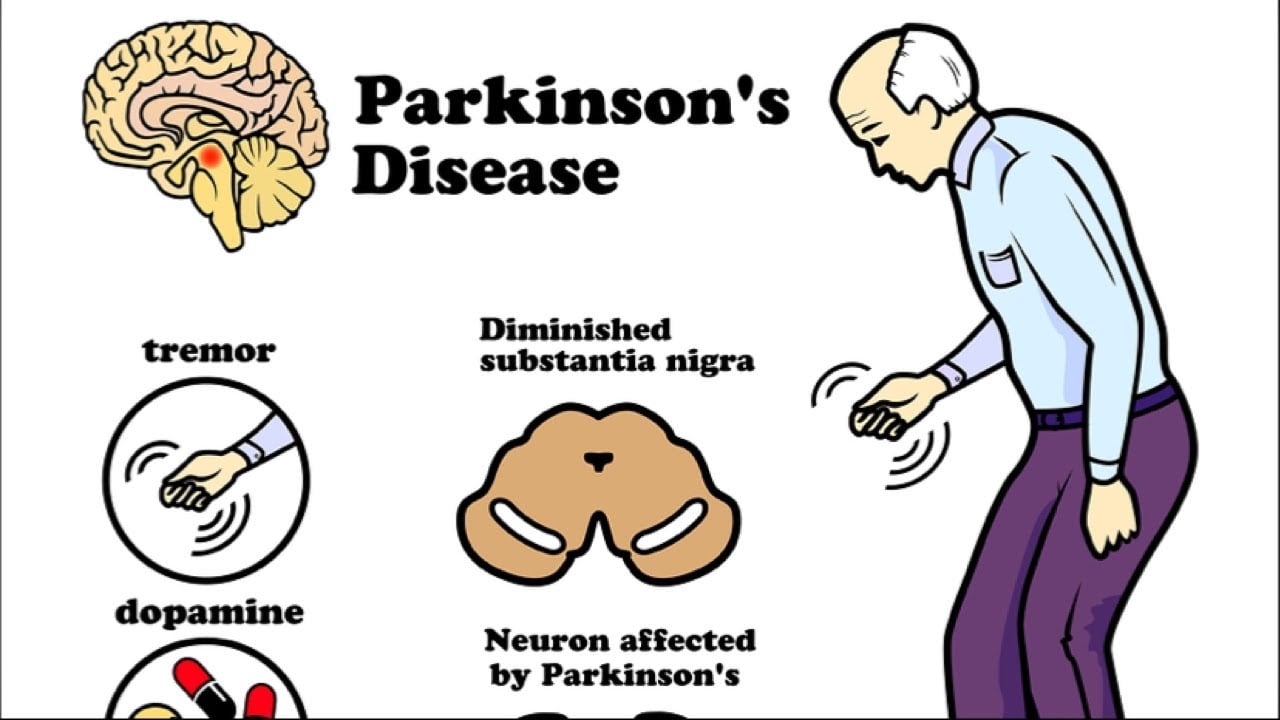
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinson’s. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinson’s also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinson’s, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson’s contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
Parkinsons Disease Vs Als Differences In Symptoms Causes And Treatment
Written byDevon AndrePublished onJuly 25, 2016
Parkinsons disease and ALS can cause difficulties in movement and are both known to be progressive neurological diseases.
ALS is part of a cluster of disorders known as motor neuron diseases that involve gradual degeneration and death of motor neurons. In a healthy individual, messages from motor neurons in the brain are transmitted to the motor neurons in the spinal cord and sent to the particular muscles. In ALS, this communication degenerates and cells begin to die. As a result, the message that is transmitted is incomplete. Unable to function, the muscles begin to weaken and waste away over time. Eventually, communication from the brain to muscles is lost completely.
In its early stage, ALS also known as Lou Gehrigs disease may appear as Parkinsons disease, which is also a neurological disease similar to ALS. Here we will outline the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for both ALS and Parkinsons disease to help you understand the differences between the two.
