Key Differences Between Tardive Dyskinesia And Parkinson’s Disease
ByJason Bacot | Submitted On April 05, 2011
Tardive dyskinesia and Parkinson’s disease are both movement disorders, and both have causes related to the neurotransmitter chemical called dopamine. Dopamine takes signals from the brain to certain parts of the body, regulating their function. Both diseases can be the result of medication side effects. Though Parkinson’s disease may be congenital , only in extremely rare cases is tardive dyskinesia congenital. Tardive dyskinesia is usually caused by certain drugs.
In the human brain, dopamine works on five types of dopamine receptors. It is produced in several parts of the brain. Though dopamine is available as an intravenous medication, it only acts on the sympathetic nervous system when given as a drug, producing a higher heart rate and increased blood pressure. Dopamine given as a drug, however, cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, and so cannot affect the central nervous system.
Inside the brain, dopamine is associated with the brain’s “reward” system, causing a feeling of enjoyment and increasing motivation. It is released by rewarding experiences like sexual activity, food, drugs, and even normally neutral stimuli that become associated with activation of the brain’s reward system. Drugs like cocaine, amphetamines, and nicotine directly or indirectly cause an increase of dopamine levels in one of the brain’s reward pathways, and this may help explain the addictive nature of these drugs.
Causes And Risk Factors
Antipsychotic meds treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other brain conditions. Doctors also call them neuroleptic drugs.
They block a brain chemical called dopamine. It helps cells talk to each other and makes the muscles move smoothly. When you have too little of it, your movements can become jerky and out of control.
You can get TD if you take an antipsychotic drug. Usually you have to be on it for 3 months or more. But there have been rare cases of it after a single dose of an antipsychotic medicine. Older versions of these drugs are more likely to cause this problem than newer ones. Some studies find a similar risk from both types, though.
Antipsychotic medications that can cause tardive dyskinesia include antipsychotics like:
You’re more likely to get it if you:
- Are a woman who has gone through menopause
- Are over age 55
- Are African American or Asian American
Akinesia / Bradykinesia / Hypokinesia
Akinesia means absence of movement. Bradykinesia means slowness of movement. Hypokinesia means decreased amplitude or range of movement. These three terms are commonly grouped together and referred to as bradykinesia. Bradykinesia is a prominent feature of parkinsonism and is mild in early disease stages but becomes more severe in advanced stages of parkinsonism.
Also Check: Parkinsons Dry Mouth Treatment
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Cause Excessive Sweating
Is Tardive Dyskinesia Brain Damage
Tardive dyskinesia is a neurological, not muscular or skeletal, problem. The problem is in the brain, which makes the problem difficult to treat, and can delay diagnosis. Doctors must often rule out other potential causes, such as Parkinson’s disease, before diagnosing a patient with tardive dyskinesia.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Dyskinesia Diagnosed
Contrary to many disorders in modern medicine, where sophisticated medical tests are required, in most instances, diagnosis of this is almost purely based on the clinical history and most importantly a physical examination. It can best be made by the well-trained eye of a movement disorder specialist.
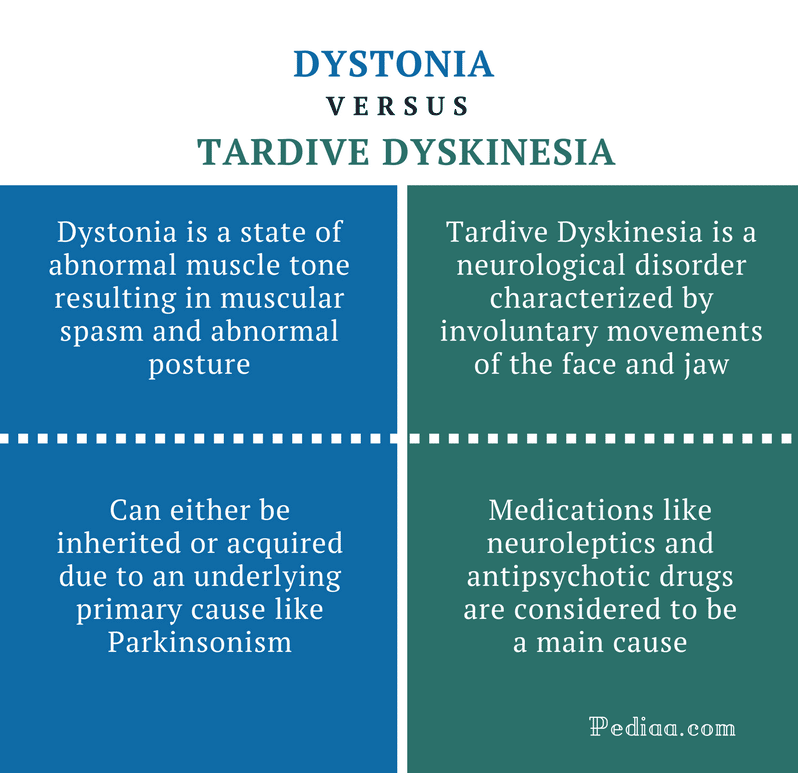
The movements can include chorea , athetosis or dystonia . They are typically random in occurrence rather than rhythmically repetitive and can range from very mild to severe. In milder cases, they can be mistaken for normal restlessness, and its not unusual for a person with Parkinsons to be totally unaware of them.
