Prevention Of The Breakdown Of Endogenous Dopamine Medications
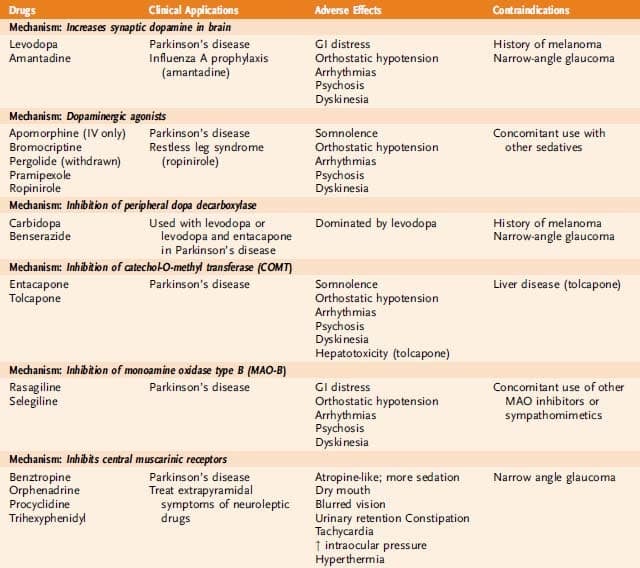
MAO-B Inhibitors work by inhibiting the enzymes involved in dopamine metabolism, which preserves the levels of endogenous dopamine. While they are sometimes sufficient for control of symptoms in early disease, most patients ultimately require levodopa-based treatment. MAO-B inhibitors may also be used in combination with levodopa-based preparations, to allow for a reduction in the levodopa dose. Commonly used MAO-B inhibitors include selegiline and rasagiline . More recently, the drug safinamide was also approved for use in PD, which appears to have multiple modes of action, one of which is thought to be inhibition of MAO-B . MAO-B inhibitors are generally well tolerated, with gastrointestinal side effects being the most common problem. Other adverse effects include aching joints, depression, fatigue, dry mouth, insomnia, dizziness, confusion, nightmares, hallucinations, flu-like symptoms, indigestion, and headache.
Catechol-O-methyl transferase inhibitors: another enzyme that is involved in dopamine degradation is COMT. These drugs are predominantly used as adjunctive therapy to levodopa, prolonging its duration of action by increasing its half-life and its delivery to the brain. COMT inhibitors come in the form of tablets and are not generally prescribed as monotherapy, as on their own they offer only limited effect on PD symptoms. Examples of COMT inhibitors include entacapone , tolcapone , and opicapone .
Impulsive And Compulsive Behavior
Some people taking dopamine agonists may experience problems with impulsive or compulsive behaviours. For example an increased desire to gamble or engage in sexual activity. These behaviours often develop slowly so may not seem to be a problem immediately. It is important for both the person living with Parkinsons and their family to be aware of this side effect. If affected by this side effect, a reduction in dose or stopping the medication will stop the behaviour.
Is Parkinson’s Disease A Type Of Dementia
Parkinsons disease is not a type of dementia. Instead, its caused by the death of brain cells in a region called the substantia nigra, which is responsible for sending signals to other parts of the body.
Parkinsons disease should not be confused with other types of dementia, such as Alzheimers or Lewy body dementia because these conditions are characterized by memory loss and other cognitive problems.
There are different types of Parkinsons disease, including idiopathic Parkinsons disease. This is the most common type and occurs without a known cause.
The other type is secondary Parkinsons disease, which occurs due to another condition or factor, such as a brain injury or using certain medications.
Don’t Miss: Vagus Nerve Stimulation And Parkinson’s
How Is It Diagnosed
A neurologist diagnoses it based on the presence of specific symptoms and a physical examination. The severity of the disease can be measured using the Hoehn and Yahr scale, which ranges from stage 1 to stage 5 .
Your doctor may also ask about your medical history. Once diagnosed with Parkinsons, youll need treatment medications for several years. In addition, you may undergo imaging scans or blood tests.
Men are more often diagnosed than women, with the average age of onset being over 60 years old. Unfortunately, there is no cure for Parkinsons disease, but drugs can help relieve symptoms such as trembling hands, stiffness, and difficulty maintaining balance.
