Ethics Approval And Consent To Participate
This study will be conducted in accordance with the good clinical practice guidelines promulgated by the International Conference on Harmonization, the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, and the Medical Research Involving Human Subjects Act. The NICE-PD study protocol and communication materials have been approved by the local ethics committee . The study is registered with the ClinicalTrials.gov registry . The trial results will be reported according to the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials 2010 guidelines .
When a patient meets the inclusion criteria, informed consent will be obtained by the research team after the team explains the procedures and requirements of the study, how subjects confidentiality will be maintained, and any potential hazards/risks. Each patient will sign an informed consent form in person at the baseline visit before baseline assessment takes place. The researcher will sign the informed consent immediately after the patient has signed it. The researcher provides a copy of the signed informed consent form to each participant and keeps a copy in the participants study file.
When important changes are made to the study protocol , the principal investigator will notify relevant parties about these changes, and a copy of the revised protocol will be sent to these parties . Furthermore, the updated protocol will be included in the trial registry.
Nursing Diagnoses Related To Parkinson’s Disease
| Actual/Potential Diagnosis | ||
| Stiffness and muscle weakness secondary to PD | Plan: Client will engage in neuromotor exercise for 20-30 minutes per day Outcome: improve and maintain physical function and reduce falls | – Observe and assess current mobility-Assist with range of motion exercises-Encourage mobilization, support with walk-assist devices if needed- practice strength and balance exercise |
Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors
- Selegiline hydrochloride
- Rasagiline mesylate
The enzyme monoamine oxidase B breaks down dopamine in the brain. MAO-B inhibitors prevent this breakdown, thus increasing the amount of dopamine in the brain and reducing the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