At the other end of the spectrum, Parkinsons Disease Dyskinesia can be quite severe and can significantly interfere with activities of daily living, even affecting gait and balance. The critical point is that these dyskinesias can occur when a person with Parkinsons needs more, not less, levodopa.
You May Like: How To Prevent Getting Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Dyskinesia In Parkinsons Disease
Dyskinesia is predominately a side effect of a medication called levodopa thats used to treat Parkinsons disease.
To the trained eye, dyskinesias look quite different , says Herrington. Dyskinesias are not rhythmic they have a more writhing quality.
Herrington points out that you can see an example of dyskinesia if you look at videos of Michael J. Fox. Usually, he says, when is on camera, he has some dyskinesia, or extra movements that are involuntary.
Also Check: Dbs Device For Parkinsons
Continuous Delivery Of Levodopa
Continuous intraduodenal infusion of the levodopa/carbidopa enteral gel has been used successfully in treating patients with advanced Parkinson disease and shows no increase in dyskinesia as compared to oral polypharmacy. Subcutaneous or intramuscular injections of levodopa methyl ester and intravenous infusion of levodopa have also given similar results., However, limitations of such strategies in clinical practice are obvious.
Recommended Reading: Strength Training Exercises For Parkinson’s
What Are The Odds
About half of people who take levodopa get dyskinesia. Your chance is higher if you:
- Take levodopa in high doses or for a long time
- Get Parkinsonâs when youâre younger
- Have the akinetic-rigid type of Parkinsonâs. This means your movements are stiff and slow, but you might not have tremors. If you have tremors, youâre less likely to get dyskinesia.
- Are under a lot of stress
Even if you have higher odds of getting dyskinesia, thereâs a lot you can do to stay as healthy as possible. Eat the right foods. Sleep well. Learn to manage stress. And get some exercise every day.
Show Sources
Potential Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Dystonia And Dyskinesia
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of corticostriatal synapse in healthy condition and in patients with PARKIN mutations . The figure shows the interaction of parkin with KAR and NMDAR and potential changes induced by loss of PARKIN function.
The molecular signatures that have recently emerged as key signals in LIDs are ERK1/2 phosphorylation , abnormal activation of mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase-1 , and phosphorylation of histone H3 . The final result of this chain of events is a change in the molecular make-up of MSNs due to alterations in gene expression and protein synthesis that might account for maladaptive morphological plasticity at the corticostriatal synapse . Morphological examination of MSNs in dopamine-depleted animals and in autopsy specimens from iPD patients has revealed dendrite atrophy, truncated dendrites, and decreased spine density . These functional and morphological changes in the corticostriatal synapses are believed to result in dyskinesias .
Recommended Reading: Activities For Parkinson’s Patients
How Can I Manage Dyskinesia
Medication Adjustments
If you experience dyskinesias that are bothersome and/or present most of the time, one management strategy is to reduce your dosage of levodopa or other related Parkinsons medications. However, if doing so would adversely affect the control of your chief Parkinsons symptoms, your doctor may prescribe treatment to target the dyskinesia specifically. For example, the FDA has approved an extended-release formulation of amantadine to treat levodopa-induced dyskinesia in people with Parkinsons. Another option is to consider other forms of amantadine, which are approved to treat Parkinsons and may be prescribed off-label to treat dyskinesia.
Calming Activities
Many people with Parkinsons find that exciting and emotional settings, even positive and joyful ones, increase dyskinesia. Strong feelings of stress, anger, and happiness can trigger the release of the brain chemical norepinephrine , which increases involuntary movement. Calming activities such as meditation, yoga, tai chi, massage, and breathing exercises do the opposite. They lessen your sympathetic nervous systems responses to emotional situations. Incorporating these practices into your daily life can strengthen your inner peace and manage your dyskinesia.
Exercise Adjustments
You May Like: Can You Slow Down Parkinsons
Tweak The Timing Of Your Medication
The timing of medication is also a consideration, because of wearing off phenomenon, in which some patients feel that the effects of the medication end about four hours after a dose. Your doctor may decide to split your daily medication into smaller, more frequent doses. Doing so may deliver a steadier amount of medication to the body, according to a 2016 research review in the European Medical Journal.
