Characteristics Of Pd Tremors
The tremors of PD characteristically occur at rest, stop with voluntary action, and recur again after you hold your new position for a few minutes. PD tremors can affect the hands, arms, face, jaw, legs, and/or feet, and are often slightly more prominent on one side than the other.
The tremor almost always begins in the hand before affecting other parts of the body, and it usually looks like you are rolling a pill between your thumb and index finger. Thats why its called a pill-rolling tremor.
A pill-rolling tremor is the most common type of PD tremor, but shaking tremorswhich may involve the hands or other areas of the bodycan also occur.
Essential Tremor Vs Parkinson’s Tremors: A Guide To The Major Differences
When people think of Parkinson’sdisease, they may picture the shaking hands commonly associated with thecondition. Persistent shaking of hands and limbsalso known as tremorcan makeit difficult to write a grocery list, hold a cup of tea, button a shirt andapply makeup, among other routine tasks. When tremors interfere with dailylife, it can be very disruptive. While tremors are a hallmark of Parkinson’spatients, there are other diseases similar to Parkinson’s that can causetremors.
In Vivo Dopaminergic And Serotonergic Imaging
Neurochemical correlates of Parkinson’s disease tremor. Correlation between age-normalized striatal I beta-CIT binding and UPDRS motor subscores for speech, facial expression, tremor , rigidity, bradykinesia, and posture and gait . Reprinted from Pirker , with permission from John Wiley and Sons. Correlation between 11C-WAY 100635 PET in the raphe and total UPDRS tremor score . Reprinted from Doder et al. , with permission from Wolters Kluwer. Correlation between pallidal FP-CIT binding and resting tremor severity , using within-patient difference scores . This procedure controls for non-specific differences between patients. Reprinted from Helmich et al. , with permission from John Wiley and Sons. These data show that tremor severity is correlated with dopamine depletion in the pallidum , but not the striatum , and also with serotonin depletion in the raphe .
Don’t Miss: Differences Between Parkinson’s And Alzheimer’s
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. A reduction in dopamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Exactly what causes the loss of nerve cells is unclear. Most experts think that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is responsible.
The Tremors Of Parkinsons Disease
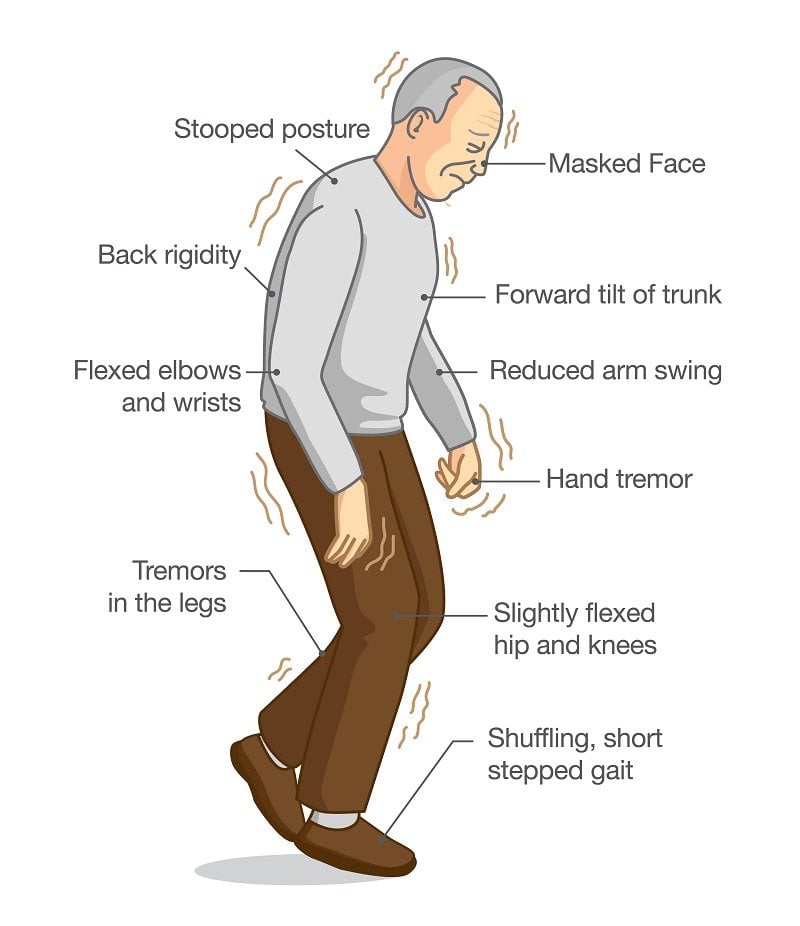
The distinction between these different tremors is not always visible to the naked eye. For example, resting tremor can re-emerge during postural holding, making it difficult to clinically distinguish it from essential tremor. This distinction can be made by focusing on the delay between adopting a posture and the emergence of tremor: in essential tremor there is no delay, while Parkinsons disease resting tremor re-emerges after a few seconds . Since the frequency of re-emergent and resting tremor can be similar, it has been hypothesized that both tremors share a similar pathophysiological mechanism. One interesting patient with Parkinsons disease had no resting tremor, but a marked 36Hz postural tremor that occurred after a delay of 24s following postural holding , thus resembling re-emergent tremor. Such observations point to heterogeneity in the circumstances under which the classical Parkinsons disease resting tremor occurs.