Treatment Of Rls In Pd
Regardless of the above discussion, it is clear that many people with PD have difficulty falling asleep because of annoying sensations in the legs accompanied by a sometimes unbearable sense of restlessness in the legs. For these people, taking dopamine agonists before bed can be helpful. Caution is in order, of course, because in some patients with PD, especially older or more advanced patients, these medications can cause confusion and hallucinations and are thus not well-tolerated. A long-acting levodopa formulation or medications such as gabapentin, gabapentin enacarbil and pregabalin can also be effective. Trying to address sleep issues such as RLS in patients who have sleep complaints can be an important aspect of maximizing therapy for PD.
Tips and Takeaways
Do you have a question or issue that you would like Dr. Gilbert to explore? Suggest a Topic
Dr. Rebecca Gilbert
APDA Vice President and Chief Scientific Officer
You May Like: Power Up For Parkinson’s
What Are Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Atypical Parkinsonian disorders are progressive diseases that present with some of the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease, but that generally do not respond well to drug treatment with levodopa. They are associated with abnormal protein buildup within brain cells.
The term refers to several conditions, each affecting particular parts of the brain and showing a characteristic course:
- Dementia with Lewy bodies, characterized by an abnormal accumulation of alpha-synuclein protein in brain cells
- Progressive supranuclear palsy, involving tau protein buildup affecting the frontal lobes, brainstem, cerebellum and substantia nigra
- Multiple system atrophy, another synucleinopathy that affects the autonomic nervous system , substantia nigra and at times the cerebellum
- Corticobasal syndrome, a rare tauopathy that typically affects one side of the body more than the other and makes it difficult for patients to see and navigate through space
Braak Pd Staging Scheme
Although the staging scheme of Braak and co-workers should be considered tentative, it nevertheless, has prompted considerable debate in the field and reawakened recognition of early nonmotor clinical features of PD . Subsequent iterations of the Braak scheme proposed that autonomic neurons in peripheral nervous system may be affected before involvement of the central nervous system and this has prompted recognition that PD is a multiorgan disease process, not merely a disorder of central nervous system . Moreover, it has fed the debate on cell-to-cell transmission of unknown putative disease factors , especially given the fact that fetal mesencephalic intrastriatal transplants to treat PD have been shown to develop Lewy body pathology , possibly by cell-to-cell transmission .
Recommended Reading: Do Parkinson’s Tremors Stop When Sleeping
What Is The Difference Between Parkinsonism Vs Parkinsons Disease
What is the difference between Parkinsonism vs Parkinsons disease? In simple terms, Parkinsons is a disease whereas Parkinsonism is a range of symptoms that are usually seen in patients with Parkinsons disease, but sometimes occurring as a result of other neurodegenerative disorders.
Unless you are a medical professional, there might appear to be very little difference between Parkinsons disease and Parkinsonism.
On the surface, they appear to be exactly the same condition: both are characterized by tremors, stiffness, balance issues, and slowness of movement, but this is where the similarities end.
Whereas Parkinsonism encompasses the four main movement problems seen in patients suffering from Parkinsons disease, Parkinsons disease itself is a progressive and highly degenerative disorder that causes many other symptoms as well as those seen in Parkinsonism.
Multiple System Atrophy Formerly Called Shy
As predicted by the name of this parkinsonism, multiple system atrophy affects multiple systems of the body. It affects both the motor skills movement system and the involuntary system of the body. Though the symptoms can often be treated with medications, there is no cure. In addition, there are no drugs that are able to slow the progress of MSA.
Recommended Reading: Prescription Drugs For Parkinson’s Disease
Is Rls More Common In Pd
But what about the other possibility? Do patients with PD have an increased risk of RLS over the general population? Is it the same RLS as the person without PD has, or is it different? These questions have been difficult to answer. Of course, since PD affects about 1.5% of the elderly, and RLS in about 4-10% of the population, there will be some coincidental overlap. In addition to this however, patients with PD can have sensations that feel like RLS when their dose of dopamine medication is wearing off. These sensations are not truly RLS since they do not have the key features of RLS described above and fluctuate with medication timing, but they can be easily confused with RLS by the person with PD.