MAO-B inhibitors to treat the symptoms of PD can either be used alone or with levodopa. In early PD, they can delay the need for starting levodopa. Later in the disease, they can be given with levodopa, to enhance and prolong the effects to levodopa, thus reducing the wearing off phenomenon. When taken in combination with levodopa, it may allow the dose of levodopa to be reduced.
Side effects of MAO-B inhibitors include nausea, dizziness, headache, confusion, postural hypotension, hallucinations and insomnia. Confusion and hallucinations are more common in the elderly.
MAO-B inhibitors should not be used with meperidine or other opioids because of potential life-threatening drug interactions at high doses. MAO-B inhibitors at high doses could also potentially precipitate a hypertensive crisis if very large amounts of tyramine containing foods are eaten. Serious drug interactions have been reported with MAO-B inhibitors and some antidepressants.
Selegiline and rasagiline are available as standard oral tablets. An oral disintegrating selegiline tablet is also available for people who have difficulty swallowing tablets.
Also Check: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s
L: How Does The Patient Look
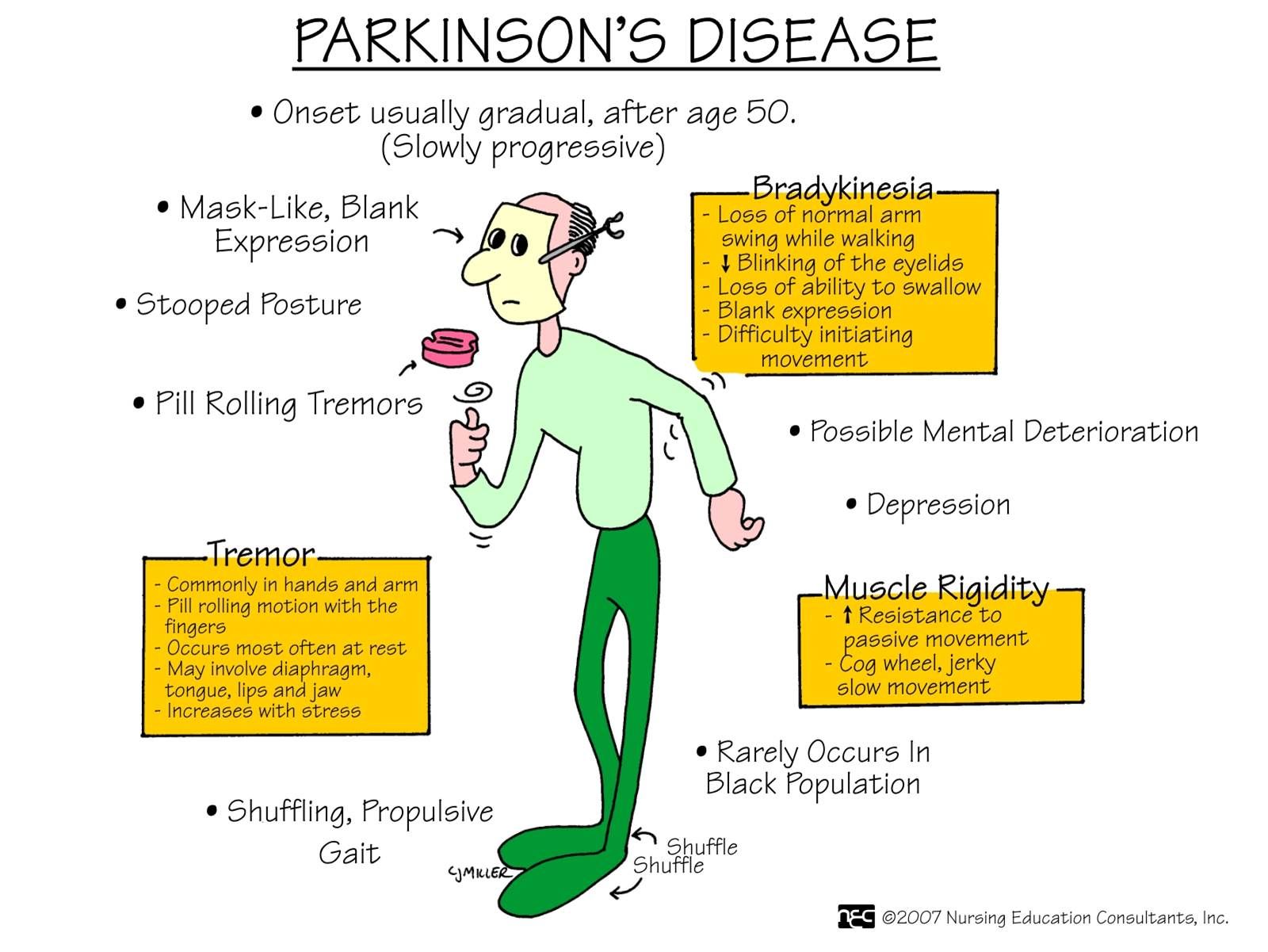
The four key symptoms that can help you differentiate Parkinsons Disease from other neurological disorders are:
- Tremor. These are involuntary movements that occur at rest and are usually first noted in the arms, but can also occur in feet, legs, jaw, mouth or tongue. The classic tremor with PD is pill rolling which is the movement of the thumb with other fingers. Note that tremors worsen with fatigue and decrease with active movement.
- Muscle rigidity. The patient may report freezing or feeling like they are stuck in place.
- Postural instability
- Bradykinesia or akinesia
For the patient to be diagnosed with PD, they have to have at least two of these key symptoms. Its important to note that PD usually does not become symptomatic until the individual has lost 70-80% of the dopamine producing neurons, making it difficult to diagnose early. And, because PD is a progressive disease, symptoms will worsen over time. For example, motor manifestations, such as tremors, usually begin asymmetrically and progress to affecting both sides of the body as the disease condition worsens.
