How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosis is difficult at every stage of the disease, but particularly in the early stages. No single test can provide a diagnosis. A diagnosis will likely involve physical and neurological examinations, conducted over time to assess changes in reflexes, coordination, muscle strength, and mental function. Your doctor might also see how you respond to medicine.
You may need to have brain imaging tests to rule out other conditions that might be causing your symptoms. Such tests could include MRI and CT scans and possibly some other types of scans. Blood tests may also be done to exclude other illnesses.
How Can You Improve Aggressiveness And Hallucinations In Parkinsons
Hallucinations may spark anger or aggression in a person with Parkinsons disease. Some ways to help include:
- Reassure them, tell them they are safe.
- Speak slowly and calmly.
- Ask questions about the persons feelings.
- Listen to the person, dont interrupt.
- Avoid sudden movements.
- Give the person space and a way out, so they dont feel cornered or threatened.
- Make an emergency plan ahead of time for what you and others in the house will do if the person experiencing hallucinations becomes a danger to themselves, you, or anyone else.
- When it is safe, help the person speak with their healthcare provider about making a plan to address the hallucinations.
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Medicine Side Effects
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinsons. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Accurate Parkinsons Disease Diagnosis

Parkinsons is challenging to diagnose because symptoms, such as difficulty walking, can be a sign of other movement disorders. Some people have parkinsonism. This group of diseases causes Parkinsons-like symptoms that do not respond to Parkinsons treatments.
At Cedars-Sinai, we consider your health history and perform a nervous system exam before confirming a Parkinsons diagnosis. Our years of experience enable us to detect subtle symptoms that do not show up on other tests.
Tests may include:
Levodopa Testing
Testing your response to a Parkinsons drug, levodopa, allows us to rule out some other movement disorders. Levodopa boosts dopamine levels and is not an effective treatment for other movement disorders. If your symptoms improve with levodopa, you likely have Parkinsons.
DaTscan Test
We may use this noninvasive imaging test to help rule out Parkinsonian syndrome. This group of disorders causes movement problems similar to Parkinsons but might not stem from the disease. Learn more about DaTscan.
Read Also: Similar To Parkinsons
Read Also: Patron Saint Of Parkinson’s Disease
Brain Imaging Can Help With Diagnosis
Doctors use two tests that take detailed pictures of your brain. Each one may help your doctor make a diagnosis. These tests are:
- PET scan: This shows how your brain functions. It shows how the brain uses sugar. This scan can help tell the difference between Parkinsons and .
- DaTscan: This shows problems with brain cells that make dopamine. Healthy brain cells light up during the test. Cells without enough dopamine appear dark. This scan can help your doctor tell the difference between Parkinsons and a brain disease called .
Imaging studies are a newer way to diagnose Parkinsons. However, not every healthcare facility can do them. It takes an experienced doctor to interpret the scans accurately. These scans also can be very expensive. Be sure to check with your insurance company ahead of time to see whether you are covered and what your out-of-pocket costs will be.
Dont Miss: On-off Phenomenon
When Do Parkinsons Patients Usually Start Working With A Movement Disorder Specialist
Generally, if you or a loved one is experiencing any unusual symptoms, its common to start by making an appointment with a primary care doctor or clinician. Primary care doctors are trained to treat hundreds of conditions and can help connect you with the right specialists and ongoing care.
However, you dont need a doctors referral to see a neurologist or movement disorder specialist. You can make an appointment directly. But its important to check with your insurance plan, so you know whats covered. Sometimes plans require a doctors referral to cover certain types of care.
You May Like: Does Weed Help With Parkinson’s
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Muscle stiffness, where muscle remains contracted for a long time
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include:
The symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Early symptoms of this disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinsons. They may see that the persons face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s disease often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward take small, quick steps and reduce swinging their arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Symptoms often begin on one side of the body or even in one limb on one side of the body. As the disease progresses, it eventually affects both sides. However, the symptoms may still be more severe on one side than on the other.