Studies of people with PD that assess for RLS and compare to a control group are hindered by the fact that the majority of patients with significant PD are under treatment with medications that affect RLS. Over the years, there have been multiple studies investigating whether RLS is more common in PD than in the general population. Different studies come to different conclusions. Studies conducted in which a group of people with PD are directly compared to a group of people without PD typically show that RLS is more common in PD than the general population.
Selection Of Regions Of Interest
18F-DMFP has a high binding affinity for dopamine transporters in the striatal region of the brain. For this reason, neuroimaging studies based on it usually focuses on that region. However, 18F-DMFP PET neuroimages contain a substantial part of the total intensity in regions other than the striatum. In order to reveal the most important regions to separate idiopathic PD from APS we carried out an univariate analysis. Specifically we performed a two-sample t-test comparing both populations under the hypothesis of data corresponding to idiopathic PD patients have lower intensity than those from APS patients. The test was carried out using the SPM software and a smoothed version of the neuroimaging data. The full-width at half maximum of the Gaussian smoothing kernel was fixed at 8 mm. The resulting map, thresholded at p< 0.001 , is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. t-test comparing patients with idiopathic PD and atypical parkinsonian syndromes. Regions in orange/yellow are significantly lower in idiopathic PD patients. Observe that most part of the thalamus, anterior cingulate gyrus and pars opercularis are covered by highlighted areas.
Finally, the t-test map was matched with the Automated Anatomical Labeling atlas and the regions of the atlas with the highest proportion of highlighted voxels in the t-test map were selected.
Also Check: Do People Die From Parkinson’s Disease
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Whats The Difference Between Lewy Body Dementia Parkinsons Disease And Alzheimers Disease
Lewy body dementia is an umbrella term for two related clinical diagnoses: dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. These disorders share the same underlying changes in the brain and very similar symptoms, but the symptoms appear in a different order depending on where the Lewy bodies first form.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory and thinking abilities that are severe enough to interfere with everyday activities. It specifically affects a persons ability to plan and solve problems, called executive function, and their ability to understand visual information. Dementia always appears first in DLB. The motor symptoms of Parkinsons such as tremor, slowness, stiffness and walking/balance/gait problems usually become more evident as the disease progresses. Visual hallucinations, REM sleep behavior disorder, fluctuating levels of alertness and attention, mood changes and autonomic dysfunction are also characteristic of DLB.
Finally, Alzheimers is characterized by different abnormal clumps called amyloid plaques, and jumbled fiber bundles called tau tangles. These microscopic structural changes in the brain were discovered by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906. These plaques and tangles, together with loss of connections between nerve cells, contribute to loss of coherence and memory, as well as a progressive impairment in conducting normal activities of daily living.
Recommended Reading: Wearable Technology For Parkinson Disease
How Do Doctors Diagnose Parkinsonism
No single test exists for doctors to diagnose Parkinsonism.
A doctor will start by taking a persons health history and review their current symptoms. They will ask for a medication list to determine if any medicines could be causing the symptoms.
A doctor will likely also order blood testing to check for underlying potential causes, such as thyroid or liver problems. A doctor will also order imaging scans to examine the brain and body for other causes, such as a brain tumor.
Doctors can perform a test that tracks the movement of dopamine in the brain. This is known as the DaT-SPECT test.
The test uses radioactive markers designed to track dopamine in the brain. This allows a doctor to watch the release of dopamine in a persons brain and identify the areas of the brain that do or do not receive it.
Because Parkinsonism does not respond to typical treatments and can have a variety of symptoms, doctors can have difficulty coming to a quick diagnosis. It may take time for doctors to rule out other conditions and begin to make treatment recommendations.
