What Are Surgery Options For Parkinsons Disease
Depending upon your needs, medical history, health, and symptoms, one of the following procedures may be considered for Parkinsons disease:
There are many other procedures being researched. One of the most promising involves the transplantation of fetal dopamine neurons into the brains of people with Parkinsons disease. The hope is that these cells will be able to re-grow the damaged dopamine-producing nerve cells.
Dont Miss: Parkinsons Hallucinations Commercial
Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease usually develop gradually and are mild at first.
There are many different symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease. Some of the more common symptoms are described below.
However, the order in which these develop and their severity is different for each individual. It’s unlikely that a person with Parkinson’s disease would experience all or most of these.
Parkinsons Disease Psychosis: The What When Why And How
Psychosis is a psychiatric term used in neurology to refer to a spectrum of abnormalities. Parkinsons disease psychosis is where people experience hallucinations or delusions. Hallucinations is seeing, hearing, or smelling things that dont exist. With tactile hallucinations, one can feel a presence that isnt there. Delusions are believing something that is not true, like that a spouse is being unfaithful or caregivers are stealing. In this one-hour talk, movement disorder specialist Christopher Goetz, MD, focuses on hallucinations and spends a little time on delusions.
Read Also: Parkinsons Disease And Chiropractic Care
You May Like: Where Does Parkinson’s Start
Surgery For Parkinsons Disease
Based on the severity of the condition and the medical profile, the doctor may recommend surgery as one treatment option for Parkinson’s disease.
There are several types of surgery that may be performed that can help patients with Parkinson’s disease. Most of the treatments are aimed at helping the tremor or rigidity that comes with the disease. In some patients, surgery may decrease the amount of medication that is needed to control the symptoms.
There are three types of surgeries that may be performed for Parkinson’s disease, including the following:
It is important to remember that surgery may help with symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, but does not cure the disease or stop the progression of the disease.
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better And How Long Will It Take To Recover
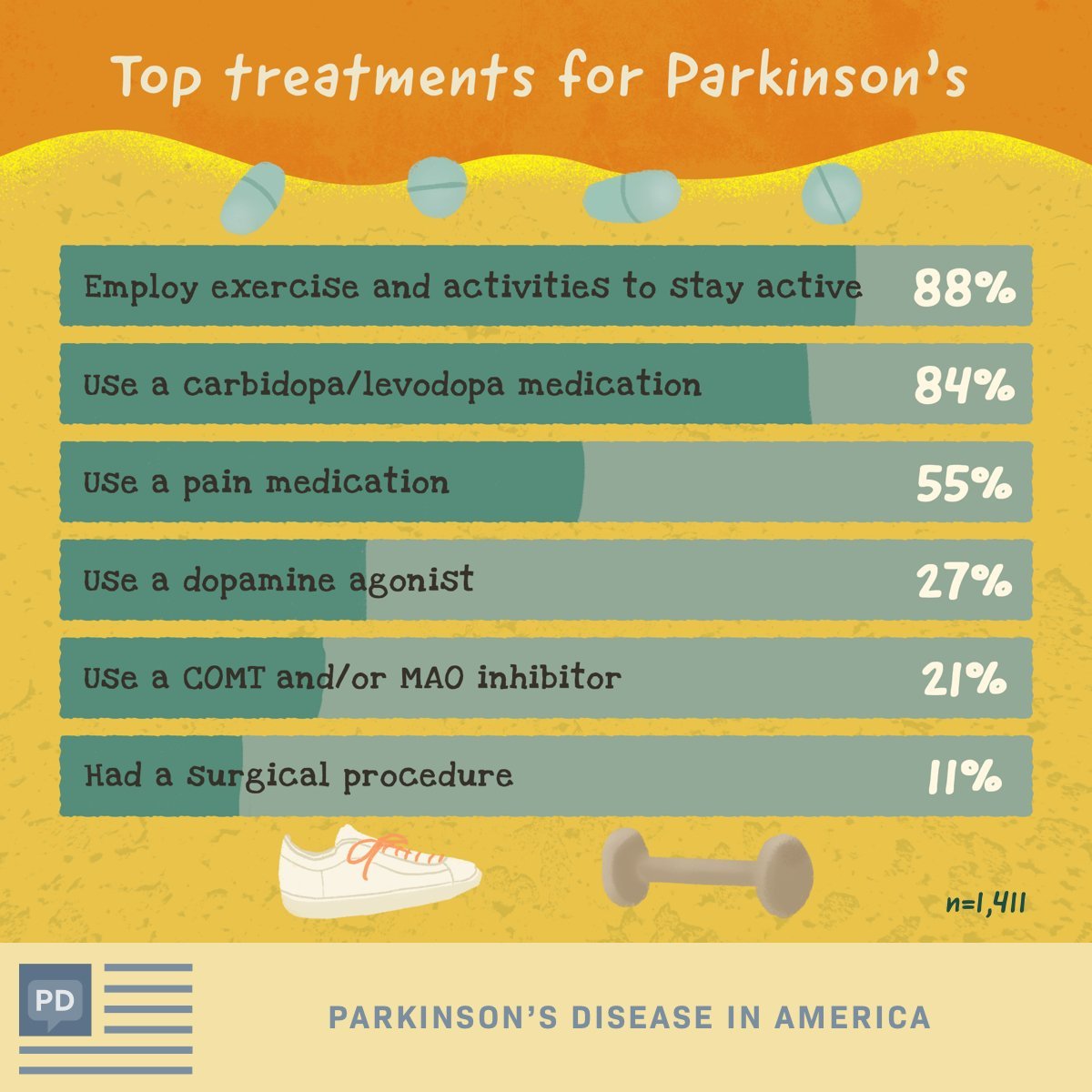
The time it takes to recover and see the effects of Parkinson’s disease treatments depends strongly on the type of treatments, the severity of the condition and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to offer more information about what you can expect from treatment. The information they give you can consider any unique factors that might affect what you experience.
You May Like: Community Resources For Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons warning signs can be motor symptoms like slow movements, tremors or stiffness. However, they can also be non-motor symptoms. Many of the possible non-motor symptoms can appear years or even decades ahead of motor symptoms. However, non-motor symptoms can also be vague, making it difficult to connect them to Parkinsons disease.
Non-motor symptoms that might be early warning signs include:
- Sleep problems such as periodic limb movement disorder , rapid eye movement behavior disorder and restless legs syndrome.
Etiology Of Psychotic Symptoms
PD is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons with cell bodies residing in the substantia nigra pars compacta with resultant decreased dopamine release in the basal ganglia. The etiology of psychosis is less understood and may involve dysfunctional dopaminergic and serotonergic, and possibly cholinergic, pathways. Indeed, drugs that block dopaminergic receptors can cause extrapyramidal symptoms.
Risk factors for PDP include: exposure to dopaminergic medications, advancing age, increasing impairment in executive function, dementia, increasing severity and duration of PD, comorbid psychiatric symptoms such as depression and anxiety, daytime fatigue, sleep disorders, visual impairment, and polypharmacy . The presence of psychosis in patients with PD is a strong predictor of institutionalization. A study comparing PD patients still living at home with those in nursing care facilities found a 16-fold higher likelihood of hallucinations in the institutionalized group . Another review of a population of PD patients with psychosis found that after 2 years, hallucinations were linked to dementia , nursing home placement or death .
Don’t Miss: Do Parkinson’s Patients Get Mean
Hallucinations According To The Duration Of The Disease
We found that the prevalence of hallucinations of all types and of visual hallucinations in the 3 months preceding inclusion in the study increased with the duration of the disease. Moreover, the duration of Parkinsons disease was an independent predictor of visual hallucinations in the multivariate analysis. Other studies gave conflicting results on the relationship between hallucinations and disease duration. In a retrospective study of 100 patients, logistic regression analysis also showed an association between `psychosis and an increased duration of the disease . An association between the duration of the disease and the occurrence of hallucinations was also found by some investigators but not by others .
Table 1
Read Also: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
When: Timing Of Advanced Therapies
Advanced treatments were once reserved as a last resort. Although they all carry a small risk of severe adverse effects and the use of the devices can be bothersome, their efficacy can be so dramatic that there is a tendency to initiate these treatments earlier in the disease course, before motor complications generate marked disability . A major contribution to this discussion was the EARLYSTIM trial, which confirmed that patients with a disease duration of at least four years, fluctuations or dyskinesia for three years or less, and mild-to-moderate impairment in social and occupational functioning, may benefit from STN DBS . Advanced therapies should only be initiated once other causes of Parkinsonism have been ruled out with relative certainty, which typically requires 34 years of disease duration. Still it is advisable to start discussing advanced therapies early in the disease course, preferably when motor fluctuations start to occur, but can still be managed by alterations in standard DRT. This reassures patients that further options remain available, gives them time to get acquainted with the advanced therapies and may facilitate decision making later on.