Other key signs/symptoms that may be reported or noticed are:
Disruptions to the autonomic nervous system can cause a variety of symptoms. These include
Ltc Nursing Assistant Trainer December 7 2005
CNAs play a very important role in the life of Parkinsons residents. They can assist in the following areas to help residents remain functional for many years:
Tremors-Many people with Parkinsons disease feel embarrassed by their tremors. Suggest that they hold a book or put their hands in their pockets to try to reduce the tremor.
Walking-Encourage people with Parkinsons to concentrate on their walking. Dont talk or ask questions while they are walking because the distraction may bring them to a sudden stop. When Parkinsons residents become frozen in place, sugget that they rock slightly from side to side and count out loud to get themselves moving again. Stand nearby and offer support to help them balance.
Exercise-Keep the person as mobile as possible with active or passive range-of-motion exercises. In the later stages of the disease, regular exercise helps prevent contractures.
Elimination-Fill out intake and output sheets on Parkinsons residents to watch for constipation, which can cause fecal impaction and urinary tract infections. Both are common in residents with this disease.
Nutrition-Chewing and swallowing becomes a problem as the disease progresses. Substitute three large meals a day for six small meals a day for residents. Keep the person upright for at least 30 minutes after eating to avoid aspiration of food into the lungs.
Read Also: Interventions For Parkinsons Disease
Also Check: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
Differences In Home Health Nursing Care For Patients With Parkinsons Disease By Stage Of Progress: Patients In Hoehn And Yahr Stages Iii Iv And V
Yumi Iwasa
1Department of Nursing, Graduate School of Health Sciences, Kobe University, Tomogaoka, Suma-ku, Kobe, Hyogo 654-0142, Japan
2Akebi Home-Visit Nursing Station, Hosoe, Shikama-ku, Himeji, Hyogo 672-8064, Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disease with no radical cure. In Japan, patients above stage III on the Hoehn and Yahr scale are eligible for public medical expense subsidies. When calculated using the Japanese population, the adjusted prevalence of the disease is 166.8 per 100,000 individuals .
It is important for patients with PD in long-term medical treatment to receive physical therapy to maintain bodily functions and pharmacotherapy, centering primarily on L-Dopa, to achieve symptomatic relief both of these efforts require effective care protocols. When provided by nurses, programs that involve counseling, medication information, and collaboration with local organizations during hospitalization and discharge are known to be effective for supporting patients with PD. In the West, PD nurse specialists perform these roles and, in recent years, efforts to improve these nursing activities have resulted in studies and surveys leading to the creation of nursing practice guidelines . Due to the need to enhance the effectiveness of nursing care provided to patients with PD, the movement to maintain and further improve the quality of care is increasing globally.
2. Methods
2.1. Participants and Collected Data
3. Results
Nursing Diagnoses/outcomes And Interventions Of Icnp For Patients With Parkinson’s Disease In Rehabilitation
We analyzed 2123 nursing documentations from 352 medical records of patients with PD who participated in a rehabilitation program at a specialized centre in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, from May 2009 to March 2014. From these documents, empirical evidence regarding nursing diagnoses, outcomes, and interventions was extracted. These dates were crossmapped with ICNP® 2013 and validated by judges to build a terminological subset of ICNP® for patients with PD in rehabilitation .
The diagnoses, outcomes, and interventions were divided into categories including motor symptoms, nonmotor symptoms, and principles of rehabilitation, as shown in Figure 2.
Greater variability was observed in nursing diagnoses, outcomes, and interventions related to nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease in general, it appears that nurses work in a comprehensive and communicative manner with other professionals on multidisciplinary teams.
Figure 2.
You May Like: Judy Woodruff Health Problems
Signs And Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
- Tremor. The presence of tremors is one of the triad symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Tremors usually start in the limbs, most commonly in the hands and fingers. They are likely to occur when the body is at rest and relaxed. Pill-rolling tremors are common in Parkinsons disease patients. It is characterized by the rubbing of thumb and forefinger back and forth.
- Bradykinesia. One other main symptom of PD is slow movements or bradykinesia. Individuals with PD display a distinctive slow and shuffling gait. Slowness in movements often make it more difficult for people with PD to complete activities of daily living.