Whats The Difference Between Progressive Supranuclear Palsy And Parkinsons
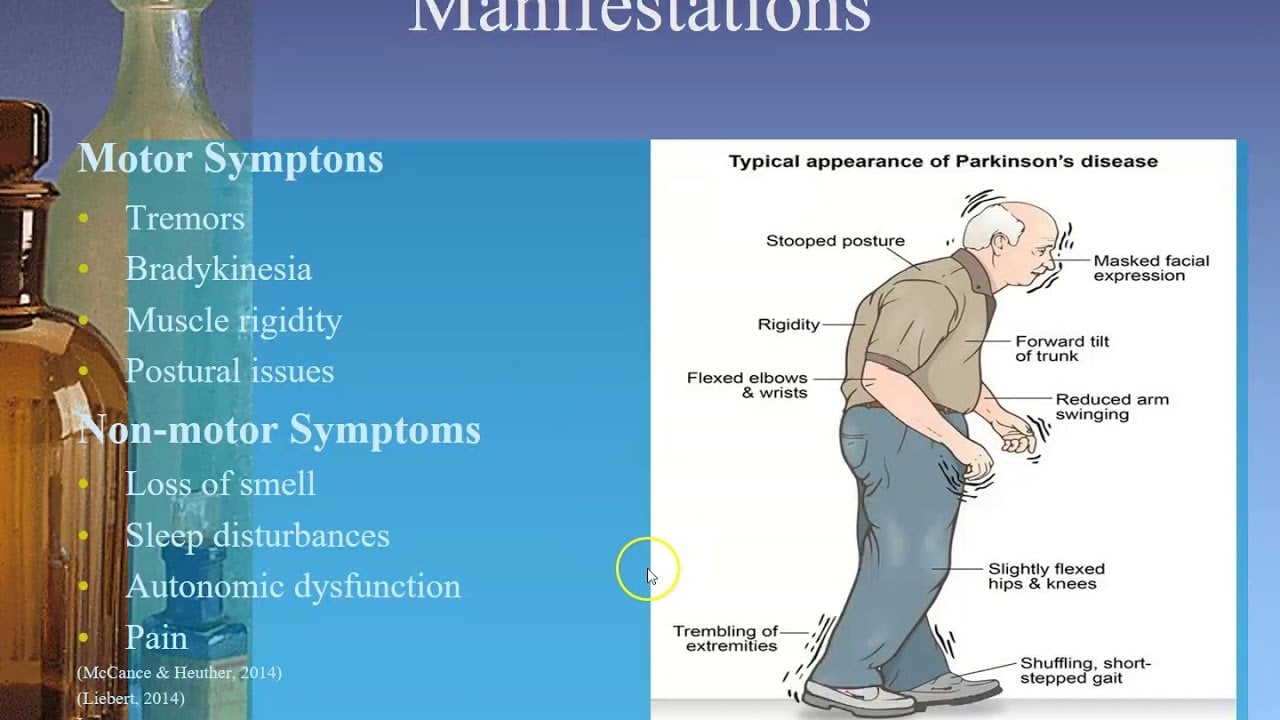
People with PSP generally progress more rapidly than people with Parkinsons. A person with Parkinsons tends to lean forward while a person with PSP tends to lean backward. Tremors are common in people with Parkinsons and rare in people with PSP. Speech and swallowing abnormalities are more severe and show up sooner in those living with PSP.
For more information on progressive supranuclear palsy, read this fact sheet and insights from the CurePSP organization website.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Loss Of Taste
Differential Diagnosis Of Parkinson Disease
Perhaps expression analysis of genes in brains of patients with various neurodegenerative and recognizing disease-specific patterns will in the future assist in differentiating PD from other parkinsonian disorders. For example, using microarray technology in SN samples from six patients with PD, two with PSP, one with FTDP, and five controls, Hauser and colleagues found 142 genes that were differentially expressed in PD cases and controls, 96 in the combination of PSP-FTDP, and 12 that were common to all three disorders. Further studies are needed to confirm this intriguing finding.
Claudia Trenkwalder, in, 2005
Lewy Body Dementia: A Common Yet Underdiagnosed Dementia
While its not a household word yet, Lewy body dementia is not a rare disease. It affects an estimated 1.4 million individuals and their families in the United States. Because LBD symptoms can closely resemble other more commonly known disorders like Alzheimers disease and Parkinsons, it is often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed. In fact, many doctors or other medical professionals still are not familiar with LBD.