You May Like: Board Games For Parkinson’s Patients
How Deep Brain Stimulation Works
Exactly how DBS works is not completely understood, but many experts believe it regulates abnormal electrical signaling patterns in the brain. To control normal movement and other functions, brain cells communicate with each other using electrical signals. In Parkinsons disease, these signals become irregular and uncoordinated, which leads to motor symptoms. DBS may interrupt the irregular signaling patterns so cells can communicate more smoothly and symptoms lessen.
What Is The Pathophysiology Of The Disease
Parkinson disease is a neurodegenerative syndrome involving multiple motor and nonmotor neural circuits., It is characterized by two major pathologic processes: premature selective loss of dopamine neurons the accumulation of Lewy bodies, composed of -synuclein, which become misfolded and accumulate in multiple systems of patients with Parkinson disease. It is unclear which process occurs first. Based on pathologic studies, there is a stepwise degeneration of neurons over many years, with each affected site corresponding to specific symptomatology in Parkinson disease . When motor symptoms become evident, there is 3070% cell loss evident in the substantia nigra on pathologic examination. The mainstay of therapy aims to replace dopamine with dopaminergic medications and modulate the dysfunctional circuit. Cognitive dysfunction, mood disorders and impulse control disorders are related to deficits of dopamine outside the basal ganglia or in serotonergic and noradrenergic systems., Autonomic dysfunction has been related to pathologies outside the brain, including the spinal cord and peripheral autonomic nervous system.
Recommended Reading: Can Tremors Turn Into Parkinson’s
Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease
Treatment of PD requires a multifaceted approach comprising pharmacological and nonpharmacological efforts. Considerable evidence suggests that patients should be encouraged to adopt a regular program of exercise from the time of diagnosis.
There are numerous other medications available to treat PD. Anticholinergic drugs are primarily used to treat tremor. Amantadine is a modestly effective agent for a variety of motor symptoms and can also reduce levodopa-induced dyskinesias. MAO-B and COMT inhibitors, by extending the duration of action of individual doses of levodopa, may be useful for treating motor fluctuations. Patients who cannot be satisfactorily controlled with medications alone are often treated surgically. Deep brain stimulation surgery of the STN or globus pallidus pars interna is associated with marked motor benefit in a large proportion of correctly selected patients due to high-frequency electrical stimulation of the stereotactically targeted structure. Pallidotomy has not often been utilized since the advent of DBS.
Stanley Fahn MD, … Peter Jenner BPharm , PhD, DSc, FRPharms, in, 2007
What Makes Some People With Parkinsons More Susceptible To Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
Not everyone living with Parkinsons will experience hallucinations and/or delusions, but there are several things that can increase your risk. Here are a few to look out for. Be sure to speak to your doctors and care partners if you notice any changes.
- Increased sleep disturbances such as REM Sleep Behavior Disorder, sleep apnea, vivid dreaming and sleep interruptions
- Vision problems such as blurry or double vision
- Hearing problems
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Muscle Spasms
What Is Parkinsons Disease Surgery
Parkinsons disease surgery is a brain operation called deep brain stimulation . The surgery is also used to treat epilepsy, obsessive-compulsive disorder and a condition called essential tremor. DBS is widely considered one of the most significant neurological breakthroughs in recent history, posing a potential treatment for major depressive disorder, stroke recovery and addiction. Parkinsons disease brain surgery aims to interrupt problematic electrical signals from targeted areas in the brain and reduce PD symptoms.
Dont Miss: Nursing Care For Parkinsons Disease
How Can People Cope With Parkinsons Disease
While PD usually progresses slowly, eventually daily routines may be affectedfrom socializing with friends to earning a living and taking care of a home. These changes can be difficult to accept. Support groups can help people cope with the diseases emotional impact. These groups also can provide valuable information, advice, and experience to help people with PD, their families, and their caregivers deal with a wide range of issues, including locating doctors familiar with the disease and coping with physical limitations. A list of national organizations that can help people locate support groups in their communities appears at the end of this information. Individual or family counseling may also help people find ways to cope with PD.