In the following sections, we will mainly focus on the classic resting tremor in Parkinsons disease. We will first describe the clinical and cerebral differences between patients with tremor-dominant and non-tremor Parkinsons disease. Then we will detail how these differences may inform us about the causes and consequences of Parkinsons disease resting tremor.
Also Check: Do You Get Pain With Parkinsons
Don’t Miss: Cbd And Parkinson’s Disease
Tremor Oscillations In The Model Of Basal Ganglia
Although pallidal and subthalamic cells and their computational models used here are known to possess burst properties under certain conditions, the modeling network exhibits tonic spiking activity under moderate values of the coupling strength . We consider these dynamics as the normal state, as no tremor-like oscillations are present in the modeling circuits.
As the coupling increases , STN and GPe neurons in the model network exhibit bursting activity with a frequency around 6 Hz. This kind of dynamics, with bursting in the STN neuron at the tremor range is considered here as a parkinsonian state, because it exhibits tremor-like oscillations.
To further explore the relevance of these model oscillations to the real tremor we will study the dynamics of the model in response to the modifications of the network, representing dopaminergic treatment and therapeutic lesions used to suppress tremor. There is no explicit representation of GPi in the model network, so that pallidotomy may be represented in the model by removing the projection from STN to the thalamo-cortical circuits. When this projection is removed from the model in the parkinsonian state the STN activity is almost tonic . Even though GPe is silent here , the tonic nature of STN discharge confirms that the system returns in a normal state.
Medical Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
Levodopa/carbidopa is the most effective medication in terms of improving the motor symptoms associated with Parkinsons disease. However due to the frequent, and sometimes serious side effects of this drug, neurologists prefer trying other medications first. Unfortunately, the medications available are not as good as levodopa/carbidopa in the control of the motor symptoms and also have some side effects that limit their use.
Selegiline a medication that does not have any major effects on the motor symptoms, might be the only medication with some protective effect of the nerve cells, but this is not yet well proven. The other medications are only used to treat the symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Signs Of Parkinson’s In Young Adults
What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Who Experiences Tremor
About 70-90% of people with PD experience a tremor at some point in their lives. Tremor appears to be slightly less common in younger people with PD, though it is still one of the most troublesome symptoms. People with resting tremor usually have a slower disease progression than people without tremor.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Autonomic Dysfunction
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking you questions and reviewing your medical history. Some diagnostic and lab tests are possible, but these are usually needed to rule out other conditions or certain causes. However, most lab tests aren’t necessary unless you don’t respond to treatment for Parkinson’s disease, which can indicate you have another condition.
Tremors Definition And Facts
Tremors are non-intentional rhythmic movements of a body part, which are the result of alternating or irregular synchronous contractions of muscles that have an opposite effect on a joint. For example, muscles that, when contracted, result in flexion of the wrist are stimulated synchronously with muscles that result in extension of the wrist. The result is a rhythmic flexion and extension of the wrist.
Facts
- This phenomenon can happen in any part of the body including: head, neck, face, thumb, or arm.