Controlled Release Madopar And Sinemet
![Neural Stem Cell Therapy for Parkinsons Disease [PD] Neural Stem Cell Therapy for Parkinsons Disease [PD]](https://www.parkinsonsdaily.com/wp-content/uploads/neural-stem-cell-therapy-for-parkinsons-disease-pd.jpeg)
Controlled release preparations have the letters CR or HBS after the drug name.
These let the levodopa enter your body slowly instead of all at once. They can increase the time between doses.
They may be used when the dose of standard levodopa starts to wear off and the person taking it no longer feels the treatment is effective.
Controlled release options can sometimes reduce involuntary movements .
You May Like: Best Hobbies For Parkinson’s Patients
Common Drugs For Parkinsons Disease
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole , .
Modified Release Controlled Release And Prolonged Release Medication
You may see that your medication is written as modified release. It can also be written as controlled release or prolonged release . All of these labels mean the same thing but drug companies can choose which one to use with their drug.
These types of medication are made to release your treatment slowly to help you have more even control of your symptoms throughout the day.
Recommended Reading: What Does It Feel Like To Have Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Most Common Medicines Used To Treat Pd
Sinemet®
Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed and most effective medicine for controlling the symptoms of PD, particularly bradykinesia and rigidity.
Levodopa is a chemical found naturally in our brains. When given as a medicine, it is transported to the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. It is then converted into dopamine for the nerve cells to use as a neurotransmitter.
Sinemet is made up of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Levodopa enters the brain and is converted to dopamine while carbidopa prevents or lessens many of the side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and occasional heart rhythm disturbances. It is generally recommended that patients take Sinemet on an empty stomach, at least ½ hour before or one hour after meals.
There are two forms of Sinemet: controlled-release or immediate-release Sinemet. Controlled-release Sinemet and immediate-release Sinemet are equally effective in treating the symptoms of PD, but some people prefer the controlled release version. Ask your doctor which approach is best for you.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists are medicines that activate the dopamine receptor. They mimic or copy the function of dopamine in the brain.
Parlodel®, Requip®, and Mirapex® are all dopamine agonists. These medicines might be taken alone or in combination with Sinemet. Generally, dopamine agonists are prescribed first and levodopa is added if the patients symptoms cannot be controlled sufficiently.
Symmetrel®
Dopaminergic Features And Their Treatment
Patients with PD usually present with features indicative of degeneration of nigrostriatal pathways. A useful clinical definition for PD is asymmetric onset of an akinetic rigid syndrome with resting tremor and a good response to levodopa. When applied by neurologists with an interest in movement disorders, this definition has a pathological correlation exceeding 98%. When treatment is considered appropriate, and this is a topic discussed in detail below, a variety of options is available. The use of dopaminergic drugs improves motor function, significantly reduces both the morbidity and mortality of PD, and improves quality of life.
Levodopa remains the drug most commonly used in PD. It is very effective in improving bradykinesia and rigidity, and in practice remains the gold standard against which other drugs are judged. Some studies, predominantly in vitro, have suggested that levodopa may be toxic. However, such data are conflicting, and some laboratory studies have suggested a growth factor-like effect for levodopa. Overall, the pre-clinical evidence for levodopa toxicity is not convincing and there are no data to indicate that any toxic action is of clinical relevance.
Table 1
Percentage of patients remaining on dopamine agonist monotherapy at years 14 and years 15 during treatment trials
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Causes Symptoms And Treatment
Side Effects And Problems With Levodopa
In the early days of taking levodopa, you may feel sickness or nausea. In most people this will pass as your body adjusts to the medication.
Overtime as Parkinsons progresses the levodopa dose will need to be adjusted. Many people will become more aware that symptoms sometimes return between doses of medication. This is called wearing off and is a sign your dose needs to be adjusted.
As levodopa is absorbed through the gut, constipation or other stomach problems may impact on uptake of the medication. In some people who have had Parkinsons for sometime extra involuntary movements can occur. Your neurologist will be able to help adjust medications to minimise dyskinesia.
