Apda Funds $235m In New Cutting
The American Parkinson Disease Association will fund a host of Parkinsons disease research projects for the coming year, including one that will examine the molecular underpinnings of anxiety and another that proposes a treatment for freezing of gait, for a total funding package of $2.35 million, a 25%
Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinsons by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinsons is levodopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brains dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapy such as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessness and reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People living with Parkinsons disease should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, like being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
The doctor may prescribe other medicines to treat Parkinsons symptoms, including:
What Causes The Disease
The precise cause of PD is unknown, although some cases of PD are hereditary and can be traced to specific genetic mutations. Most cases are sporadicthat is, the disease does not typically run in families. It is thought that PD likely results from a combination of genetics and exposure to one or more unknown environmental factors that trigger the disease.
The protein alpha-synuclein. The affected brain cells of people with PD contain Lewy bodiesdeposits of the protein alpha-synuclein. Researchers do not yet know why Lewy bodies form or what role they play in the disease. Some research suggests that the cells protein disposal system may fail in people with PD, causing proteins to build up to harmful levels and trigger cell death. Additional studies have found evidence that clumps of protein that develop inside brain cells of people with PD may contribute to the death of neurons.
Genetics. Several genetic mutations are associated with PD, including the alpha-synuclein gene, and many more genes have been tentatively linked to the disorder. The same genes and proteins that are altered in inherited cases may also be altered in sporadic cases by environmental toxins or other factors.
Environment. Exposure to certain toxins has caused parkinsonian symptoms in rare circumstances . Other still-unidentified environmental factors may also cause PD in genetically susceptible individuals.
What Diseases And Conditions Resemble Parkinsons Disease
PD is the most common form of parkinsonism, in which disorders of other causes produce features and symptoms that closely resemble Parkinsons disease. Many disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of PD, including:
Several diseases, including MSA, CBD, and PSP, are sometimes referred to as Parkinsons-plus diseases because they have the symptoms of PD plus additional features.
In very rare cases, parkinsonian symptoms may appear in people before the age of 20. This condition is called juvenile parkinsonism. It often begins with dystonia and bradykinesia, and the symptoms often improve with levodopa medication.
Don’t Miss: Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Turning Off The Switch
Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease caused by the death of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. More than 10 million people worldwide are living with Parkinsons disease, including more than 80,000 Australians.
Currently there are no approved drugs that can slow or stop the progression of Parkinsons disease, with available therapies only able to treat and alleviate symptoms.
PhD student and first author Zhong Yan Gan said the research provided an unprecedented view of a protein called PINK1, known to play a critical role in early onset Parkinsons disease.
Many papers from laboratories around the world including ours have captured snapshots of the PINK1 protein. However, the differences in these snapshots has in some ways fuelled confusion about the protein and its structure, Mr Gan said.