Patients With A Previous Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease
The diagnosis of probable Parkinson’s disease was confirmed in 109 of the 131 patients with this diagnosis , including three in whom atypical features were found but were insufficient to invalidate the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease . Two additional patients were found to have possible Parkinson’s disease. However, in 20 of the 131 patients the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease was unequivocally rejected . The alternative diagnoses were non-parkinsonian tremor in four patients , vascular parkinsonism in six , progressive supranuclear palsy in four , and multiple system atrophy in three . Two patients received a diagnosis of idiopathic torsion dystonia, and one of dementia without parkinsonism. When only those patients who had seen a specialist at some point in the past were considered, the diagnosis was changed from Parkinson’s disease to a different diagnosis in 11%.
Patients with an initial diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease
Read Also: Power For Parkinson’s Exercise Videos
What Are The Treatments
Currently there is no cure for Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms can be mild in the early stages of the condition and people might not need immediate treatment. Your doctor and specialist will monitor your situation.
There are several different types of drugs used to treat Parkinsons disease. Drug treatments are tailored to each individuals needs and are likely to involve a combination of different drugs. Your medication should be reviewed regularly. It is likely that, over time, changes will be made to the types of drugs you take and the doses you take each day.
The main types of drug treatment for Parkinsons disease are:
- drugs which replace dopamine
- drugs which mimic the role of dopamine
- drugs which inhibit the activity of acetylcholine
- drugs which prevent the body breaking down dopamine
- other drugs such as anti-sickness medication
Everybody is affected differently by medication. The possible side effects of Parkinsons disease drugs include nausea , vomiting , tiredness and dizziness. Some people might experience confusion, nightmares and hallucinations. For some people, dopamine agonists have been linked to compulsive behaviour such as addictive gambling or hypersexuality .
The effectiveness of the main drug treatment levodopa can wear off over time and its long-term use can cause some people to develop involuntary twisting or writhing movements of the arms, legs or face . To reduce the risk, doctors might delay the use of levodopa for younger people.
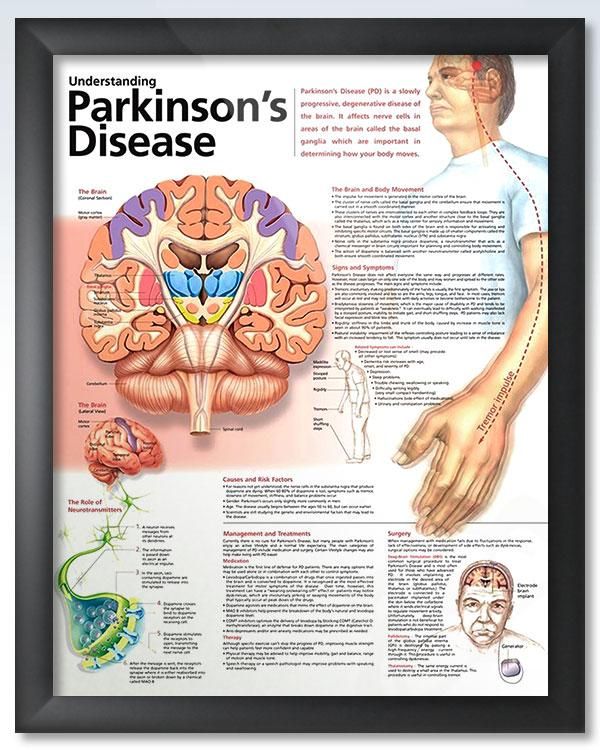
How Does This Condition Affect My Body
Parkinsons disease causes a specific area of your brain, the basal ganglia, to deteriorate. As this area deteriorates, you lose the abilities those areas once controlled. Researchers have uncovered that Parkinsons disease causes a major shift in your brain chemistry.
Under normal circumstances, your brain uses chemicals known as neurotransmitters to control how your brain cells communicate with each other. When you have Parkinsons disease, you dont have enough dopamine, one of the most important neurotransmitters.