Other side effects may include:
- Psychological changes
- Sleepiness, fainting or dizziness
Side effects of levodopa can sometimes be improved by changing your dose, the form of the drug or how often you take it. If this doesnt work, other types of drug may be combined with levodopa.
Speak to your GP or specialist about the right treatment for you.
Glucagonlike Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists And Other Antidiabetic Agents
Biological processes involved in PD share common features with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus , including the dysregulation of insulin signaling in the brain. The term brain insulin resistance has been suggested to describe decreased sensitivity of CNS pathways to insulin, followed by disturbances in synaptic, metabolic and immune response functions . Strategies to normalize insulin sensitivity in neurons have thus been in the spotlight of clinical trials aiming to establish whether they may provide neuroprotective actions.
The neuroprotective effect of GLP-1 RAs is assumed to be mediated by improved brain insulin sensitivity however, human studies evaluating their biological effect in the CNS are limited. Functional MRI imaging studies have primarily focused on investigating brain networks involved in the anorectic effect of GLP-1 RAs , but sparse mechanistic data are available for understanding neuroprotective effects of these drugs. In a more recent trial of exenatide in PD, disease modifying effects measured by nigrostriatal dopamine transporter imaging were reported . Subsequently, brain insulin and Akt signaling pathways were also evaluated in neuronal-derived exosomes and it was shown that exenatide treatment, but not placebo, activated these pathways . This significant, secondary analysis of the trial increases understanding of the molecular mechanism underlying the treatment effect and provides a possible biomarker to measure target engagement.
Also Check: Rigidity In Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinsons Treated In The Early Stages
Three main groups of medication are used to treat Parkinsons in the early stages:
- Levodopa : is converted into dopamine in the brain.
- Dopamine agonists: stimulate the nerve receptors responsible for the uptake of dopamine.
- MAO-B inhibitors : block the breakdown of dopamine in the brain.
The medications are usually taken in tablet form. Some dopamine agonists are also available as patches.
In the early stages, some people with mild symptoms cope just fine without medication. If at some stage the symptoms become too much of a problem, levodopa and dopamine agonists are the main medication options. They work slightly differently to each other, and some products may cause side effects more often or have worse side effects than others. But both are very effective in the early stages of the illness. That helps many people with Parkinsons to live a fairly symptom-free life for at least a few years.
How Do I Prevent Falls From Common Hazards
- Floors: Remove all loose wires, cords, and throw rugs. Minimize clutter. Make sure rugs are anchored and smooth. Keep furniture in its usual place.
- Bathroom: Install grab bars and non-skid tape in the tub or shower. Use non-skid bath mats on the floor or install wall-to-wall carpeting.
- Lighting: Make sure halls, stairways, and entrances are well-lit. Install a night light in your bathroom or hallway and staircase. Turn lights on if you get up in the middle of the night. Make sure lamps or light switches are within reach of the bed if you have to get up during the night.
- Kitchen: Install non-skid rubber mats near the sink and stove. Clean spills immediately.
- Stairs: Make sure treads, rails, and rugs are secure. Install a rail on both sides of the stairs. If stairs are a threat, it might be helpful to arrange most of your activities on the lower level to reduce the number of times you must climb the stairs.
- Entrances and doorways: Install metal handles on the walls adjacent to the doorknobs of all doors to make it more secure as you travel through the doorway.
Read Also: Long Term Care For Parkinson’s Patients
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
At present, we do not know the cause of Parkinsons disease. In most people there is no family history of Parkinsons Researchers worldwide are investigating possible causes, including:
- environmental triggers, pesticides, toxins, chemicals
- genetic factors
- combinations of environment and genetic factors
The Clinical Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Department of Neurology, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford, Essex, CM1 7ET UK
Queen Mary School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of London, London, UK
Department of Neurology, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford, Essex, CM1 7ET UK
Queen Mary School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of London, London, UK
Don’t Miss: How Does Parkinson’s Disease Spread From Person To Person
Symptomatic And Neuroprotective Therapy
Pharmacologic treatment of Parkinson disease can be divided into symptomatic and neuroprotective therapy. At this time, there is no proven neuroprotective or disease-modifying therapy.