What we have been able to do is to take a series of snapshots of the protein ourselves and stitch them together to make a live action movie that reveals the entire activation process of PINK1. We were then able to reconcile why all these previous structural images were different they were snapshots taken at different moments in time as this protein was activated to perform its function in the cell.
Were Funding Trailblazing Science
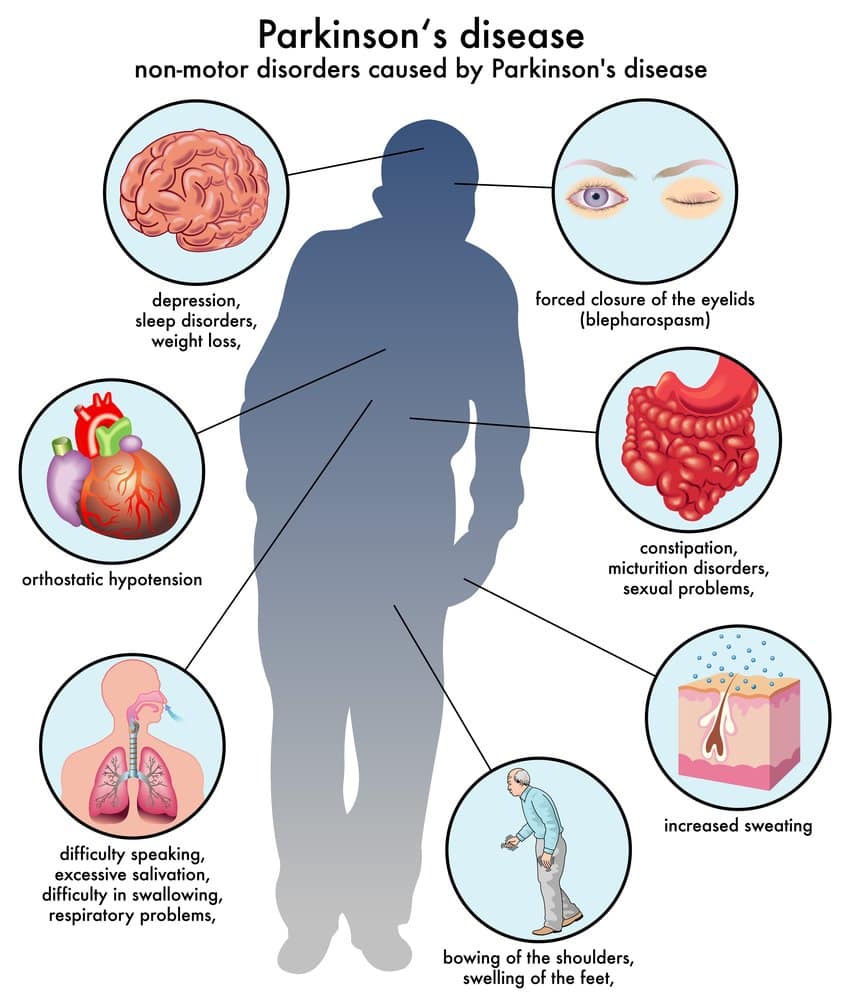
When it comes to finding a cure, impatience is a virtue. Weve invested in groundbreaking projects, generating major discoveries. Projects like a 10-year study to reveal the long-term benefits of DBS . Projects like our GDNF clinical trial, which developed robot surgery to deliver a potential treatment to brain cells buried deep inside the brain.
Unlocking new treatments also means delving into the causes of Parkinsons. Thats why we fund the Parkinson’s UK Brain Bank the world’s only brain bank dedicated to Parkinson’s research.
You May Like: All The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Updates On Currently Approved Pd Treatments
Table 1 Approved dopaminergic drugs
Later, DA receptor agonists, such as those shown in Table , were developed either as monotherapies or combination therapies with L-DOPA for the treatment of PD. Five types of DA receptors, D1D5, exist in the brain. The D1 and D5 receptors are grouped together as D1-like receptors based on their stimulatory effects on adenylyl cyclase , and the D2, D3, and D4 receptors are classified as D2-like receptors due to their inhibition of cAMP activity. Many synthetic DA agonists, including pramipexole and apomorphine, activate D2-like receptors, and have a lower incidence of motor fluctuations and dyskinesia .
Herbal Formulation With Anti
Ban Xia Hou Po Tang can significantly improve the swallowing reflex in Parkinsons disease patients . Bushen Yanggan Xifeng Decoction has effects on neurotransmitters and DA receptors in the striatum of PD model mice . Chuanxiong Chatiao pelvis has neuroprotective effects against MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in mice models of Parkinsons disease. Huanglian Jiedu Decoction has protective effects on the injury of PC12 cells induced by MPP+ . Kami-shojo-san has effects against tremors due to antipsychotic-induced PD . Liuwei Dihuang Pill can protect dopaminergic neurons in MPTP-induced PD mice . San-Huang-Xie-Xin-Tang has neuroprotective effects in the MPP+/MPTP models of PD in vitro and in vivo . Tianma Gauteng Yin has protective effects against apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons and oxidation stress response in Parkinsons disease model rats . Yeoldahansotang has neuroprotective effects on the PD model via autophagy enhancement . Zhen-wu-tang has ameliorative and neuroprotective effects on rats induced by MPTP through keeping DA stable and vesicular monoamine transporter 2/DA transporter mRNA in balance . Zeichen Soup has the effect of promoting neural stem cell differentiation in PD model rats .
Dont Miss: Young Onset Parkinsons Symptoms
Don’t Miss: Is Essential Tremor Related To Parkinson’s Disease
Who Gets Parkinsons Disease
Risk factors for PD include:
- Age. The average age of onset is about 70 years, and the incidence rises significantly with advancing age. However, a small percent of people with PD have early-onset disease that begins before the age of 50.
- Sex. PD affects more men than women.
- Heredity. People with one or more close relatives who have PD have an increased risk of developing the disease themselves. An estimated 15 to 25 percent of people with PD have a known relative with the disease. Some cases of the disease can be traced to specific genetic mutations.
- Exposure to pesticides. Studies show an increased risk of PD in people who live in rural areas with increased pesticide use.
Parkinsons Protein Blueprint Could Help Fast
Researchers have solved a decade-long mystery about a critical protein linked to Parkinsons disease that could help to fast-track treatments for the incurable disease.
The research, published in Nature, has for the first time produced a live action view of the protein, called PINK1, in exquisite molecular detail.