Read Also: What New In Parkinson Treatment
Whats The Difference Between Corticobasal Degeneration And Parkinsons
The main difference between CBD and Parkinsons is that it usually starts on one side with the gradual loss of use of one hand or leg , and there may be little flicks of involuntary muscle jerks. Walking and balance difficulties usually occur later in CBD than in Parkinsons. Also, in CBD, a person may have trouble with purposeful movements, such as buttoning a shirt or cutting food.
For more information on corticobasal degeneration, read this information page.
Recognizing Other Causes Of Parkinsonism
Although the symptoms and signs of Parkinson’s disease are fairly specific, a significant fraction of patients with parkinsonism do not have PD.
In an epidemiologic study of patients with parkinsonism, Schrag et al found that
- 65% had PD
- 6% had atypical but non-specific features
- 2.5 % had progressive supranuclear palsy
- 2% had dementia with parkinsonism
- 1.7 % had multiple system atrophy
Identifying patients with atypical parkinsonism is important since these patients
- respond less reliably to dopaminergic agents,
- do not respond favorably to surgical treatments of PD, and
- develop additional clinical problems.
Atypical parkinsonism should be considered particularly
- in patients with poor dopamine responsiveness
- early loss of balance
Medication-induced Parkinsonism
Although tremor and postural instability may be less prominent, this condition may be indistinguishable from PD. Medications frequently associated with the development of parkinsonism include:
- antipsychotics
- some calcium-channel blockers
The parkinsonism usually resolves after some months after discontinuing the offending medication.
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
Characteristic of PSP is the early onset of
- imbalance
- axial rigidity
- eye movement problems
There is no specific treatment for PSP. Dopaminergic treatment should be tried but often offers little benefit. Supportive measures such as speech therapy, physical therapy and antidepressants may help.
Corticobasal Degeneration
References:
Don’t Miss: Is Massage Good For Parkinson’s
Environmental Factors And Exposures
Exposure to pesticides and a history of head injury have each been linked with PD, but the risks are modest. Never drinking caffeinated beverages is also associated with small increases in risk of developing PD.
Low concentrations of urate in the blood is associated with an increased risk of PD.
Drug-induced parkinsonism
Different medical drugs have been implicated in cases of parkinsonism. Drug-induced parkinsonism is normally reversible by stopping the offending agent. Drugs include:
Whats The Outlook For People With Parkinsons Plus
Although there currently isnt a treatment to halt the progression of Parkinsons plus syndrome, there are treatments that can help you manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life.
The exact outlook for Parkinsons plus syndrome depends on the person and the specific condition they have. Someone who is otherwise healthy when theyre diagnosed will typically have a longer life expectancy than someone who is already facing other health conditions when theyre diagnosed. Your doctor will monitor your condition over time and can let you know how its progressing.
Also Check: Dopamine Supplements For Parkinson’s
Whats The Difference Between Vascular Parkinsonism And Parkinsons
As the name implies, vascular parkinsonism is caused by cerebrovascular disease which affects the blood supply to the brain. Vascular parkinsonism is caused by one or more small strokes, while Parkinsons is caused by a gradual loss of nerve cells. One major difference from Parkinsons is that its not progressive, while Parkinsons becomes worse with time. Another difference is that there are no tremors in vascular parkinsonism.
For more information on vascular parkinsonism, read this journal article.