- It is this rhythmic quality that defines and distinguishes tremors from any other abnormal movements.
- Two tremors classes including: physiologic and pathologic
You May Like: Pfnca Wellness Programs
You May Like: Gamma Knife For Parkinson’s Disease
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better And How Long Will It Take To Recover
The time it takes to recover and see the effects of Parkinson’s disease treatments depends strongly on the type of treatments, the severity of the condition and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to offer more information about what you can expect from treatment. The information they give you can consider any unique factors that might affect what you experience.
What Are The Causes Of Parkinsons Tremor
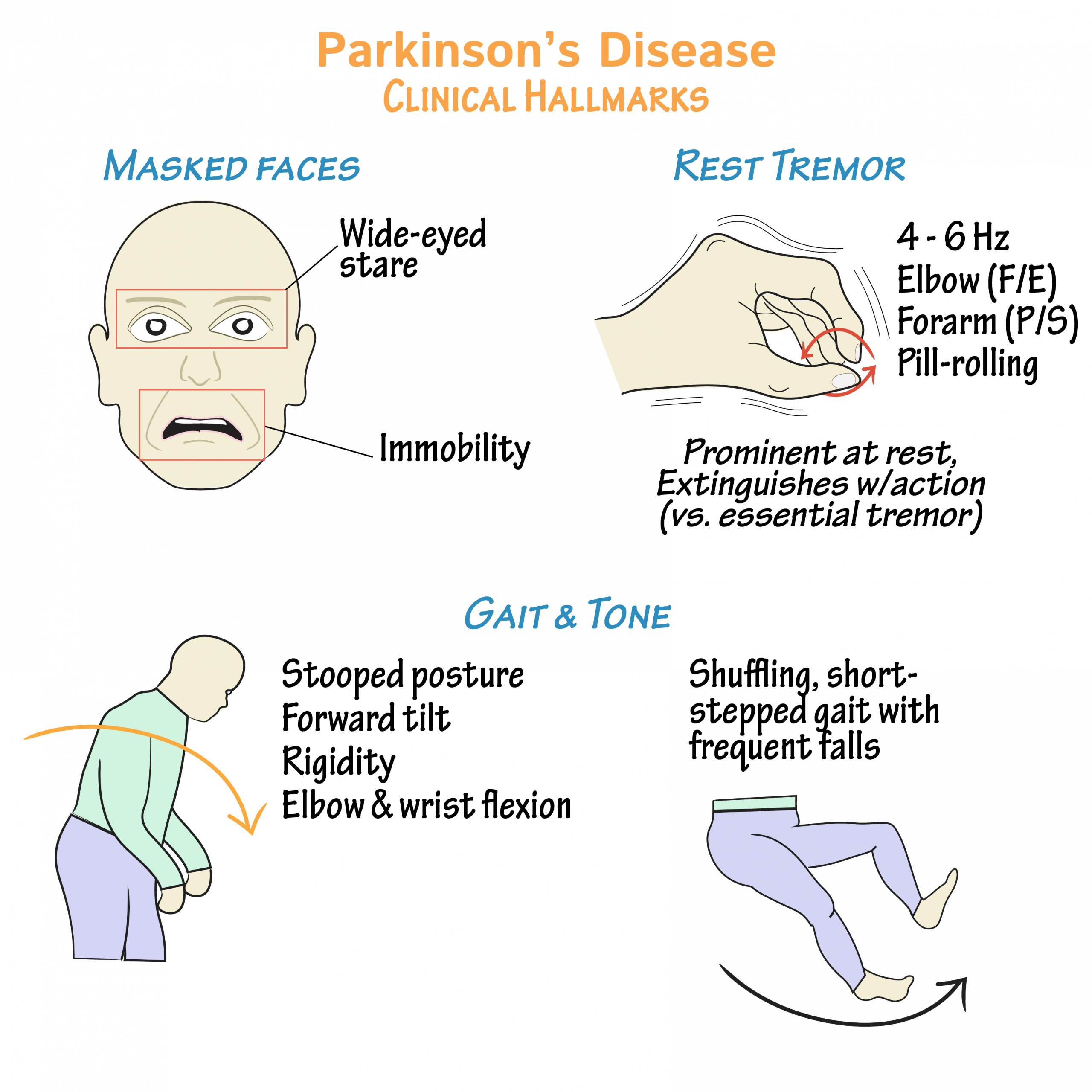
The exact cause of tremors in Parkinsons isnt fully understood. It may be tied to the degradation of cells that produce dopamine in the brain. And the causes may vary for different tremors.