Your doctor may also suggest a switch to extended-release pills, which work in a similar manner. The downside to these formulations, however, is that they tend to require more of the drug to achieve the same result.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Charity Donations
Acknowledgements And Conflict Of Interest Disclosure
RM acknowledges grants from the Spanish Ministries de Economía y Competitividad and of Sanidad Política Social e Igualdad, ISCIII: BFU2010-20664, PNSD, CIBERNED ref. CB06/05/0055 and Comunidad de Madrid ref. S2011/BMD-2336, JRGM is supported by ICyTDF México MTH acknowledges the support by CIBERNED CB05/05/505, SAF2007-062262 and FIS PI10-02827. RH and KC were supported by the German Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung, Grant 01GN1006B. NS gratefully acknowledges Sardinia Regional Government for financial support . The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
All experiments were conducted in compliance with the ARRIVE guidelines.
You May Like: Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
Prevalence And Risk Of Td

The mean prevalence of TD in people treated with APs was 2025% according to meta-analyses of articles published between 1959 and 2015.27,28 A 20-year longitudinal study initiated prior to the widespread use of second-generation APs calculated a yearly cumulative incidence of TD of 4%5%.27 The frequent occurrence of TD and acute extrapyramidal symptoms, such as drug-induced parkinsonism and acute dystonia, encouraged the development of second-generation APs, which were intended to minimize the incidence of adverse neurological effects. Although acute drug-induced parkinsonism and acute dystonia are lessened, TD has not been eliminated. The annual prevalence of TD among patients receiving APs was estimated to be 7.6 to 9.7 per 1000 people according to a large retrospective observational study of electronic health records, with nearly 80% of study participants using second-generation APs.15 A direct comparison of annualized incidence between first- and second-generation APs indicates a reduced but not eliminated risk of TD with use of second-generation APs .6,29
The most important risk factors for the development of TD include older age and cumulative exposure to the DRBA. Other risk factors include the dopamine-receptor binding affinity of the DRBA in question, female sex, mood disorders, dementia, and prior drug-induced parkinsonism.4, Smoking and substance abuse may also be associated with a higher risk of developing TD.33
You May Like: Guidelines For Speech-language Therapy In Parkinson’s Disease
The Potential Role Of Parkin At The Corticostriatal Synapse
In vitro studies have revealed that parkin can localize at the pre-synapse, where it associates with the cytoplasmic surface of synaptic vesicles and binds to synaptotagmin-11, a pre-synaptic protein involved in synaptic vesicle formation, docking, and recycling . The loss of parkin function may inhibit endocytosis and the processes of vesicle replenishment and recycling, leading to as yet undefined changes in neurotransmitter release. Interestingly, the pre-synaptic functions of parkin resemble the function of synuclein, another key protein involved in PD pathogenesis and a regulator of pre-synapse size and synaptic vesicle pool organization , additionally, the roles of other PD genes such as DNAJC6, SYNJ1, SH3GL2, LRRK2, and VPS35 in the regulation of synaptic vesicle trafficking SVE are beginning to emerge .
This raises the possibility that parkin could be involved in D1 receptor hypersensitization after dopaminergic denervation, an important mechanism underlying the dyskinesia in iPD . Accordingly, a recent paper showed that parkin ubiquitinates and regulates the levels of STEP61, the striatal enriched protein tyrosine phosphatase, whereas clinically relevant parkin mutants fail to do so. Because STEP61 substrates include ERK1/2, it is conceivable that a parkin-induced increase in STEP61 might influence D1 signaling in MSNs .
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Disease Age Of Onset
Consider Deep Brain Stimulation
For severe symptoms that don’t improve with medicine, your doctor may recommend a surgical treatment, such as deep brain stimulation. This type of procedure, which involves attaching thin wires onto specific parts of the brain that control movement and delivering electronic pulses through the wires, has been shown to reduce dyskinesia by more than 80 percent, according to the 2016 review.
After the surgery, most people are able reduce their need for medications, which may be related to the improvement in dyskinesia. It’s also possible that the stimulation itself helps counteract dyskinesia.
“Deep brain surgery has the greatest promise on an individual level,” says Pantelyat. But there are also risks. “Depending on the experience of the surgeon, he says, there’s a risk of bleeding or trauma to the brain, as well as a slight hit to verbal memory for example, the ability to remember names of animals or words starting with the letter f may be impaired for a while. Usually it’s a short-term problem, but in some people it can be a long-term one.”