When your brain sends activation signals that tell your muscles to move, it fine-tunes your movements using cells that require dopamine. Thats why lack of dopamine causes the slowed movements and tremors symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
As Parkinson’s disease progresses, the symptoms expand and intensify. Later stages of the disease often affect how your brain functions, causing dementia-like symptoms and depression.
Don’t Miss: Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinson’s Disease Success Rate
Referral To A Specialist
If your GP suspects Parkinson’s disease, you’ll be referred to a specialist.
This will usually be:
- a neurologist, a specialist in conditions affecting the brain and nervous system
- a geriatrician, a specialist in problems affecting elderly people
The specialist will most likely ask you to perform a number of physical exercises so they can assess whether you have any problems with movement.
Special brain scans, such as a single photon emission computed tomography scan, may also be carried out in some cases to try to rule out other causes of your symptoms.
How Is It Diagnosed

Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking you questions and reviewing your medical history. Some diagnostic and lab tests are possible, but these are usually needed to rule out other conditions or certain causes. However, most lab tests aren’t necessary unless you don’t respond to treatment for Parkinson’s disease, which can indicate you have another condition.
Recommended Reading: How Can Stem Cells Help Cure Parkinson’s Disease
What Should You Look For In A Movement Disorder Specialist If You Have Parkinsons Disease
Finding the right Parkinsons disease specialist isnt much different than searching for any other type of expert. Start by asking around. Primary care doctors, neurologists and Parkinsons support groups can be good sources for recommendations.
Here are a few more things to look for when choosing a movement disorder specialist:
- Group or board certification Certification is a mark of distinction. It shows that your doctor or clinician has not only completed their necessary training, but also gone above and beyond to be certified by their specialtys certifying board.
- Part of a multidisciplinary team Your care and treatment plan should be tailored to you. And that means several specialists will need to work together to make sure you get the right care. Working with a movement disorder specialist who is part of a multidisciplinary team can help streamline services and communication.
- Access to the latest treatments and specialized programming Access to the right treatment can make all the difference for a person with Parkinsons disease. We proudly offer the latest science-backed treatments, as well as the possibility of being involved in experimental treatment trials at Struthers Parkinsons Center in Golden Valley and HealthPartners Neuroscience Center in St. Paul.
Parkinsons Foundation Center Of Excellence
Mount Sinai Beth Israel is designated as a Center of Excellence by the Parkinsons Foundation, specialized team of neurologists, movement disorder specialists, physical and occupational therapists, mental health professionals and others who are up-to-date on the latest Parkinson’s disease medications, therapies, and research to provide the best care.
You May Like: Do Parkinson Patients Shake During Sleep
The Cause Of Parkinsons Delusions And Hallucinations
Some risk factors associated with the development of psychosis in Parkinsons disease include:
- Age: Parkinsons disease usually occurs in people over age 60.
- Duration and severity of Parkinsons disease: Psychosis is more common in advanced or late-stage Parkinsons disease.
- Later onset: Occurring later in life
- Hyposmia: A decreased sense of smell
- Cognitive impairment: Problems with thinking, including trouble remembering, difficulty learning new things, difficulty concentrating, problems making decisions that affect everyday life
- Depression: People who have both depression and Parkinsons disease are at a greater risk of developing psychosis.
- Diurnal somnolence: Daytime sleepiness
- REM sleep behavior disorder: A sleep disorder in which you physically act out dreams involves making vocal sounds and sudden, often extreme, arm and leg movements during REM sleep
- Visual disorders: Impaired vision
- Severe axial impairment: Speech, swallowing, balance, freezing of gait
- Autonomic dysfunction: Impairment of the autonomic nervous system , which controls involuntary or unconscious actions such as heart rate, breathing, body temperature, blood pressure, digestion, and sexual function
- High medical comorbidity: The existence of more than one condition or illness in the same person at the same time with Parkinsons disease, may include conditions such as dementia, depression, and sleep disorders
What Causes The Condition
Although there are several recognized risk factors for Parkinsons disease, such as exposure to pesticides, for now, the only confirmed causes of Parkinsons disease are genetic. When Parkinsons disease isnt genetic, experts classify it as idiopathic . That means they dont know exactly why it happens.
Many conditions look like Parkinson’s disease but are instead parkinsonism from a specific cause like some psychiatric medications.
Familial Parkinsons disease
Parkinsons disease can have a familial cause, which means you can inherit it from one or both of your parents. However, this only makes up about 10% of all cases.
Experts have linked at least seven different genes to Parkinson’s disease. They’ve linked three of those to early-onset of the condition . Some genetic mutations also cause unique, distinguishing features.
Idiopathic Parkinsons disease
Experts believe idiopathic Parkinsons disease happens because of problems with how your body uses a protein called -synuclein . Proteins are chemical molecules that have a very specific shape. When some proteins dont have the correct shape a problem known as protein misfolding your body cant use them and can’t break them down.
With nowhere to go, the proteins build up in various places or in certain cells . The buildup of these Lewy bodies causes toxic effects and cell damage.
Induced Parkinsonism
The possible causes are:
Read Also: Cardinal Signs Of Parkinson’s
What We Treat In South Florida
The specialists at The Pauline Braathen Neurological Center provide high quality care and treatment for complex neurological conditions. Using a multidisciplinary approach that brings together a team of specialists, we offer medical management and innovative surgical options for patients diagnosed with a variety of movement disorders including:
Recommended Reading: Cleveland Clinic Parkinsons Bicycle Study 2017
Parkinsons Disease: Causes Symptoms And Treatments
Parkinsons disease is a brain disorder that causes unintended or uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination.
Symptoms usually begin gradually and worsen over time. As the disease progresses, people may have difficulty walking and talking. They may also have mental and behavioral changes, sleep problems, depression, memory difficulties, and fatigue.
While virtually anyone could be at risk for developing Parkinsons, some research studies suggest this disease affects more men than women. Its unclear why, but studies are underway to understand factors that may increase a persons risk. One clear risk is age: Although most people with Parkinsons first develop the disease after age 60, about 5% to 10% experience onset before the age of 50. Early-onset forms of Parkinsons are often, but not always, inherited, and some forms have been linked to specific gene mutations.
You May Like: Stages Of Parkinson’s What To Expect
What Are Parkinsons Disease
Delusions are false beliefs that are not based on reality. These beliefs are fixed. People experiencing them are unlikely to change or abandon these beliefs, even when presented with evidence that they are false.
Delusions experienced by people with Parkinsons disease are usually of a common theme. These may include:
- Spousal infidelity
- Thinking that people are stealing their belongings
- Thinking people are trying to harm them
- Thinking people may put poison in their food
- Thinking people are switching out or substituting their medications
- Other beliefs based on paranoia
Sensitivity Specificity And Predictive Value Of A Previous Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease
Of 126 patients with a pre-existing clinical diagnosis of probable and possible Parkinson’s disease in the overall sample , 111 were confirmed as having Parkinson’s disease, resulting in a sensitivity of 88.1% similarly, it was confirmed that 54 of 74 patients did not have Parkinson’s disease, resulting in a specificity of 73.0% . The positive and negative predictive values of a previous clinical diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease were 84.7% and 78.3% . In other words, in 85% of patients with a previous diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease this diagnosis was confirmed, and 78% of patients with a diagnosis other than Parkinson’s disease did not have the disease .
When this was broken down by a specialist or other doctor diagnosis, the diagnostic validity was as follows. Neurologists and geriatricians had a sensitivity and specificity of 93.5% and 64.5% , respectively, compared with 73.5% and 79.1% for non-specialists. The positive predictive values were greater for specialists than for other doctors , but the negative predictive values were equivalent v non-specialist 79.1% ).
You May Like: What Is The Va Disability Rating For Parkinson’s Disease