People with PD may also benefit from being proactive and finding out as much as possible about the disease in order to alleviate fear of the unknown and to take a positive role in maintaining their health. Many people with PD continue to work either full- or part-time, although they may need to adjust their schedule and working environment to accommodate their symptoms.
Read Also: How To Live With Someone With Parkinson’s
Dopaminergic Features And Their Treatment
Patients with PD usually present with features indicative of degeneration of nigrostriatal pathways. A useful clinical definition for PD is asymmetric onset of an akinetic rigid syndrome with resting tremor and a good response to levodopa. When applied by neurologists with an interest in movement disorders, this definition has a pathological correlation exceeding 98%. When treatment is considered appropriate, and this is a topic discussed in detail below, a variety of options is available. The use of dopaminergic drugs improves motor function, significantly reduces both the morbidity and mortality of PD, and improves quality of life.
Levodopa remains the drug most commonly used in PD. It is very effective in improving bradykinesia and rigidity, and in practice remains the gold standard against which other drugs are judged. Some studies, predominantly in vitro, have suggested that levodopa may be toxic. However, such data are conflicting, and some laboratory studies have suggested a growth factor-like effect for levodopa. Overall, the pre-clinical evidence for levodopa toxicity is not convincing and there are no data to indicate that any toxic action is of clinical relevance.
Table 1
Percentage of patients remaining on dopamine agonist monotherapy at years 14 and years 15 during treatment trials
Who Gets Parkinsons Disease
Risk factors for PD include:
- Age. The average age of onset is about 70 years, and the incidence rises significantly with advancing age. However, a small percent of people with PD have early-onset disease that begins before the age of 50.
- Sex. PD affects more men than women.
- Heredity. People with one or more close relatives who have PD have an increased risk of developing the disease themselves. An estimated 15 to 25 percent of people with PD have a known relative with the disease. Some cases of the disease can be traced to specific genetic mutations.
- Exposure to pesticides. Studies show an increased risk of PD in people who live in rural areas with increased pesticide use.
You May Like: Sarah Raven Arthur Parkinson Podcast
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
At present, we do not know the cause of Parkinsons disease. In most people there is no family history of Parkinsons Researchers worldwide are investigating possible causes, including:
- environmental triggers, pesticides, toxins, chemicals
- genetic factors
- combinations of environment and genetic factors
Therapy Services Nutrition And Wellness Plans
An integral part of Parkinsons disease treatment is ensuring that each patient receives all the support services they need to help manage the impact the disease has on their overall health and well-being.
Part of the multidisciplinary care provided at Brigham and Womens Hospital, many patients with Parkinsons disease also benefit from:
Also Check: Foods That Help Parkinson’s
Which Brain Targets Should Be Used To Implant The Dbs Lead
- There are three brain targets that the FDA has approved for use in Parkinsons: the subthalamic nucleus and the globus pallidus interna are the most common.
- The target choice should be tailored to a persons individual needs.
- There are many ongoing studies that will help refine target choice for individual people.
- Although the picture is not yet clear on the issue of target choice, the STN seems to provide more medication reduction, while GPi may be slightly safer for language and cognition.
Delusions From Parkinsons Disease

Delusions affect only about 8 percent of people living with PD. Delusions can be more complex than hallucinations. They may be more difficult to treat.
Delusions often start as confusion that develops into clear ideas that arent based on reality. Examples of the types of delusions people with PD experience include:
- Jealousy or possessiveness. The person believes someone in their life is being unfaithful or disloyal.
- Persecutory. They believe that someone is out to get them or harm them in some way.
- Somatic. They believe they have an injury or other medical problem.
- Guilt. The person with PD has feelings of guilt not based in real behaviors or actions.
- Mixed delusions. They experience multiple types of delusions.
Paranoia, jealousy, and persecution are the most commonly reported delusions. They can pose a safety risk to caregivers and to the person with PD themselves.
PD isnt fatal, though complications from the disease can contribute to a shorter expected life span.
Dementia and other psychosis symptoms like hallucinations and delusions do contribute to increased hospitalizations and increased rates of death .
One study from 2010 found that people with PD who experienced delusions, hallucinations, or other psychosis symptoms were about 50 percent more likely to die early than those without these symptoms.
But early prevention of the development of psychosis symptoms may help increase life expectancy in people with PD.