Symptoms of Parkinsons can also differ among people. About 75 percent of people with Parkinsons disease report the presence of some kind of tremor, but not everyone who has the condition experiences tremors.
Rest tremors are frequently an early sign of the condition and are often used to make a Parkinsons diagnosis. But studies have shown that several types of tremors can affect people with Parkinsons.
For example, in a 2018 study involving nearly 400 people with Parkinsons:
- 20 percent of the participants had no rest tremor at the start of the study
- almost 90 percent had some sort of tremor
- about 70 percent reported rest tremors
- 50 percent reported both postural and kinetic tremors
Many people have also reported changes in the type, severity, and location of tremors throughout the course of their experience with Parkinsons disease.
Tremors in the hands are most common, but some people may also have Parkinsons tremors in the:
In the early stages of the disease, tremors usually only appear on one side of the body, but tremors can spread to both sides of the body as the condition progresses.
Other factors like stress or difficult emotional events can also affect the strength or frequency of tremors.
You May Like: Michael J Fox And Parkinson’s Disease
What Causes Tremor In Parkinsons
Imbalances in neurotransmitters cause tremors. As dopamine cells disappear because of Parkinsons, a neurotransmitter called acetylcholine becomes over-expressed, and this excess results in involuntary shaking movements. In the early stages of Parkinsons, tremor is typically seen on one side of the body, often starting in a hand however, as Parkinsons progresses, tremor may impact both sides and affect more body regions. The patterns, forms, and progression of tremors are individual to each person.
What Is The Difference Between Essential Tremor Andparkinson’s
The exact cause of essential tremor is unknown while Parkinson’sdisease is better understood.
In Parkinson’s disease, neurons located in the part of the brain thatcontrols movement become impaired or die. These neurons usually produce achemical called dopamine which enables regular body movements. When the neuronscan’t produce necessary levels of dopamine, tremors can occur, along withrigidity of limbs and decreased coordination.
Also Check: University Of Florida Parkinson’s Center
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosis is difficult at every stage of the disease, but particularly in the early stages. No single test can provide a diagnosis. A diagnosis will likely involve physical and neurological examinations, conducted over time to assess changes in reflexes, coordination, muscle strength, and mental function. Your doctor might also see how you respond to medicine.
You may need to have brain imaging tests to rule out other conditions that might be causing your symptoms. Such tests could include MRI and CT scans and possibly some other types of scans. Blood tests may also be done to exclude other illnesses.
Clinical History And Testing
Diagnostic tests can be used to establish some features of the condition and distinguish them from symptoms of other conditions. Diagnosis may include taking the persons , a physical exam, assessment of neurological function, testing to rule out conditions that may cause similar symptoms, brain imaging, to assess cognitive function,, or myocardial scintigraphy. Laboratory testing can rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as abnormal , , , or vitamin deficiencies that may cause symptoms similar to dementia.
Typical dementia screening tests used are the and the . The pattern of cognitive impairment in DLB is distinct from other dementias, such as AD the MMSE mainly tests for the memory and language impairments more commonly seen in those other dementias and may be less suited for assessing cognition in the Lewy body dementias, where testing of visuospatial and executive function is indicated. The MoCA may be better suited to assessing cognitive function in DLB, and the scale and the may help understand cognitive decline relative to fluctuations in DLB. For tests of attention, , , and can be used for simple screening, and the Revised Digit Symbol Subtest of the may show defects in attention that are characteristic of DLB. The , and are used for evaluation of executive function, and there are many other screening instruments available.
Read Also: Best Walking Cane For Parkinson’s
Neural Mechanisms Underlying Parkinsonian Resting Tremor
Parkinsonian tremor is caused mainly by central, rather than peripheral mechanisms . Evidence for this view comes from work showing that peripheral deafferentation , peripheral anaesthesia of tremulous muscles and mechanical perturbations have little effect on Parkinson’s disease tremor although peripheral reflexes may interact with central oscillations .
Neuronal correlates of Parkinson’s disease tremor. Simultaneous recording of thalamic posterior VL single-unit activity and peripheral EMG during tremor in a parkinsonian patient. These data show continuous synchronization between internal globus pallidus activity and peripheral EMG. Reprinted from Lenz et al. , with permission from the Society for Neuroscience. Simultaneous recording of internal globus pallidus multi-unit activity and peripheral EMG during tremor in a patient with Parkinson’s disease . The two plots illustrate the raw signals of two epochs of data sampled 5min apart. Note that in the left trace the peaks in the spike density function coincide with the EMG bursts, whereas in the right trace the oscillations in the spike density function occur at a lower frequency than the EMG. These data show that synchronization between neuronal activity in internal globus pallidus and peripheral EMG is transient in nature. Reprinted from Hurtado et al. . Copyright National Academy of Sciences, USA.
What Are The 5 Stages Of Parkinson Disease
The 5 Stages of Parkinsons Disease Stage One . Individuals experience mild symptoms that generally do not interfere with daily activities. Stage Two . Symptoms worsen, including tremor, rigidity and other movement symptoms on both sides of the body. Stage Three. This is considered mid-stage. Stage Four . Symptoms are severe and limiting. Stage Five.
You May Like: Ohio Parkinson Foundation Northeast Region
What Makes A Parkinsons Tremor Different
The tremor that occurs in Parkinsons disease is different from almost all other tremors because it is a resting tremor since it presents primarily at rest. It goes away with movement, but often returns when the limb, usually a hand or fingers, are held in one position. While holding a spoon or fork to the mouth, the tremor can reappear which is why those with Parkinsons are known to spill things. Parkinsons disease tremor may affect almost any part of the body, but most commonly involves the fingers, followed next most commonly by the hands, jaw, and feet.
How Is Tremor Diagnosed

Tremor is diagnosed based on a physical and neurological examination and an individuals medical history. During the physical evaluation, a doctor will assess the tremor based on:
- whether the tremor occurs when the muscles are at rest or in action
- the location of the tremor on the body
- the appearance of the tremor .
The doctor will also check other neurological findings such as impaired balance, speech abnormalities, or increased muscle stiffness. Blood or urine tests can rule out metabolic causes such as thyroid malfunction and certain medications that can cause tremor. These tests may also help to identify contributing causes such as drug interactions, chronic alcoholism, or other conditions or diseases. Diagnostic imaging may help determine if the tremor is the result of damage in the brain.
Additional tests may be administered to determine functional limitations such as difficulty with handwriting or the ability to hold a fork or cup. Individuals may be asked to perform a series of tasks or exercises such as placing a finger on the tip of their nose or drawing a spiral.
The doctor may order an electromyogram to diagnose muscle or nerve problems. This test measures involuntary muscle activity and muscle response to nerve stimulation.
You May Like: 5 Signs You Ll Get Parkinsons
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Cause Excessive Sweating
Model : The Thalamic Filter Hypothesis
This hypothesis is also based on in vitro data and proposes that parkinsonian resting tremor emerges when high-frequency oscillations in the basal ganglia are transformed into a 46Hz pattern by thalamic anterior VL neurons. The key feature of this hypothesis is that the tremor pacemaker is primarily located in the basal ganglia , with pallido-thalamic interactions determining the net frequency of the tremor. This hypothesis seems to fit with recent data in non-human primates, where it was found that 10Hz pallidal oscillations were only present in tremor-dominant vervet monkeys but not in non-tremor macaques . In contrast, pallidal oscillations at 5Hz were present in both species. However, high-frequency stimulation of the pallidum did not spread to the motor cortex . This makes it unlikely that high-frequency oscillations in the basal ganglia drive Parkinson’s disease resting tremor . Other work also questions the specific role of high-frequency basal ganglia oscillations in the generation of tremor. That is, dopaminergic treatment reduced the pathologically enhanced 835Hz rhythms in the STN of patients with Parkinson’s disease, but this improved only akinesia and rigidity, not tremor . Therefore, most authors relate the increased high-frequency oscillations in the basal ganglia of patients with Parkinson’s disease to akinesia, but not to tremor .