Link Between Parkinsons Disease And Als
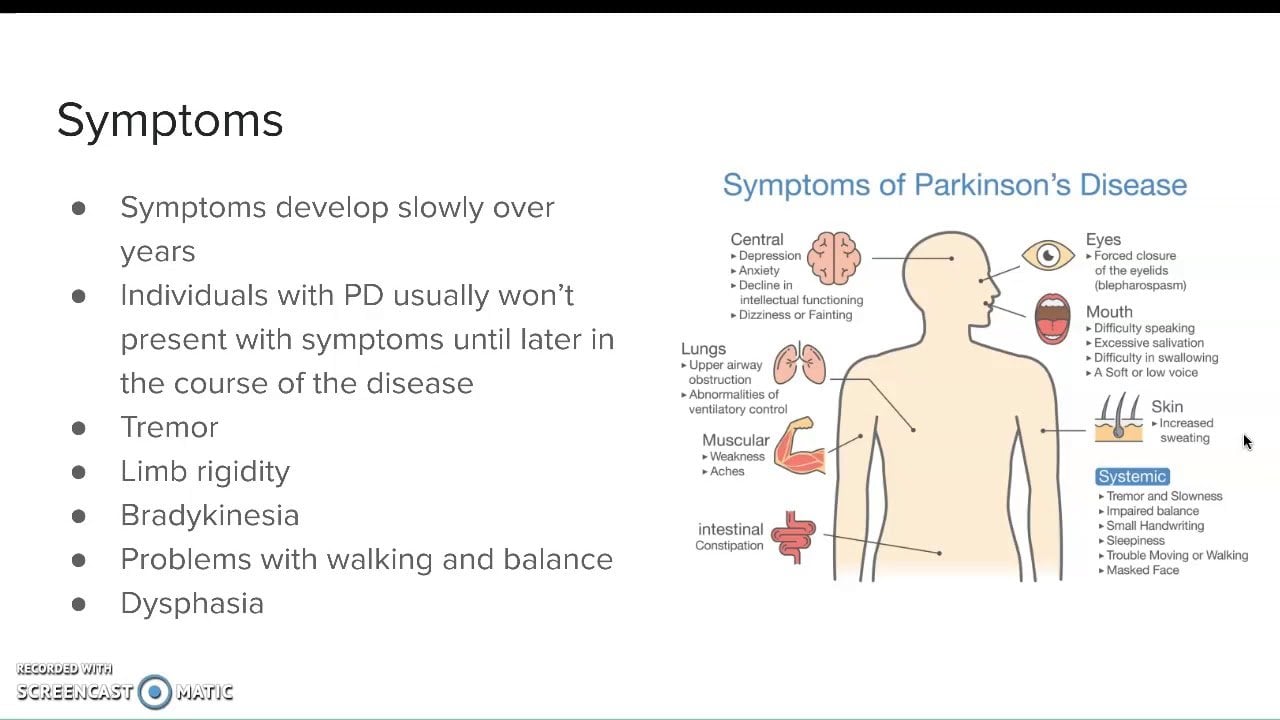
Parkinsons disease and ALS are a lot more similar than you may think. The two neurological diseases share neurons that are highly sensitive to stress, misfolded proteins and reduced protein recycling, toxic proteins that spread from neuron to neuron, and neuroinflammation which is triggered by the immune system and aggravates the condition.
These commonalities between ALS and Parkinsons disease allow researchers to better hone in on more effective treatments for both diseases.
You May Like: Back Brace For Parkinson’s Posture
Clinical Confirmation Of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
The clinical manifestations of PSP-tau pathology are variable, and diagnosis can be difficult at times because of the subtle early signs that may be difficult to discern from other physical or psychological symptoms. The diagnosis of PSP should be considered in all patients presenting with parkinsonism not responding to levodopa therapy postural instability with falls executive dysfunction slowing of vertical saccades/supranuclear vertical gaze palsy or dysarthria/dysphagia .
Practical Management Of Sleep Disorders In Parkinsonism
Some patients with parkinsonism and sleep disturbance require a polysomnogram for diagnosis of the cause of the sleep disorder. Patients who complain about daytime sleepiness with sudden onsets of sleep during the day should be screened for sleep apnea syndrome, and may then require respiratory polysomnography. Patients who present with probable RBD and hallucinations may need a polysomnogram to evaluate better whether both syndromes are relevant, because the treatment options are different. Simultaneous closed-circuit television monitoring and surface electromyographic monitoring of all four extremities often is helpful if nocturnal myoclonic movements or the RBD is contributing to the sleep disturbance.
If daytime sleepiness is a prominent complaint, a multiple sleep latency test helps to determine its severity and circadian variation. It is usually best to record the patient while he or she is on the usual medication schedule, but if medications appear to be a major factor in the sleep disturbance, definite diagnosis may require 2 or more nights of recording under different treatment regimens.
Federico Eduardo Micheli, María Graciela Cersósimo, in, 2007
You May Like: Are There Prenatal Tests For Parkinson Disease