Don’t Miss: Steroids And Parkinson’s Disease
A Neurobiomedicine Functional Restoration Prescription Treatment Program
healABILITY: Preservation of health and wellness through the promotion of well-being prevention of disease, and promotion and support of the inherent or innate recuperative abilities of the body.
Dr. James F. Farley, DC, BA, BS, MS, BCIM, FAAIM, FAIS
Dr. James F. Farley, DC, BA, BS, MS, BCIM, FAAIM, FAIS
Allostatic Stress, Neurobiomedicine Health System creates healability
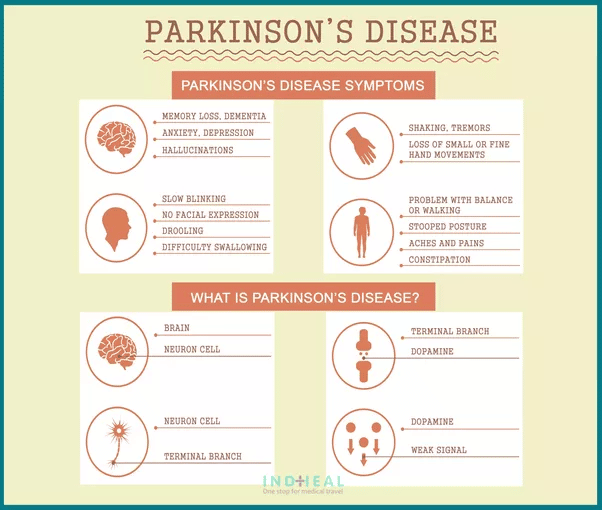
What Are The Symptoms
The best-known symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve loss of muscle control. However, experts now know that muscle control-related issues aren’t the only possible symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Motor-related symptoms
Motor symptoms which means movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease include the following:
Additional motor symptoms can include:
- Blinking less often than usual. This is also a symptom of reduced control of facial muscles.
- Cramped or small handwriting. Known as micrographia, this happens because of muscle control problems.
- Drooling. Another symptom that happens because of loss of facial muscle control.
- Mask-like facial expression. Known as hypomimia, this means facial expressions change very little or not at all.
- Trouble swallowing . This happens with reduced throat muscle control. It increases the risk of problems like pneumonia or choking.
- Unusually soft speaking voice . This happens because of reduced muscle control in the throat and chest.
Non-motor symptoms
Several symptoms are possible that aren’t connected to movement and muscle control. In years past, experts believed non-motor symptoms were risk factors for this disease when seen before motor symptoms. However, theres a growing amount of evidence that these symptoms can appear in the earliest stages of the disease. That means these symptoms might be warning signs that start years or even decades before motor symptoms.
Non-motor symptoms include:
Stages of Parkinsons disease
Read Also: Tardive Dyskinesia Parkinson’s Disease
Icipating In Clinical Trials
Clinical trials and their participants have revolutionized Parkinsons treatment, and have changed the lives dramatically of those affected. They have helped make available many new treatments in addition to improving the delivery methods of medications and new deep brain stimulation techniques.
Clinical trials are essential to the future of Parkinsons research, and APDA is committed to this vital effort.
What Medications And Treatments Are Used
Medication treatments for Parkinsons disease fall into two categories: Direct treatments and symptom treatments. Direct treatments target Parkinsons itself. Symptom treatments only treat certain effects of the disease.
Medications
Medications that treat Parkinsons disease do so in multiple ways. Because of that, drugs that do one or more of the following are most likely:
Several medications treat specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Symptoms treated often include the following:
- Erectile and sexual dysfunction.
- Hallucinations and other psychosis symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation
In years past, surgery was an option to intentionally damage and scar a part of your brain that was malfunctioning because of Parkinsons disease. Today, that same effect is possible using deep-brain stimulation, which uses an implanted device to deliver a mild electrical current to those same areas.
The major advantage is that deep-brain stimulation is reversible, while intentional scarring damage is not. This treatment approach is almost always an option in later stages of Parkinson’s disease when levodopa therapy becomes less effective, and in people who have tremor that doesnt seem to respond to the usual medications.
Experimental treatments
Researchers are exploring other possible treatments that could help with Parkinsons disease. While these arent widely available, they do offer hope to people with this condition. Some of the experimental treatment approaches include:
Recommended Reading: Google Scholar Parkinson’s Disease