Other Concerns To Be Aware Of
There are a few other possible concerns to be aware of when having surgery. Again, not everyone will experience these issues, but it is wise to understand them and be aware so that you can plan accordingly and be prepared.
- The effect of even mild dehydration may be exacerbated in PD.
- People with PD may have swallow dysfunction. This can be exacerbated by anesthesia and make people with PD at higher risk for aspiration, defined as the tendency for food or liquid to get into the airway. Therefore, it is best to introduce soft foods slowly after surgery.
- People with PD may have significant fluctuations of blood pressure which can be magnified in the post-operative period. Episodes of low blood pressure can cause dizziness and even fainting. This problem is most prominent when changing head position that is moving from lying down, to sitting to standing. Therefore, these changes should be made very slowly.
- Urinary dysfunction is common in PD, and people with PD may be particularly prone to urinary tract infections . It is important to note that UTIs or any infection may first manifest as an unexplained worsening of PD symptoms or initiation of hallucinations.
- People with PD are particularly prone to constipation and this can be exacerbated in the post-operative period. Taking a daily medication to prevent constipation may become necessary after surgery.
Tips and takeaways
What Are The Risks
As with any surgery, there are risks associated with deep brain stimulation. If you have DBS, you have about a 3% risk of seizure, infection and confusion. Parkinson’s disease deep brain stimulation also carries a small chance of stroke. Once the neurotransmitter device is turned on, you may experience side-effects such as numbness, muscle tightness, tingling sensations balance problems or mood changes these can be managed with help from your doctor.
Your doctor will work with you to assess your Parkinsons disease and surgery eligibility and discuss the advantages and disadvantages of this treatment route. If you have any questions, do not hesitate to run them past your treatment provider or call the National Parkinsons Foundation helpline on 1-800-4PD-INFO for more information.
APA ReferenceSmith, E. . How Effective is Brain Surgery for Parkinsons Disease?, HealthyPlace. Retrieved on 2022, September 23 from https://www.healthyplace.com/parkinsons-disease/treatment/how-effective-is-brain-surgery-for-parkinsons-disease
Deep Brain Stimulation At Michigan Medicine
For carefully selected patients with Parkinsons disease, Essential Tremor, and Dystonia, deep brain stimulation offers a therapeutic surgical option that can reduce or eliminate movement-related problems and greatly improve quality of life. At the University of Michigan Health System, our STIM program brings together a team of medical experts who are leaders in their respective fields and on the cutting-edge of the latest research.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Start In The Legs
What Particular Risks Are Faced
Some of the risks relate to Parkinsons disease itself and others to the effects of omitting medication. A retrospective cohort study of 234 people with Parkinsons disease and 40979 controls undergoing major abdominal surgery found a higher incidence of aspiration pneumonia, bacterial infection, and urinary tract infection in the group with Parkinsons.2
Case reports have described other perioperative complications in people with Parkinsons disease, including postoperative respiratory failure and postextubation laryngospasm. Other reports mention exacerbation of Parkinsons symptoms during surgery and a case of severe neuroleptic malignant like syndrome precipitated by perioperative starvation for coronary artery bypass grafting.34
Access to the correct medication at the right time remains a problem for people with Parkinsons disease when they are admitted to hospital. This concern has led to a national awareness campaign from the charity Parkinsons UK.7 Lack of awareness of the importance of maintaining medication at the time of surgery places patients at increased risk.
What Happens During The Surgery
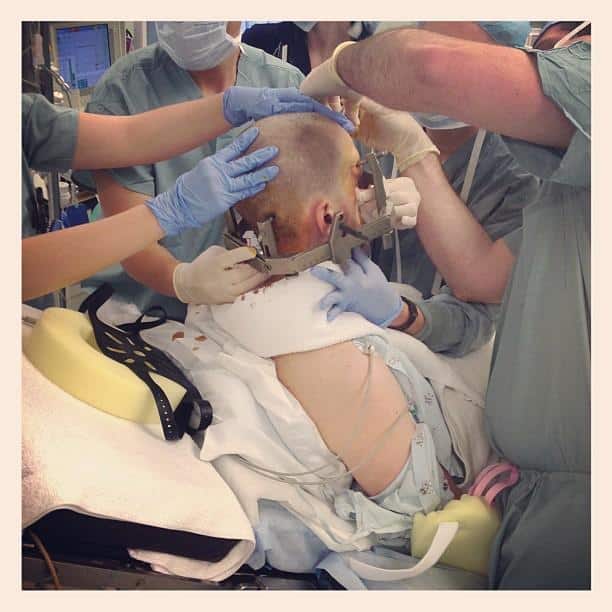
The surgery is generally carried out in two stages. First, a local anesthetic is applied to the scalp before surgery and very fine wires are inserted into the brain at the targeted region.
The second stage may be carried out under general anesthesia. A wire is implanted to connect the electrodes to a neurostimulator, which generates the electrical pulse that is delivered by the electrodes. The neurostimulator is generally implanted below the collarbone, but can also be placed in the lower chest.
Once the device has been implanted, the symptoms can be monitored and the setting of the neurostimulator can be adjusted to best suit the patients needs. Re-programming is noninvasive because it can be performed wirelessly using an antenna held near the site of the neurotransmitter.
Read Also: Natural Foods For Parkinson’s Disease
How Surgery May Help
Surgery for Parkinsons can give some people better control of their symptoms, but it is not a cure, so the condition will continue to progress. Most people will still need to take some medication.
Not everyone will be suitable for surgery, so you may want to discuss this option with your specialist. However, all surgery – including Deep Brain Stimulation – carries risk.
You may be referred to a consultant neurologist or surgeon at a hospital that performs surgery for Parkinsons. If you are a suitable candidate for surgery there is a lengthy and comprehensive assessment to help ensure the best possible outcome.
Do I Need General Anesthesia
You may want to ask your doctor if you need general anesthesia for your surgery. People with PD may have more problems with general anesthesia than others. This may be due to a variety of reasons, including:2,3
- The need to fast for hours before surgery. This usually includes not taking your normal PD drugs, which can cause increased PD symptoms.
- Increased sleepiness after surgery. Sometimes the effects of general anesthesia last for longer than they should.
- Increased confusion after surgery. Known as post-surgical delirium, this is more common in those with PD. This may complicated or prolong your recovery, so avoiding this complication is a goal.
- Problems with swallowing after surgery. Some people with PD have problems with swallowing, and general anesthesia may make this worse. Your nurse will introduce soft foods first while recovering from your procedure to avoid complications.
This does not mean you cannot have general anesthesia if you need it. Talk to your doctor about the best option for you. Not everyone with PD will have complications related to drugs used in surgery.2,3
You May Like: What Classes Of Drugs Are Used To Treat Parkinson’s Disease
How Does Dbs Work
In DBS surgery, electrodes are inserted into a targeted area of the brain, using MRI and, at times, recordings of brain cell activity during the procedure. A second procedure is performed to implant an impulse generator battery , which is similar to a heart pacemaker and approximately the size of a stopwatch.
The IPG is placed under the collarbone or in the abdomen and delivers an electrical stimulation to targeted areas in the brain that control movement. Those who undergo DBS surgery are given a controller to turn the device on or off and review basic parameters such as battery life.
Going Into Hospital For Surgery
If you are having surgery for something not connected to your Parkinsons, make sure the healthcare professionals involved know about your condition.
This will mean that anything about your Parkinsons that could create problems, such dystonia or a tremor, can be taken into account so you can still be treated properly.
If you need to have an emergency operation, it is important that the healthcare team looking after you know you have Parkinsons as soon as possible.
You will usually meet your anaesthetist on the ward before your surgery. It is very important that your anaesthetist knows you have Parkinsons and what medication you take for the condition.
Some anaesthetics may make Parkinsons symptoms worse or interfere with Parkinsons medication. The anaesthetist can plan your care appropriately around this.
When you meet the anaesthetist they will go through your answers to the pre-admission questions. They will also discuss your Parkinsons symptoms and how they may affect you during surgery, as well as explaining any risks or side effects of the drugs you might have.
Can I keep taking my Parkinson’s medication right up until the time of surgery?
Its important that you can keep taking your Parkinsons medication as close to your surgery as possible, and as soon as possible after the operation.
Organising your medication regime is also easier if you know what time your surgery will be in advance.
Levodopa
Apomorphine
Dopamine agonists
Low blood pressure
You May Like: Can Alcohol Cause Parkinson’s
How Should I Care For The Surgical Area Once I Am Home
- Your stitches or staples will be removed 10 to 14 days after surgery.
- Each of the four pin sites should be kept covered with band aids until they are dry. You will be able to wash your head with a damp cloth, avoiding the surgical area.
- You may only shampoo your hair the day after your stitches or staples are removed, but only very gently.
- You should not scratch or irritate the wound areas.
Purpose Of Brain Surgery For Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease surgery is used to treat motor effects of Parkinsons disease, such as tremor, but it does not help non-motor effects, such as reduced facial expression and dry skin.
Parkinsons disease can range from mild to severe, and it can be very disabling when the disease is severe. When high doses of medication are needed to control the symptoms, the medication can cause side effects such as dyskinesia , hallucinations, or both.
You might benefit from surgery if your symptoms do not improve adequately with medication or if you experience severe medication side effects.
You May Like: Traveling With Parkinson’s Disease
Inductionregional Versus General Anaesthesia
Several factors affect the choice of anaesthesia. Regional anaesthesia allows monitoring of Parkinsons symptoms and should be considered in people who require very frequent dopaminergic medication. In exceptional circumstances oral medication can be administered intraoperatively, although a case of exacerbation of parkinsonism despite using this approach has been reported.3
Some motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, such as severe dyskinesia, might make a general anaesthetic preferable. The anaesthetist should be aware of the effects of routinely used anaesthetic drugs on parkinsonism. Propofol is commonly used to induce anaesthesia and two case studies have shown that it can exacerbate dyskinesia.11 However, propofol may temporarily suppress tremor associated with Parkinsons disease12so it continues to be the first choice of most anaesthetists. Its antiemetic effect may also be beneficial.
The need for intubation should be assessed on an individual basis. Severe Parkinsons disease is associated with excessive salivation that is often due to swallowing dysfunction. If dysphagia is suspected, intubation is the safer choice. In these patients, anticholinergics can increase the viscosity of saliva, further impairing swallowing, and should be used with caution.13
Everyday Activities And Travel
Most everyday activities are safe. However, welding is not safe nor is any activity where you are exposed to strong electrical currents. There are some sports that could damage the system.
If youve had deep brain stimulation you can travel by plane, but you should inform airport security that you have a pacemaker-like device installed and carry a card that explains that you have had this type of surgery.
Exposure to electromagnetic radiation such as those at security screening points may accidently affect the stimulator and you will need to be manually checked.
You should also carry the hand-held programmer when travelling. This is in case the stimulator is accidentally switched off.
Read Also: Items To Help Parkinson’s Patients
What Is Brain Surgery For Parkinsons Disease
Brain surgery for Parkinsons disease is done to balance the activity in certain areas of the brain that control physical movement. The surgery can involve placement of a stimulator device or creation of a surgical lesion in the brain.
The areas of the brain that are affected by Parkinsons disease are very small, and they are located deep within the brain. These procedures are done with precision and often with imaging guidance so your surgeon can see the structure of your brain with real-time pictures during the surgery.
Parkinsons Disease Brain Surgery: What To Expect
Parkinsons disease brain surgery can either be done under general anesthetic or with you awake and alert with a local anesthetic to numb your skull. Either way, you shouldn’t feel anything during the procedure because there are no pain receptors in the brain. The surgery is performed in two parts: one for the insertion of electrodes into your brain, and one for the placement of the neurotransmitter in your chest.
After surgery, your device will be turned on at the doctors office and you will be given a remote control to take home with you. From then onwards, your doctor will work with you to help you manage your symptoms. You may also decide to turn the device off at certain times. It could take a few months to find the right setting for you.
Read Also: Parkinson’s End Of Life Signs
Potential Complications Of Missing Medication
The consequences of missing Parkinsons medication can vary enormously. Some people can tolerate a missed tablet without experiencing any major effects. Others become immobile. However, in some situations, missing dopaminergic medication can precipitate a condition known as neuroleptic malignant like syndrome, associated with fever, confusion, raised concentrations of muscle enzyme, and even death. This syndrome is most common in people with more severe Parkinsons symptoms and those on the largest doses of levodopa.6
What Is The Prognosis
Although most people still need to take medication after undergoing DBS, many people experience considerable reduction of their PD symptoms and can greatly reduce their medications. The amount of reduction varies from person to person. The reduction in dose of medication can lead to decreased risk of side effects such as dyskinesia.
There is a 1 to 3% chance of infection, stroke, bleeding in the brain, or other complications associated with anesthesia. It is best to discuss associated risks with your neurologist and neurosurgeon, as diabetes and heart and lung conditions all may influence these risks and the decision to pursue surgery.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Cause Pain In Legs
Advice From A Specialist
Even with an agreed advance plan or a written protocol, patients who do not rapidly regain the ability to take their usual Parkinsons medication should be seen by a Parkinsons disease specialist nurse or movement disorder consultant at the earliest opportunity. This allows the treatment plan to be adjusted according to the initial response.
Review of Parkinsons patients by a neurologist following knee replacement has been shown to reduce length of stay.19 Further research is required to establish whether this benefit can be transferred to Parkinsons patients undergoing different types of surgery.
Being Prepared & Anticipating Problems
Because of the concerns that we will discuss below, it is prudent to have your neurologist speak to your surgeon and anesthesiologist prior to the surgery so he/she can discuss the potential issues that may arise during and after the surgery. It is also very useful to have your neurologist write a letter with all the necessary information so it can be dispersed to other members of the medical team who will be responsible for your day-to-day care after the surgery.
Depending on the type of surgery, there may be more than one option for anesthesia. General anesthesia may not be the only option, and a more localized form of anesthesia may be possible. Local anesthesia typically causes fewer side effects. Discuss what anesthesia options you have with the surgeon and anesthesiologist prior to the surgery.
In addition, if the surgery requires you to stay in the hospital overnight, consider having a family member or friend stay with you. This person can provide a calming presence, helping to prevent agitation or distress. He or she can keep an eye on whether you are taking your own medications correctly and what additional medications you are bring given.
Don’t Miss: Mucuna Pruriens Dosage For Parkinson’s
Resources For More Information
- Surgical option a potential life-changer for patients with OCD: Read and watch Erins story as she, a lively 21-year-old woman, fought her battle with OCD. This article explores how deep brain stimulation gave Erin her life back. The procedure was the first of its kind performed at Albany Medical Center the only facility offering this treatment between New York and Boston. In Erins own words, Now, I can be who I really am and tell people my story and hopefully inspire people and help people along the way.
- Karen and Jims Story: A Shared Journey of Life, Love and DBS: Read about Karen and Jim. They were each diagnosed with Parkinsons before they met. Follow them on their journey as they fall in love after meeting each other from an online support group. See how they embraced each other and DBS.
- Kays Story A Parkinsons Disease Patient: Read about Kay, a 68-year-old woman suffering from Parkinsons disease. The article and video explore how DBS helped her regain her life. In Kays own words, Its like I had been turned on again. It was like a miracle.
Dont Miss: How To Tell Difference Between Parkinsons And Essential Tremor
What Is Deep Brain Stimulation

Deep brain stimulation is a surgical procedure that involves implanting electrodes in the brain, which deliver electrical impulses that block or change the abnormal activity that cause symptoms.
The deep brain stimulation system consists of four parts:
- Leads that end in electrodes that are implanted in the brain
- A small pacemaker-like device, called a pulse generator, that creates the electrical pulses
- Extension leads that carry electrical pulses from the device and are attached to the leads implanted in the brain
- Hand-held programmer device that adjusts the devices signals and can turn the device off and on.
In deep brain stimulation, electrodes are placed in the targeted areas of the brain. The electrodes are connected by wires to a type of pacemaker device placed under the skin of the chest below the collarbone.
Once activated, the pulse generator sends continuous electrical pulses to the target areas in the brain, modifying the brain circuits in that area of the brain. The deep brain stimulation system operates much the same way as a pacemaker for the heart. In fact, deep brain stimulation is referred to as the pacemaker for the brain.
Also Check: How Does One Get Parkinson’s Disease