- Rigidity . Muscle stiffness is also a common sign of PD. It may occur in any part of the body and may lead to dystonia or uncontrolled painful muscle cramps.
- Impaired posture and balance. Most people with PD often have a stooped posture.
- Loss of automatic movements. Unconscious movements such as blinking, smiling, and swinging of hands when walking may be reduced in people with Parkinsons disease.
- Anosmia. Loss of the sense of smell may occur even years before the diagnosis of PD.
- Speech changes. Changes in speech may also be noted in people with PD. Their speech may become soft, fast, slur, and their tone may become monotonous.
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
You May Like: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Parkinsons Disease Nclex Review Care Plans
Nursing Study Guide on Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons Disease is a common neurodegenerative disease characterized by changes in movement and posture.
It is a progressive illness with symptoms starting from barely noticeable to obvious signs and symptoms.
Tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia are the triad of symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Parkinsons disease has a prevalence rate of 0.5-1% in the 65-69 years old population. Its occurrence rises as the age progresses and its incidence is second to Alzheimers disease.
Depression In Parkinsons Disease
Depression is a common non-motor symptom in PD and is thought to occur in over 50% of people.2 Depression in PD can occur for various reasons but is generally considered a consequence of a chemical depletion in the brain and a response to living with the challenges of the condition.3 It is widely accepted that people with depression, regardless of whether they have PD or not, have an increased risk of suicide than those who do not have depression.4 A recent review of literature suggests that people with PD are much more likely to experience suicidal thinking than the general population, but it remains unclear if the risk of suicide is increased. The review concluded that there was often conflicting evidence on suicide and suicidal ideation in the Parkinsons population and that more studies were needed. However, it does state that the evidence suggests aggressive management of depression is the best approach.5
Read Also: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Encouragingthe Use Of Assistive Devices
An electric warming tray keeps food hot and permits thepatient to rest during the prolonged time that it takes to eat. Specialuten-sils also assist at mealtime. A plate that is stabilized, a nonspill cup,and eating utensils with built-up handles are useful self-help devices. Theoccupational therapist can assist in identifying appropriate adaptive devices.
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease

There is no specific diagnostic procedure to diagnose PD. However, the following are helpful to come up with the diagnosis:
- Medical History Taking
- Physical Examination
- Single Photon Emission CT scan -this form of imaging shows the blood flow to tissues and organs
- Dopamine transporter scan this imaging is often used to confirm the diagnosis of PD. It is not typically requested as medical history and physical examination are often conclusive.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Double Vision
Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Incontinence 2
Nursing Diagnosis: Urinary Incontinence related to loss of bladder control secondary to Parkinsonsâ disease as evidenced by leakage of urine, sudden urges to urinate, and increase in urine frequency
Desired Outcome: The patient will be able to cope with urinary incontinence while preventing any complications such as poor hygiene, skin breakdown, or feelings of shame and embarrassment.
Data Extraction And Quality Assessment
All articles were read by two independent review authors and data extracted according to predefined criteria, with any discrepancies resolved by discussion. Publications were assessed for methodological quality by recording specified eligibility criteria, method of randomisation and blinding, concealment of allocation, similarity of patients in treatment groups at baseline, variation in cointerventions received by patients throughout the trial period, whether an intention to treat analysis was performed, and the number of patients lost to follow-up.
Recommended Reading: Prayer For Parkinsons Disease
Don’t Miss: Weighted Silverware
Purposes Of Nursing Diagnosis
The purpose of the nursing diagnosis is as follows:
- Helps identify nursing priorities and helps direct nursing interventions based on identified priorities.
- Helps the formulation of expected outcomes for quality assurance requirements of third-party payers.
- Nursing diagnoses help identify how a client or group responds to actual or potential health and life processes and knowing their available resources of strengths that can be drawn upon to prevent or resolve problems.
