The Diagnosis Of Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease
The first component to the diagnosis of PD is establishing that the patient has parkinsonism. This is a clinical diagnosis and relies on three key elements: bradykinesia, tremor, and rigidity. Of these, bradykinesia must be present, with at least one of the other two. PD is an asymmetrical condition, so during the clinical assessment, the parkinsonism should be more apparent on one side and may be purely unilateral in early disease . is a classical illustration of parkinsonism, with a description by William Gowers.
A case of Parkinsons disease as described and illustrated by William Gowers: the aspect of the patient is very characteristic. The head is bent forward, and the expression of the face is anxious and fixed, unchanged by any
Support For People With Parkinsons Disease
Early access to a multidisciplinary support team is important. These teams may include doctors, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, speech therapists, dietitians, social workers and specialist nurses. Members of the team assess the person with Parkinsons disease and identify potential difficulties and possible solutions.There are a limited number of multidisciplinary teams in Victoria that specialise in Parkinsons disease management. But generalist teams are becoming more aware of how to help people with Parkinsons disease.
Patients With A Previous Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease
The diagnosis of probable Parkinson’s disease was confirmed in 109 of the 131 patients with this diagnosis , including three in whom atypical features were found but were insufficient to invalidate the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease . Two additional patients were found to have possible Parkinson’s disease. However, in 20 of the 131 patients the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease was unequivocally rejected . The alternative diagnoses were non-parkinsonian tremor in four patients , vascular parkinsonism in six , progressive supranuclear palsy in four , and multiple system atrophy in three . Two patients received a diagnosis of idiopathic torsion dystonia, and one of dementia without parkinsonism. When only those patients who had seen a specialist at some point in the past were considered, the diagnosis was changed from Parkinson’s disease to a different diagnosis in 11%.
Patients with an initial diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease
Recommended Reading: How Much Coq10 Should I Take For Parkinson’s
What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons warning signs can be motor symptoms like slow movements, tremors or stiffness. However, they can also be non-motor symptoms. Many of the possible non-motor symptoms can appear years or even decades ahead of motor symptoms. However, non-motor symptoms can also be vague, making it difficult to connect them to Parkinson’s disease.
Non-motor symptoms that might be early warning signs include:
- Sleep problems such as periodic limb movement disorder , rapid eye movement behavior disorder and restless legs syndrome.
Parkinsons Disease Psychosis Causes And Risks
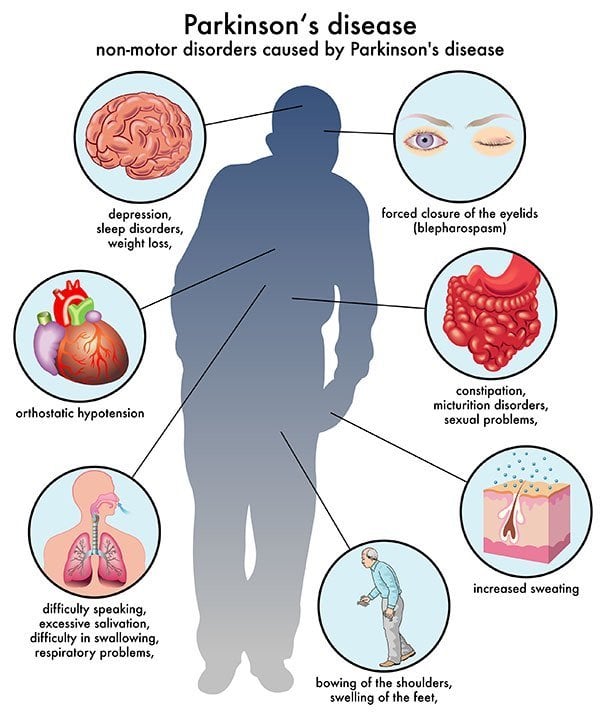
While the cause of psychosis related to Parkinsons was long thought to be a side effect of treatments used to address the motor symptoms of the disease, more recent understanding points to underlying mechanisms secondary to the disease itself, such as neuronal damage to multiple transmitter systems caused by the deposition of Lewy bodies.1,2
People at risk of developing psychosis include:
- those with more advanced Parkinsons disease
- those with cognitive impairment
- low daily activities
Don’t Miss: Dopamine Medication For Parkinson’s
Response To Parkinsons Drugs
After examining you, and depending on the severity of your symptoms, your specialist may suggest you take medication for Parkinsons. If your symptoms improve after taking Parkinsons medication for a few weeks or months, your specialist may confirm a Parkinsons diagnosis. However, some people with other forms of parkinsonism will also respond well to these drugs.