The discovery explains how the protein is activated in the cell, where it is responsible for initiating the removal and replacement of damaged mitochondria. When the protein is not working correctly, it can starve brain cells of energy, causing them to malfunction and in the long term die, as happens to dopamine-producing cells in Parkinsons disease.
The discovery is the culmination of a project spanning eight years and provides the first detailed blueprint for the discovery and development of therapeutic agents that could help to slow or even stop the progression of Parkinsons disease.
Led by PhD student Mr Zhong Yan Gan and Professor David Komander, the multidisciplinary team at WEHI used innovative cryo-electron microscopy facilities and research to make the discovery.
Read Also: Foods To Avoid With Parkinson’s Disease
Icipate In A Research Study
Many research studies into Parkinsons disease need human volunteers to answer specific health questions. Your participation in these research studies allows you to access new treatments for Parkinsons disease before they are widely available and contributes to medical research.
You May Like: Parkinsons Bike Therapy
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Probiotics may also be beneficial for a condition known as small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in which there is excessive bacteria in the small intestine SIBO can cause symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, chronic diarrhea, and weight loss. Research studies have shown that this condition is more common in people with PD than in the general population, and has also been linked to worsened motor fluctuations in PD. Using probiotics to help treat SIBO may work by re-establishing a more normal bacterial environment. More research is necessary to better understand SIBO in patients with PD and to ascertain if probiotics are helpful for SIBO, specifically in the context of PD.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Electrical Stimulation
Apda Center For Advanced Research
Boston University School of Medicine is home to an Advanced Center for Parkinsons Research supported by the American Parkinson Disease Association. The Center is directed by Marie Hélène Saint-Hilaire, MD, FRCPC, with a comprehensive team of experts.
APDA Centers for Advanced Research must meet the highest academic standards and be distinguished leaders in the field of PD research. There are eight such centers across the country.
The funding of this Center supports a large research program, which includes: Biomarker studies, studies of non-motor symptoms, studies of self-management strategies, an active clinical trials program, 3500 patient visits per year, a Deep Brain Stimulation program, and a fellowship program in Movement Disorders.
Parkinsons disease affects more than 1 million people in the United States annually, with at least 60,000 new cases diagnosed each year. The chronic and progressive neurological condition is the second most common neurodegenerative aging disorder, after Alzheimers disease.
For more information contact:
Medical Director: Marie-Hélène Saint Hilaire, MD, FRCPPhone: 800-651-8466
A New Era For Parkinsons Disease Treatment
A non-invasive ultrasound treatment for Parkinsons disease that was tested in a pivotal trial led by University of Maryland School of Medicine researchers is now broadly available at the University of Maryland Medical Center .
Howard Eisenberg, MD, Dheeraj Gandhi, MD, MBBS, Paul Fishman, MD, PhD, Bert W. OMalley, MD.
The device, called Exablate Neuro, was approved in November by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat advanced Parkinsons disease on one side of the brain. The approval was based on findings from the UMSOM clinical trial and effectively expands access to focused ultrasound beyond clinical trial participation.
Rapid Reversal of Symptoms
Focused ultrasound is an incisionless procedure, performed without the need for anesthesia or an in-patient stay in the hospital. Patients, who are fully alert, lie in a magnetic resonance imaging scanner, wearing a transducer helmet. Ultrasonic energy is targeted through the skull to the globus pallidus, a structure deep in the brain that helps control regular voluntary movement. MRI images provide doctors with a real-time temperature map of the area being treated. During the procedure, the patient is awake and providing feedback, which allows doctors to monitor the immediate effects of the tissue ablation and make adjustments as needed.
Patient: Focused Ultrasound Changed My Life
A New Era for Parkinsons Disease Treatment
You May Like: Is Parkinsons Disease An Autoimmune Disease
Don’t Miss: Why Do Parkinson’s Patients Have Trouble Sleeping
Parkinsons Disease Diagnosis And Prognosis
A Parkinsons disease diagnosis cannot be determined by a single test but is rather assigned based on a patients medical history, symptoms, and a series of neurological and physical exams. Each patients Parkinsons disease prognosis is different, as the disease is unique to each person. While all patients will experience some degree of motor dysfunction, the severity and course that the disease takes may differ from person to person.
Also Check: Art Therapy Parkinsons Disease
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease is movement disorder of the nervous system that worsens over time. As nerve cells in parts of the brain weaken or are damaged or die, people may begin to notice problems with movement, tremor, stiffness in the limbs or the trunk of the body, or impaired balance. As these symptoms become more obvious, people may have difficulty walking, talking, or completing other simple tasks. Not everyone with one or more of these symptoms has PD, as the symptoms appear in other diseases as well.
