. Monopolar stimulation through the contacts of the DBS electrode was sequentially performed to assess for additional therapeutic effects and/or the presence of side effects. One patient did not tolerate the off-medication condition, and surgery was performed under general anaesthesia. The STN was visualised on stereotactic T2-weighted MRI sequences and directly targeted using manual calculation and/or planning software , without MER. An immediate postoperative stereotactic MRI was performed to verify accurate electrode placement. The pulse generator was implanted in the subclavicular area and connected subcutaneously to the electrodes under general anaesthesia either immediately or a few days after electrode implantation.
Stimulation was initiated within the first postoperative week, and optimal settings were selected through a screening process. Stimulation and medication were further titrated according to clinical response over subsequent visits.
Identification Of Pertinent Literature
A systematic analysis of the international literature was carried out by selecting articles published in peer-review journals, using PubMed, and BioRxiv databases. The last search was conducted on September 11, 2020. Restrictions were made, limiting the study to academic publications in which the full text was published in English. Search terms were as follows: subthalamic nucleus AND stimulation AND and subthalamic nucleus AND .
Recommended Reading: Hand Brace For Parkinson’s
Substantia Nigra Pars Reticulata
Neuronal activity corresponding to the SNpr was detected immediately ventral to the STN in a high number of recording tracks. In the normal monkey, the SNpr has a mean firing rate of 60 Hz and maintained the general somatotopic organization of the basal ganglia . In the MPTP monkey, neuronal firing and metabolic markers in the SNpr are elevated above normal . In Parkinson’s disease, Hutchison and colleagues reported a mean firing rate of 71 ± 23 Hz , and the pattern of discharge was tonic . Our results coincide almost exactly with Hutchison and colleagues’ data. We found a mean firing rate of 71 ± 59 Hz. The CV of the ISI was 0.85 according with the marked tonic discharge pattern of SNpr neurones, and in keeping with findings in MPTP monkeys . Sensorimotor responses were infrequent in the SNpr compared with the findings in the STN and GPm of Parkinson’s disease patients. Tremor-related cells were never recorded.
Table 1
Somatotopic Organization Of The Stn
One hundred and eleven neurones of 350 recorded neurones responded to active and/or passive movement. Five neurones found to respond to both the upper and lower limb of one side, or to the ipsilateral limbs, were excluded from the analysis. Neurones with multi-joint responses within the same limb were included. The distribution of the 111 neurones with movement-related activity in the dorsoventral and mediolateral planes is summarized in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. In the parasagittal plane, the majority of neurones were localized in the dorsal third of the nucleus. No neurone with sensorimotor response was found in the ventral segment of the nucleus. Thus, all neurones with movement-related activity were located in the dorsal two-thirds of the STN . Within this plane a somatotopic arrangement was noticed. The majority of neurones responding to movement of the leg were located in the upper dorsal third of the STN. Arm-related neurones were predominantly in the upper dorsal third, but also in the medial segment, and orofacial-related neurones were evenly distributed throughout the dorsal two-thirds . From medial to lateral planes, the proportion of neurones responding to movements of the leg decreased, while those responding to arm movement activation increased . Neurones sensitive to orofacial movements were mainly found in the 13 mm plane . Overall, about two-thirds of neurones with sensorimotor responses were lateral to the 12 mm plane.
Read Also: Best Parkinson’s Doctors In Usa
Determining The Neural Mechanisms Underlying The Effects Of Stn
Optogenetics refers to a suite of engineered ion channels that are activated by light in a specific wavelength, and flux ions in response to activation. Channelrhodopsin is non-selective cation channel, that when exposed to blue light , allows sodium and calcium to flow into the cell along their concentration gradients, thereby inducing depolarization and action potentials . Conversely, the inhibitory halorhodopsin is a chloride pump that is activated upon stimulation with amber light , increases the intracellular chloride concentration, thereby hyperpolarizing the cell and inhibiting the firing action potentials . The location of the injected virus expressing the opsin and placement of the optic fiber for light delivery allows for spatial control of neural activation, while cell-type or projection-specific control of neural populations can be achieved by expressing viruses using intersectional genetic strategies. Finally, the pattern of light stimulation allows for tight temporal control of neural activity . Optogenetics has yielded highly valuable insight to functional connectivity and activity within intact or pathological circuits, and could be leveraged to resolve outstanding questions regarding STN-DBS mechanisms.
What Happens During Surgery
For stage 1, implanting the electrodes in the brain, the entire process lasts 4 to 6 hours. The surgery generally lasts 3 to 4 hours.
Step 1: attach stereotactic frameThe procedure is performed stereotactically, which requires attaching a frame to your head. While you are seated, the frame is temporarily positioned on your head with Velcro straps. The four pin sites are injected with local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. You will feel some pressure as the pins are tightened .
Step 2: MRI or CT scanYou will then have an imaging scan, using either CT or MRI. A box-shaped localizing device is placed over the top of the frame. Markers in the box show up on the scan and help pinpoint the exact three-dimensional coordinates of the target area within the brain. The surgeon uses the MRI / CT scans and special computer software to plan the trajectory of the electrode.
Step 3: skin and skull incisionYou will be taken to the operating room. You will lie on the table and the stereotactic head frame will be secured. This prevents any small movements of your head while inserting the electrodes. You will remain awake during surgery. Light sedation is given to make you more comfortable during the initial skin incision, but then stopped so that you can talk to the doctors and perform tasks.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Surgery Success Rate
Accuracy Of The Stereotactic Technique
For more than 70 years, stereotactic procedures are performed with head-mounted stereotactic frames. It provides a stable platform and offers a high degree of accuracy. However, application inaccuracies do occur. The total error, usually expressed as the 3D distance between the stereotactic coordinates of the tip of the DBS lead and those of the intended target, comprises errors associated with each procedural step, including imaging, target selection, vector calculations, and the mechanical errors of the applied stereotactic technique. In 1994, Maciunas et al. reported on more than 21,500 independent accuracy test measurements of a test phantom made with 11,000 computed tomography images and employing four commonly used stereotactic devices: the BrownRobertsWells frame, the CosmanRobertsWells frame, the KellyGoers Compass frame, and the Leksell frame . In recent years, several groups have reported on inaccuracies during DBS procedures, including groups employing frameless systems and robot-assisted procedures . On the basis of these results, one should take into account the possibility of a 3D inaccuracy of up to 2 mm of the applied stereotactic technique when targeting the dorsolateral STN, underlining the need for intraoperative imaging to verify lead localization.
Table 1 Studies reporting on inaccuracies of the stereotactic technique
Evaluation Of The Stimulation Hotspot
Stereotactic coordinates of the center of the active contact at final stimulation programming were retrieved using the co-registered iCT used for DBS lead accuracy evaluation and defined as the center of stimulation. When 2 or more contact points were activated simultaneously, for instance in double monopolar, bipolar, or interleaving stimulation, the midpoint between active contacts was set as center of stimulation. The stereotactic coordinates of the center of stimulation relative to the medial STN border were averaged and compared with the predefined theoretic stimulation hotspot .
Read Also: Npj Parkinson’s Disease Impact Factor