Your specialist may suggest you have a scan to help make a diagnosis. However, scans alone cant make a definite diagnosis of Parkinsons, so they are not commonly used.
Onset Of Psychotic Symptoms
Some data suggest that psychotic symptoms arise 10 years or more after the initial diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, with more updated evidence suggesting that these symptoms can arise in nearly 50% of patients within 4 years of diagnosis.7
Data from hospital-based studies report hallucinations in 8% to 40% of patients receiving long-term treatment for Parkinsons disease, while other recent data show that 55.4% of people with late-stage Parkinsons disease have psychotic symptoms and 72.5% present with a comorbid psychiatric diagnosis.8
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Research Paper
Patients With A Previous Diagnosis Other Than Parkinson’s Disease
Among all patients seen, two were referred for diagnostic purposes without a previous diagnosis, and 69 of 202 patients had a previous diagnosis other than Parkinson’s disease . Among these, 56 patients had been given a diagnosis of non-parkinsonian tremor, two of vascular parkinsonism, one of atypical parkinsonism, and 10 had been prescribed an antiparkinsonian drug for parkinsonian features without a specific diagnosis . Thirteen of the 69 patients with different diagnoses and the two patients referred for diagnostic purposes fulfilled strict clinical criteria for Parkinson’s disease . In two additional patients who had a previous diagnosis of non-parkinsonian tremor, a diagnosis of possible Parkinson’s disease was made . If only patients who had at some point in the past seen a specialist were considered, the diagnosis was changed to probable Parkinson’s disease in five and to possible Parkinson’s disease in one .
Sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values for the overall sample* and by type of clinician
Tests To Rule Out Other Conditions
Blood tests can help rule out other possible causes of the symptoms, such as abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
An MRI or CT scan can check for signs of a stroke or brain tumor, which may cause similar symptoms.
Hydrocephalus due to atrophy can occur with some types of dementia and would be visible with one of these imaging tests. If the person has neurologic symptoms but a normal scan result, Parkinsons disease may be present.
The doctor a lumbar puncture to rule out inflammation or a brain infection.
Read Also: Copd And Parkinson’s Disease
Definition Of Terms Used In The Analysis
Sensitivity: Proportion of patients with a final diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease who were previously diagnosed as having Parkinson’s disease: A/.
Specificity: Proportion of patients without a final diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease who were previously diagnosed as not having Parkinson’s disease: D/.
Positive predictive value: Proportion of patients with a previous diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease who received a final diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease: A/.
Negative predictive value: Proportion of patients with a previous diagnosis of not having Parkinson’s disease who received a final diagnosis of not having Parkinson’s disease: D/.
Diagnosis Of Parkinson Disease: Motor Symptoms
The clinical diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is based on the presence of characteristic motor symptoms: bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability, and resting tremor but neuropathology is still considered the gold standard for definite diagnosis. Differentiating PD from other movement disorders can be challenging throughout the disease course, because signs and symptoms often overlap. Indeed, neuropathology studies reveal that clinical diagnosis of PD can be confirmed with an accuracy of about 75%. Good response to levodopa is often used to support the diagnosis of PD. However, cases of pathologically proven PD with poor response to levodopa have also been reported.
Misdiagnosis of PD can occur for several reasons. In a community-based study of patients taking antiparkinsonian medication, the most common misdiagnosis were essential tremor, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular parkinsonism. In addition, many of the prominent features of PD may also occur as a result of normal aging or from comorbid and multifactorial medical conditions .
R. Savica, … G. Logroscino, in, 2016
Don’t Miss: Sister Disease To Parkinson’s
Medications For People With Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease result from the progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the brain and other organs such as the gut, which produce a neurotransmitter called dopamine. This causes a deficiency in the availability of dopamine, which is necessary for smooth and controlled movements. Medication therapy focuses on maximising the availability of dopamine in the brain. Medication regimes are individually tailored to your specific need. Parkinsons medications fit into one of the following broad categories:
- levodopa dopamine replacement therapy
- dopamine agonists mimic the action of dopamine
- COMT inhibitors used along with levodopa. This medication blocks an enzyme known as COMT to prevent levodopa breaking down in the intestine, allowing more of it to reach the brain
- anticholinergics block the effect of another brain chemical to rebalance its levels with dopamine
- amantadine has anticholinergic properties and improves dopamine transmission
- MAO type B inhibitors prevent the metabolism of dopamine within the brain.
What Is A Datscan And What Role Does It Play In A Parkinsons Diagnosis
In 2011, the FDA approved the use of a scan called a dopamine transporter scan . A DaTscan is an imaging technology that allows visualization of the dopamine system in the brain. It is similar to an MRI, but looks at the function of the brain rather than the structure.
A DaTscan involves injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug that is then measured by a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner . The SPECT scanner measures the levels and location of the drug in the brain.
It is important to know that a negative DaTscan does not rule out PD, especially early in the disease, but a positive DaTscan can help confirm it. A positive DaTscan can differentiate PD from essential tremor as there is no dopamine deficiency in the latter. However, DaTscan abnormalities can be seen in PD as well as other forms of atypical parkinsonism that cause a loss of dopamine . This means that a positive result does not differentiate Parkinsons disease from other forms of atypical parkinsonism.
Also Check: Chemicals Linked To Parkinson’s Disease
Living With Parkinson’s Disease
Coming to terms with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s and living with the disease is challenging and will take a lot of adjustment. There are still things you can do that can help you to feel more in control of your situation and to stay positive. Some things that might help could include:
- choosing to lead a healthy lifestyle
- making informed decisions related to your treatment
- keeping a diary of your symptoms in preparation for meetings with health and social care professionals
- attending a self-management course
Sensitivity Specificity And Predictive Value Of A Previous Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease
Of 126 patients with a pre-existing clinical diagnosis of probable and possible Parkinson’s disease in the overall sample , 111 were confirmed as having Parkinson’s disease, resulting in a sensitivity of 88.1% similarly, it was confirmed that 54 of 74 patients did not have Parkinson’s disease, resulting in a specificity of 73.0% . The positive and negative predictive values of a previous clinical diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease were 84.7% and 78.3% . In other words, in 85% of patients with a previous diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease this diagnosis was confirmed, and 78% of patients with a diagnosis other than Parkinson’s disease did not have the disease .
When this was broken down by a specialist or other doctor diagnosis, the diagnostic validity was as follows. Neurologists and geriatricians had a sensitivity and specificity of 93.5% and 64.5% , respectively, compared with 73.5% and 79.1% for non-specialists. The positive predictive values were greater for specialists than for other doctors , but the negative predictive values were equivalent v non-specialist 79.1% ).
You May Like: Can Stress Cause Parkinson’s
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
The most prominent signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease occur when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems associated with the disease. Scientists still do not know what causes the neurons to die.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons disease contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons andLewy body dementia.
Response To Medication Can Matter
Other movement disorders can act like Parkinson’s. That makes it hard to know for sure whether you have the disease, even after a complete exam. However, the loss of dopamine causes Parkinson’s. It’s a chemical made by brain cells. It is important for movement.
For this reason, your doctor may want you to take a dopamine replacement drug called levodopa. Then your doctor will watch to see whether your symptoms improve. If you get better on levodopa, it’s more likely that you have Parkinson’s.
Don’t Miss: First Line Medication For Parkinson’s
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease, the physician may prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication. In the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Pd Diagnosis Disease Severity And Disease Progression
The diagnosis of PD is essentially clinical , and we believe that the clinical evaluation of patients will not be replaced by modern imaging techniques. Nevertheless, as pointed out earlier, misdiagnosis can approach 20% of cases . Recently, in line with the European Union, the U.S. FDA approved DAT scan as a diagnostic tool to help differentiate between PD and Essential Tremor. This is the only current FDA-approved subsidiary examination to aid in PD diagnosis.
The role of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of PD is still not fully established. Traditionally, it has been seen as a means to potentially exclude alternate diagnoses such as vascular parkinsonism, or more importantly , atypical forms of degenerative parkinsonism such as MSA or progressive supranuclear palsy . Traditional structural MRI findings of these latter diagnoses such as increased pallidal iron, rim of putaminal hyperintensity, hot cross bun sign and/or cerebellar atrophy in MSA or the hummingbird or penguin sign in PSP may not be reliable, particularly in early disease.
Figure 5. Multimodal MRI in PD. Differences are noted between patients with PD and controls through voxel-based analysis of R2, mean diffusivity, and fractional anisotropy maps.
-
Low dopamine transporter uptake in basal ganglia demonstrated by SPECT or PET imaging.*
Brent A. Vogt, in, 2019
You May Like: Adaptive Devices For Parkinson’s Disease
How Parkinsons Disease Is Diagnosed
Parkinsons disease is usually diagnosed clinically, meaning that a physician looks for the presence or absence of the possible symptoms of Parkinsons disease by interviewing the patient and performing a detailed neurologic examination.
While there is presently no definitive test for Parkinsons, it can often be identified by a general neurologist, who is trained to diagnose and treat neurologic disorders. To avoid misdiagnosis, consultation with a movement disorder specialist is recommended. A movement disorder specialist is a physician who has undergone additional, subspecialty training in the diagnosis and treatment of movement disorders, such as Parkinsons, after training in general neurology.
What to expect during your visit with a physician
Typically, a trained physician will only consider the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease if the person being examined has at least two of the core motor symptoms of Parkinsons, including tremor, the characteristic bradykinesia , or rigidity. At the end of your visit, the physician should discuss with you why you may or may not have Parkinsons disease and the level of certainty about the diagnosis. This determination is based on your medical history and examination at this visit.
Brain imaging and other tools to aid diagnosis of Parkinsons
How Is Parkinson’s Diagnosed
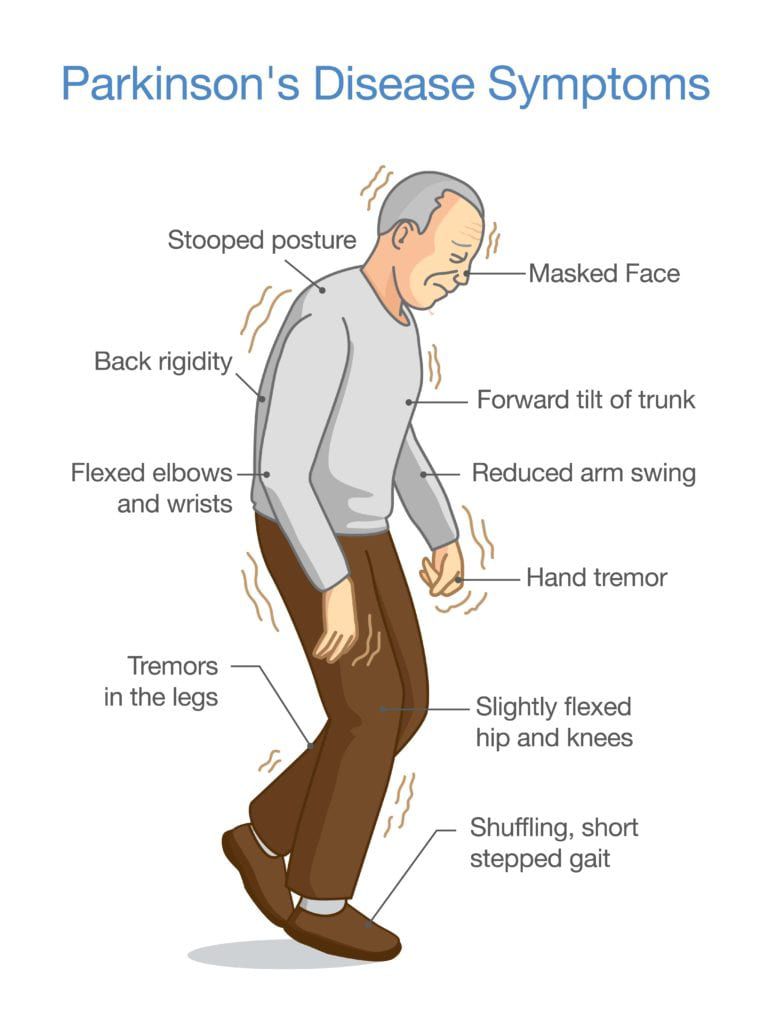
Current evidence suggests that Parkinsons tends to develop gradually. It may be many months, even years, before the symptoms become obvious enough for someone to go to the doctor.
This information looks at what parkinsonism is, how Parkinsons and other similar conditions may be diagnosed, and explains some of the tests that may be involved in the process.
Parkinsonism is a term used to describe symptoms or signs that are found in Parkinsons, but which can also be found in other conditions that cause slowness of movement, stiffness and tremor.
Most people with a form of parkinsonism have idiopathic Parkinsons disease, also known as Parkinsons. Idiopathic means the cause is unknown.
Other less common forms of parkinsonism include multiple system atrophy , progressive supranuclear palsy , drug-induced parkinsonism and vascular Parkinsons.
If youre concerned about symptoms youve been experiencing, you should visit your GP. If your GP suspects you have Parkinsons, clinical guidelines recommend they should refer you quickly to a specialist with experience in diagnosing the condition .
Its not always easy to diagnose the condition. So its important that you see a Parkinsons specialist to get an accurate diagnosis and to consider the best treatment options.
Diagnosing Parkinsons can take some time as there are other conditions, such as essential tremor , with similar symptoms. There is also currently no definitive test for diagnosing Parkinsons.
Read Also: Earliest Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Molecular Imaging In Parkinson’s Disease
The diagnosis of PD relies on the clinical manifestation of cardinal motor symptoms, bradykinesia, and tremor at rest or rigidity . A positive response to dopaminergic drugs is supportive of the diagnosis. Single photon emission computed tomography or PET ligands that are specific for dopamine transporters indirectly enable the quantification of the deficit of dopaminergic nigrostriatal projections and can provide further support of diagnosis . Deficiencies of monoamine synthesis can be measured with dihydroxyphenylalanine which is a substrate for the enzyme aromatic amino acid decarboxylase in all monoaminergic neurons including noradrenergic neurons .
The role of deficits of noradrenaline in motor and non-motor symptoms is not clear and research on the noradrenergic system in PD patients has been hindered by lack of specific methods to visualize the noradrenergic neurons and projections in vivo. We have recently carried out PET studies to investigate the role of noradrenaline in non-motor symptoms in PD patients and these studies will form the basis of discussions in the paragraphs below.
Paul Johns BSc BM MSc FRCPath, in, 2014