Levodopa, coupled with carbidopa, a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor , remains the gold standard of symptomatic treatment for Parkinson disease. Carbidopa inhibits the decarboxylation of levodopa to dopamine in the systemic circulation, allowing for greater levodopa distribution into the central nervous system. Levodopa provides the greatest antiparkinsonian benefit for motor signs and symptoms, with the fewest adverse effects in the short term however, its long-term use is associated with the development of motor fluctuations and dyskinesias. Once fluctuations and dyskinesias become problematic, they are difficult to resolve.
Monoamine oxidase -B inhibitors can be considered for initial treatment of early disease. These drugs provide mild symptomatic benefit, have excellent adverse effect profiles, and, according to a Cochrane review, have improved long-term outcomes in quality-of-life indicators by 20-25%.
Neuroprotective therapy aims to slow, block, or reverse disease progression such therapies are defined as those that slow underlying loss of dopamine neurons. Although no therapy has been proven to be neuroprotective, there remains interest in the long-term effects of MAO-B inhibitors. Other agents currently under investigation include creatine and isradipine.
What Should I Know About Parkinsons Disease And Medications
There have been rapid and remarkable changes over the past decade in treating Parkinsons disease . The development of new medicines and the understanding of how best to use them and the older drugs have significantly improved the quality of life for people with the disease.
There is currently no treatment that has been proven to affect the disease progression or development of medication that can slow the disease process. There are two general approaches to the treatment of PD improve the symptoms with medications and engage in physical therapy. Most patients with PD can be adequately treated with medicines that alleviate their symptoms. For the approximately 15% of patients for whom medicines are not sufficiently effective, new, highly effective, and safe surgical treatments are available.
Choices about medicines made early in the course of the disease have a strong impact on the long-term course of the illness. Therefore, you should seek the advice of doctors specially trained in treating PD even when the illness is only suspected. Movement disorders specialists are neurologists who have completed their training in neurology and have received special advanced training in treating PD and other related diseases.
Also Check: Markers For Parkinson’s Disease
How Quickly Does Parkinsons Progress In The Elderly
Symptoms usually get worse over time, and new ones probably will pop up along the way. Parkinsons doesnt always affect how long you live. But it can change your quality of life in a major way. After about 10 years, most people will have at least one major issue, like dementia or a physical disability.
Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Mount Sinai specialists are skilled in providing the full range of therapies for Parkinsons disease. While your treatment plan may include medications, and possibly surgery, we also believe in the importance of maintaining a regular exercise regimen and eating a healthy, balanced diet.
Medications: The most common treatment for Parkinsons disease is dopamine replacement therapy, usually levodopa, which generally produces significant improvements in walking and movement, as well as reductions in stiffness and tremors. We also use other medications that target either the synthesis or breakdown of dopamine in the body.
Deep Brain Stimulation: Mount Sinais Center for Neuromodulation is recognized for its excellence in performing deep brain stimulation surgery for selected patients with Parkinsons disease. In deep brain stimulation, electrodes are placed in the areas of the brain responsible for symptoms. We connect these electrodes through a wire to a neurostimulator, also called a battery pack, which delivers electrical stimulation to the brain and can modulate the symptoms of PD. We can adjust the electrical parameters of the device to obtain very good control over symptoms. Most patients experience dramatic improvement.
Read Also: Do You Have Pain With Parkinsons Disease
Read Also: Can You Have Parkinson’s Without Tremors
Iidopamine Receptor Supersensitivity In Parkinsons Disease
Treatment of Parkinsons disease with L-DOPA remains the primary therapy. While a very effective therapy, long-term treatment invariably leads to the development of dyskinesias . We have proposed that L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the treatment of Parkinsons disease results from an aberrant switch in the linkage of the D1 receptor to signal transduction systems that activate the protein kinase, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase . As discussed, dopamine depletion of the striatum results in opposite effects on the function of D2-indirect and D1-direct pathway neurons evidenced by changes in gene expression . While, either L-DOPA or selective D2 and D1 receptor agonist treatments reverse some of the gene expression changes, the response of D1 receptor-expressing direct pathway neurons is supersensitive to these treatments, which is evident by the induction of a large number of so called immediate-early genes .
E. Cubo, CG. Goetz, in, 2014
Recommended Reading: Drugs That Cause Parkinson Like Symptoms