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Cause Weight Gain
Overview Of Tardive Dyskinesia
TD is characterized by a delayed onset of involuntary motor movements in the face, trunk, and limbs after exposure to DRBAs.4,17 Involuntary movement are classically peri-oral, including grimacing, tongue protrusion, and lip puckering, but also include neck, shoulder, and limb movements.18 In some cases, symptoms can be severe enough to interfere with breathing, speaking, eating, and ambulation.19,20
TD is often irreversible and can impose long-lasting burdens on psychosocial, physical, and economic health.4, Historically, assumptions that those afflicted are unaware of their symptoms or unconcerned with them have obscured these burdens, especially among persons with schizophrenia who can have limited insight into their physical and mental health.24,25 However, a recent study of those with a history of AP use for the treatment of schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, mood disorder, and other psychiatric disorders, found that nearly 80% of subjects with a clinician-confirmed diagnosis of possible TD reported noticing recent involuntary movements.21 Many of these individuals also felt that the uncontrollable movements impacted their ability to engage in daily activities, talk, or socialize.21
Make A Difference By Getting To Know Td
TD is classified by delayed and persistent abnormal, involuntary, and repetitivenot rhythmicmovements.6 Specifically, the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition, defines TD as Involuntary athetoid or choreiform movements generally of the tongue, lower face and jaw, and extremities developing in association with the use of neuroleptic medication for at least a few months.7 Generally, symptoms of TD persist beyond 4 to 8 weeks.7
TD is classically thought of as oro-buccal-lingual dyskinesia but is increasingly recognized as a syndrome that may include a variety of motor manifestations.9 TD is one of several movement disorders associated with exposure to antipsychotic therapy another to be discussed herein is drug-induced parkinsonism.10 While both movement disorders share exposure to DRBAs as the underlying cause, they each typically follow different time courses, have different clinical manifestations, and respond to different therapies because of their different pathophysiologies .
The Figure helps to illustrate movements that may help differentiate TD from drug-induced parkinsonism.1,5
Also Check: Infrared Helmet For Parkinson’s Disease
Talk To Your Doctor About Continuous Drug Infusion
One way to potentially avoid fluctuations in medication delivery and dopamine levels is through a continuous drug delivery system such as duodenal infusion, in which the medication travels through a tube directly into the intestine. Another option is continuous subcutaneous apomorphine infusion, in which a small device similar to an insulin pump is clipped to the clothing, according to the Parkinsons Foundation. A wire then enters the skin to deliver a steady dose of the medication apomorphine , a dopamine agonist, which may reduce the off periods, when levodopa stops working, and may minimize dyskinesia symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Support Group For Caregivers
Pharmacologic Strategies To Directly Address The Incidence Of Dyskinesias
Restoration of striatal dopaminergic stimulation is the goal in the treatment of parkinsonian motor symptoms. Levodopa provides the greatest benefit for treating parkinsonian motor dysfunction, but because its use is associated with the development of motor complications, one of the great unmet needs for the treatment of PD is a medication that will match the efficacy of levodopa but not cause motor complications. Until such a medication is available, it is useful to identify treatment strategies that can provide adequate efficacy while minimizing motor complications.
The short half-life of levodopa and the resultant pulsatile dopaminergic stimulation appear at least in part to be responsible for the development of motor complications . Therefore, CDS may delay the onset of dyskinesias in early disease and alleviate dyskinesias in advanced disease.
Don’t Miss: What Percentage Of Parkinson’s Patients Develop Dementia
Current Therapeutic Strategies For Td In Older Patients
The first step in developing the optimal treatment strategy for TD is timely diagnosis, which requires the clinician to be routinely vigilant.67 Diagnosis is based on history of exposure to DRBAs, and a minimum duration of only 1 month of AP exposure is required to diagnose TD in individuals aged 60 years, compared with 3 months in younger adults.2,7,60
An early strategy to mitigate TD symptoms involves modification of the existing AP medication regimen if clinically feasible.68 However, success with this approach is often limited.23,68,69 Two vesicular monoamine transporter 2 inhibitors, valbenazine and deutetrabenazine, have been approved by the US FDA to treat TD.68,70,71 Recent guidelines for the treatment of schizophrenia recommend VMAT2 inhibitors as first-line therapy for patients who have moderate to severe or disabling TD or for patients with mild TD on the basis of such factors as patient preference, associated impairment, or effect on psychosocial functioning.72 In two recent studies of subjects aged 55 years who had participated in clinical trials conducted by the manufacturer, Sajatovic et al demonstrated that valbenazine and deutetrabenazine (mean age: 63.1 years, range: 5581 years are well tolerated in older individuals.73,74 Of note, VMAT2 inhibition manages the symptoms of TD but does not cure them dyskinetic movements generally return when the VMAT2 inhibitor is discontinued.75