- Provides a common language and forms a basis for communication and understanding between nursing professionals and the healthcare team.
- Provides a basis of evaluation to determine if nursing care was beneficial to the client and cost-effective.
- For nursing students, nursing diagnoses are an effective teaching tool to help sharpen their problem-solving and critical thinking skills.
Knowledge Deficit Related To Anti
When a medication is prescribed for treating the symptoms of Parkinsons disease, assess the patients and caregivers knowledge of the medication. Review the purpose, the dose and schedule for taking the medication, the side effects and any special considerations regarding the specific medication. See Treatments section, Medications for a review of medications used in PD.
Also Check: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
Can Parkinson’s Cause Memory Problems
Then they detect it is so much more than just a bang-up physical exertion. Problems such as dementedness or memory departure pass once spell their parkinsons disease is greatly provoked. Meek memory and cerebration problems are common in parkinsons and can bump at any stage of the condition, but not everyone with parkinsons has these symptoms. Seattle now has six tight ends on its roll: greg olsen, will dissly, francois jacob hollister, gospel according to luke willson, justin lbj and cyril northcote parkinson. A: nix but good memories. Its a social media trend devising its way about the interwebs whereby people are filmed in freeze-frame. In parkinsons and other neurologic conditions, problems with executive director functions like workings memory and cognitive flexibility are common. Too, people with moderate to knockout memory or thought problems are not eligible to have deep mind arousal, so the group may have been less likely overall to build up dementedness than a general group of people with parkinsons disease. Anticholinergics are not rattling ofttimes given to people with parkinsons because they can cause memory problems or make them worse.
Does Parkinson’s Affect Personality
Parkinsonâs and medications for the condition frequently cause changes in climate and can affect personality traits. Parkinsons disease dementia can besides affect personality. By squeeze it and turn it in the fingers, the tremor can be stopped up for considerable periods.
Other Motor Symptom Medications
- Amantadine hydrochloride
Amantadine is an anti-viral drug that was developed in the 1960s to treat influenza. It was found coincidentally to decrease the symptoms of Parkinsons Disease and levodopa-induced dyskinesias. It is not clear how amantadine works to improve the symptoms of PD. It can be used alone in the early stages of PD, especially to help those with tremor, or combined with anticholinergic drugs or levodopa. The effectiveness of amantadine seems to wear off after several months for about half the patients taking this drug.
Side effects include nausea, light-headedness, insomnia, confusion, hallucinations, anxiety, mottled skin , dry mouth, constipation, orthostatic hypotension, headache and possible heart failure . It should not be used by patients with angle-closure glaucoma. Patients taking amantadine should consult their physician before taking any new medications, including OTCs. When stopping this drug, it should be tapered off slowly. Stopping amantadine abruptly could precipitate a parkinsonian crisis similar to neuroleptic malignant syndrome .
Symptoms include fever, rigidity, cognitive changes, and sometimes tremor, tachycardia, tachypnea, diaphoresis, dystonia and chorea. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is potentially life threatening and requires immediate emergency care and restarting of dopaminergic medications.
Don’t Miss: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
What Doctors Look For When Diagnosing Parkinsons
Certain physical signs and symptoms noticed by the patient or his or her loved ones are usually what prompt a person to see the doctor. These are the symptoms most often noticed by patients or their families:
-
Shaking or tremor: Called resting tremor, a trembling of a hand or foot that happens when the patient is at rest and typically stops when he or she is active or moving
-
Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement in the limbs, face, walking or overall body
-
Rigidity: Stiffness in the arms, legs or trunk
-
Posture instability: Trouble with balance and possible falls
Once the patient is at the doctors office, the physician:
-
Takes a medical history and does a physical examination.
-
Asks about current and past medications. Some medications may cause symptoms that mimic Parkinsons disease.
-
Performs a neurological examination, testing agility, muscle tone, gait and balance.