No cure for PD exists today, but research is ongoing and medications or surgery can often provide substantial improvement with motor symptoms.
Don’t Miss: Environmental Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
A Clinical Study Of Nly01 In Patients With Early Parkinsons Disease
open to eligible people ages 30-80
This is a phase 2 study designed to assess the safety, tolerability and efficacy of NLY01 in subjects with early untreated Parkinsons disease . Evidence suggests NLY01, a pegylated form of exenatide, may be beneficial in PD and is being developed as a potential treatment for neurodegenerative disorders. For more information, please visit: PrismPDstudy.com
San Francisco, California and other locations
What Will A Cure For Parkinsons Look Like
Parkinsons varies so much from person to person. There are over 40 symptoms of Parkinsons. Tremor. Pain. Hallucinations. Everyones experience is different.
Because of this, there may not be a single cure.
Instead we may need a range of different therapies to meet the needs of the individual and their specific form of the condition.
This mix may include treatments, therapies and strategies that can:
- slow or stop the progression of the condition
- replace or repair lost or damaged brain cells
- control and manage particular symptoms
- diagnose Parkinsons at the earliest possible stage.
And this could involve medical treatments, such as drugs and surgical approaches, as well as lifestyle changes, for example to diet and exercise.
Dont Miss: Drug Holiday For Parkinson Disease
Recommended Reading: How Do You Treat Parkinson’s Disease Naturally
Strategies For The Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease: Beyond Dopamine
- 1Laboratorio de Neurobiología, Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad San Sebastián, Concepción, Chile
- 2Department of Biological Sciences, University of Limerick, Limerick, Ireland
- 3Health Research Institute, University of Limerick, Limerick, Ireland
- 4Department of Psychology and Neuroscience, Center for Neuroscience, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, United States
- 5Research & Development Service, Bay Pines VA Healthcare System, Bay Pines, FL, United States
Parkinsons disease is the second-leading cause of dementia and is characterized by a progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra alongside the presence of intraneuronal -synuclein-positive inclusions. Therapies to date have been directed to the restoration of the dopaminergic system, and the prevention of dopaminergic neuronal cell death in the midbrain. This review discusses the physiological mechanisms involved in PD as well as new and prospective therapies for the disease. The current data suggest that prevention or early treatment of PD may be the most effective therapeutic strategy. New advances in the understanding of the underlying mechanisms of PD predict the development of more personalized and integral therapies in the years to come. Thus, the development of more reliable biomarkers at asymptomatic stages of the disease, and the use of genetic profiling of patients will surely permit a more effective treatment of PD.
Recent Advances In The Preclinical Study Of Dopaminergic Drugs For Pd
Based on the multiple pathogenesis of PD, multifunctional agents may be good alternative options for PD treatment . Unfortunately, no such agents are available in the clinic. Table summarizes the chemical structures and binding or agonistic activity of preclinical dopaminergics.
Table 4 Polypharmacological dopaminergics for preclinical PD treatment
You May Like: Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative
Latest Research On Covid
UPDATE: This post has been updated with the latest information available.We will continue to keep this post up-to-date as new information develops.
As citizens of the world, we all continue to grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic. And as members of the Parkinsons disease community, we continue to have specific concerns about COVID-19 and how it relates to PD. There is so much information out there, some of it misinformation, so it is important to rely on credible, trusted sources. In this post, I will cover the latest information that investigates the relationship between PD and COVID-19.
Nerve Damage Seen In Skin Can Predict Parkinsons Progression

In Parkinsons patients, greater nerve damage in the skin around the ankle is significantly associated with subsequent progression of motor symptoms, while the presence of such damage in neck skin is linked to progressive cognitive decline, a study shows. Notably, this nerve damage progression was not related to increased
You May Like: Does Vitamin B12 Help Parkinsons
You May Like: Power Over Parkinson’s Monterey
What We Know So Far
- Weve uncovered clues to the causes and genetic involvement in Parkinsons.
- Were figuring out the chain of events that leads to the damage and loss of brain cells.
- Were working to advance new treatments and therapies.
- Were exploring repurposing drugs to help manage some of the more distressing symptoms, like hallucinations and falls.
- And we know that, although people with Parkinsons share symptoms, each persons experience of the condition and response to treatment is different.
Now, the science is ready for us to develop the new treatments and cure that people with Parkinsons so desperately need.
Research takes time but if you have Parkinsons, you need better treatments now. Thats why weve launched the Parkinsons Virtual Biotech to speed up the most promising potential treatments. The more we can invest, the sooner well get there.
You May Like: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa