Differentiating Multiple Sclerosis Symptoms With Parkinsons Disease
Signs and symptoms of multiple sclerosis include numbness or weakness in one or more limbs, partial or complete vision loss, prolonged double vision, tingling or pain, electric-shock sensations, tremors and lack of coordination, fatigue, dizziness, slurred speech, and problems with bowel and bladder function.
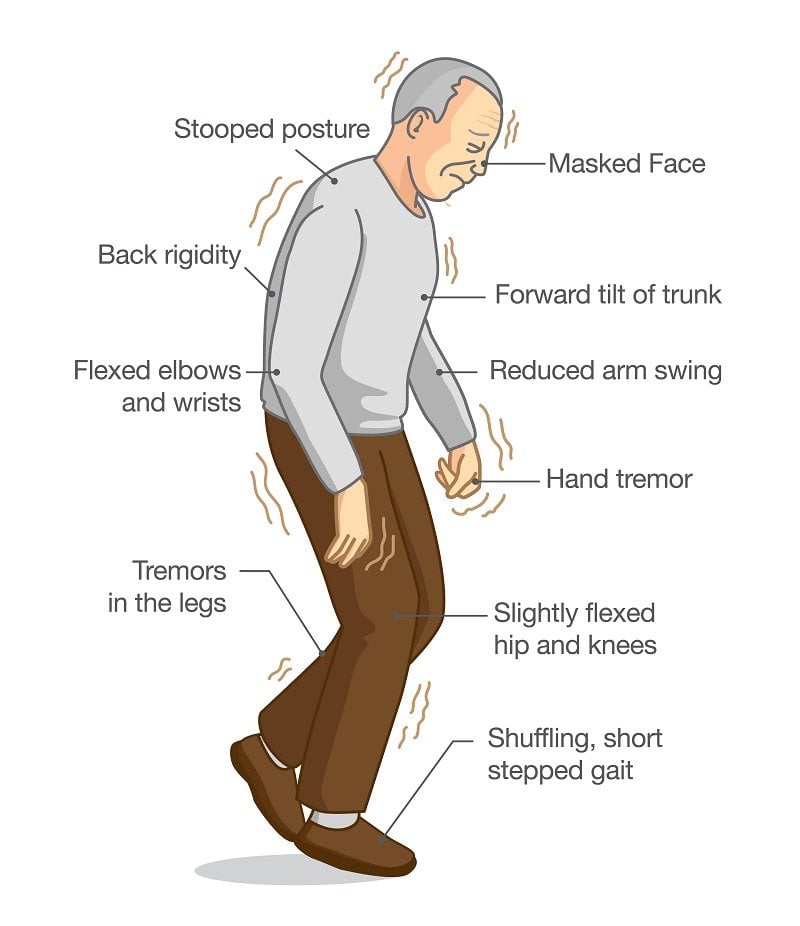
Parkinsons disease symptoms typically begin with tremors followed by muscle stiffness, difficulty standing or walking, changes in speech, slow movements, impaired posture and balance, loss of automatic movements, and writing changes.
As you can see, Parkinsons disease and multiple sclerosis do have some symptoms in common, which can make early diagnosis difficult.
Read Also: Parkinsons Information For Patients
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease causes physical symptoms at first. Problems with cognitive function, including forgetfulness and trouble with concentration, may arise later. As the disease gets worse with time, many people develop dementia. This can cause profound memory loss and makes it hard to maintain relationships.
Parkinson disease dementia can cause problems with:
- Speaking and communicating with others
- Problem solving
- Paying attention
If you have Parkinson disease and dementia, in time, you likely won’t be able to live by yourself. Dementia affects your ability to care of yourself, even if you can still physically do daily tasks.
Experts don’t understand how or why dementia often occurs with Parkinson disease. Its clear, though, that dementia and problems with cognitive function are linked to changes in the brain that cause problems with movement. As with Parkinson disease, dementia occurs when nerve cells degenerate, leading to chemical changes in the brain. Parkinson disease dementia may be treated with medicines also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, another type of dementia.
Medications And Parkinsons Symptoms
Taking certain medicationsspecifically ones that block the action of dopaminecould cause Parkinsons disease symptoms. Its a condition called drug-induced parkinsonism, and while it isnt Parkinsons disease itself, it can look and feel a lot like it.
Here are some of the drugs can cause Parkinsons disease symptoms:
- Anti-nausea medications
- Drugs that treat hyperkinetic movement disorders
Keep in mind that even though these medications could cause symptoms similar to Parkinsons, they dont cause the disease itself. And most of the time, the symptoms go away within hours or days once you stop taking that drug, per the Parkinsons Disease Society.
In some cases, the Parkinsons symptoms dont go away after a person stops taking the medication that led to them, and theyre eventually diagnosed with Parkinsons disease.
Researchers dont think that the medication was the cause of Parkinsons in those cases, but that those individuals dopamine levels were already depleted, and the side effects of the drugs revealed their underlying Parkinsons disease. Put another way, the medication was the straw that broke the camels back, according to the American Parkinson Disease Association.
Research on what causes Parkinsons disease continues to grow. If you experience symptoms of Parkinsons, such as a tremor, slowed movement, balance problems, or changes in your speech or writing, connect with a doctor to diagnose the condition.
Don’t Miss: Hallucinations And Delusions In Parkinson’s Disease
Genetic And Environmental Interactions
Although several genetic mutations have been identified to be associated with a higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease most people do not have these genetic variations.
On the other hand, even though pesticides and head traumas are associated with PD, most people do not have any obvious exposure to these environmental factors.
Parkinson’s is caused by a combination of genes, environmental and lifestyle influences. The interaction of all three components determines if someone will develop Parkinson’s. Parkinsons-specific research is critical to better understanding how these components interact to cause PD and how to prevent it.
Page reviewed by Dr. Lauren Fanty, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence.
Types Of Parkinsons Pain

Most of the time, discomfort in muscles and joints is secondary to the motor features of Parkinsons lack of spontaneous movement, rigidity, and abnormalities of posture what is known as musculoskeletal pain. The most commonly painful sites are the back, legs, and shoulders and it is usually more predominant on the side more affected by parkinsonism.
But there are many other categories of pain associated with Parkinsons disease. Radicular or neuropathic pain is experienced as a sharp pain that can start in the neck or lower back with radiation to arm or leg respectively and is often associated with numbness or tingling, or a sensation of coolness in the affected limb. It is usually secondary to a pinched nerve due to something like a slipped disc.
Dystonia related pain occurs as its name suggests, at times of dystonia most often experienced in the foot, neck or face and arm at different points in the dosing schedule, particularly the off phase when there is not enough dopamine replacement but can uncommonly also occur at peak-dose times. It can be one of the most painful symptoms those with Parkinsons can face.
Akathisia pain is experienced as restlessness, a subjective inner urge to move, an inability to stay still and the inherent feelings of discomfort that it brings. It is primarily experienced in the lower limbs and can often be relieved by walking around.
You May Like: Botox And Parkinsons Disease
Don’t Miss: Best Adjustable Beds For Parkinson’s Patients
Inflammation May Contribute To Both Joint And Nerve Degeneration
byNancy Walsh, Contributing Writer, MedPage Today June 9, 2021
Patients with osteoarthritis are at increased risk for developing Parkinsons disease, a longitudinal Taiwanese study found.
Incidence rates for developing Parkinsons disease were 0.99 per 1,000 person-years among patients with osteoarthritis compared with 0.71 per 1,000 for controls, reported Shin-Liang Pan, MD, PhD, and colleagues from the National Taiwan University in Taipei.
Accordingly, the risk among patients with osteoarthritis was 41% higher compared with controls, with an adjusted HR of 1.41 , the researchers wrote online in Arthritis Care & Research.
It is now recognized that inflammation plays a major role in the development of osteoarthritis, while neuroinflammation is characteristic of Parkinsons disease.
Because a growing body of literature reports that peripheral inflammation may induce neuroinflammation in the brain, leading to neurodegeneration, we hypothesized that having osteoarthritis may increase peoples risk of later developing Parkinsons disease, Pan and colleagues wrote.
Therefore, they analyzed data from Taiwans National Health Insurance system, which covers more than 97% of the population, identifying 33,360 individuals ages 50 to 64 who were diagnosed with osteoarthritis during the years 2002 to 2005, matching them by age and sex with the same number of controls.
- Knee or hip osteoarthritis, HR 1.55
- Non-knee or hip, HR 1.42
- Uncategorized, HR 1.32
Types And Symptoms Of Cognitive Changes
Discuss all of these possible causes of cognitive problems with your health care team. This will help you receive the correct diagnosis and treatment.
Mild cognitive changes
Sometimes survivors experience changes in their ability to remember or concentrate after they have chemotherapy. This typically mild form of cognitive change is sometimes called chemo-brain. Even these typically mild cognitive changes can disrupt daily living and the ability work. Symptoms include:
- Difficulty concentrating and multi-tasking.
- Inability to think clearly.
Neurocognitive effect of tumors
A tumor or cancer cells in the brain can injure healthy cells and can cause cognitive changes. Chemotherapy, radiation and surgery are treatments that are used to remove or destroy cancer cells. However, they can also damage some of the surrounding healthy cells either by direct administration or by impacting the brain indirectly. Depending on how much damage occurs, there could be noticeable symptoms such as with thinking, memory, speech, visual-spatial problems and behavior changes.
Acute onset cognitive changes
Acute onset cognitive changes are those that occur suddenly. Some acute changes, such as delirium, come and go with no real pattern. This can happen during treatment with certain medications and chemotherapy agents, and may be reversible. Symptoms include:
- Fluctuating alertness and orientation.
Other cognitive changes in cancer survivors
You May Like: Weighted Cups For Parkinson’s
What Causes Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease arises from decreased dopamine production in the brain. The absence of dopamine makes it hard for the brain to coordinate muscle movements. Low dopamine also contributes to mood and cognitive problems later in the course of the disease. Experts don’t know what triggers the development of Parkinson disease most of the time. Early onset Parkinson disease is often inherited and is the result of certain gene defects.
Peripheral Neuropathy And Parkinsons Disease
A number of studies have tried to determine if PN is more common among people with PD as opposed to people without PD. PN is a relatively common condition in the general population, which makes it difficult to ascertain whether or not it is even more common among people with PD.
The available studies have varying results and are difficult to compare with each other as they:
- Include different types of populations of people with PD
- Assess peripheral neuropathy differently
- Assess for causes of peripheral neuropathy differently
A recent review looked at all the available data and determined that large fiber neuropathy was present in 16% of patients with PD, about double the prevalence of this condition in the general population. Skin biopsy-proven small fiber neuropathy was present in over 50% of people with PD, although this result was based on a small sample of patients.
Don’t Miss: Lsvt Exercises For Parkinson’s
Pain Due To Fluctuations Dyskinesia Or Dystonia
To reduce potentially pain provoking motor fluctuations and dyskinesias, the optimization of therapy aiming to smoothen dopaminergic plasma level is recommended. The use of prolonged acting dopamine agonists or substances reducing the dopamine degradation such as MAO-B or COMT inhibitors are thought to reduce painful motor fluctuations during day- and night-time as well as early-morning akinesia. PD patients with motor fluctuations, who received the finally not approved partial dopamine D2 agonist Pardoprunox as adjunct therapy to levodopa, showed in a post-hoc analysis of a RCT a greater decrease in VAS pain scores compared to placebo . Amantadine might be helpful for painful dyskinesia, but data is missing.
A second substance with a potential specific effect on pain might be safinamide. In a post-hoc analysis based on pooled data of two large RCTs, safinamide applied as add-on therapy to levodopa treatment was associated with less consumption of pain medication compared to placebo and a significant reduction of pain in two of three sub-items of the PDQ-39 scale reflecting musculoskeletal and neuropathic pain . Noteworthy, in the safinamide group a slightly higher percentage of patients had additional pain medication at study baseline. In summary, this limited benefit needs to be confirmed by dedicated future studies.
No One Definitive Cause Of Parkinsons
There are no biomarkers or objective screening tests that indicate one has Parkinsons. That said, medical experts have shown that a constellation of factors are linked to it.
Parkinsons causes are likely a blend of genetics and environmental or other unknown factors. About 10 to 20 percent of Parkinsons disease cases are linked to a genetic cause, says Ted Dawson, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Institute for Cell Engineering at Johns Hopkins. The types are either autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive .
But that leaves the majority of Parkinsons cases as idiopathic, which means unknown. We think its probably a combination of environmental exposure to toxins or pesticides and your genetic makeup, says Dawson.
Age. The biggest risk factor for developing Parkinsons is advancing age. The average age of onset is 60.
Gender. Men are more likely to develop Parkinsons disease than women.
Genetics. Individuals with a parent or sibling who is affected have approximately two times the chance of developing Parkinsons. Theres been an enormous amount of new information about genetics and new genes identified over the past 10 or 15 years that have opened up a greater understanding of the disease, says Dawson.
You May Like: Different Stages Of Parkinson’s
Parkinsons Disease And Cancer: Whats The Connection
Researchers have long tried to understand the relationship between Parkinsons disease and cancer, with multiple studies conducted over the years. Intuitively, PD and cancer are not at all similar, and can even be thought of as biochemically opposite in one disease , cells die unexpectedly and in the other , cells divide too often and are perpetuated for too long. In fact, there have been many epidemiological studies over past decades that have shown that patients who have had cancer have a lower risk of developing PD than the general population. Other studies have shown that people with PD have lower overall cancer risks than people without PD.
Despite many papers demonstrating this inverse relationship between PD and overall cancer risk, an occasional study has been conducted which concluded that people with PD have an increased risk of cancer. It can be confusing to understand the different studies and determine how the resulting information may or may not apply to you.
Here we highlight some of the more common cancer-related topics when it comes to PD:
Recommended Reading: Does Weed Help With Parkinsons
How Is It Treated And Is There A Cure
For now, Parkinsons disease is not curable, but there are multiple ways to manage its symptoms. The treatments can also vary from person to person, depending on their specific symptoms and how well certain treatments work. Medications are the primary way to treat this condition.
A secondary treatment option is a surgery to implant a device that will deliver a mild electrical current to part of your brain . There are also some experimental options, such as stem cell-based treatments, but their availability often varies, and many aren’t an option for people with Parkinsons disease.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Va Disability Rating
Mold Health Impact : Irritability And Rage
Mold toxic patients often feel out of control in their own brain, describing the feeling by saying that it feels as if their brain is hot wired. This sensation can be hard to understand without personally experiencing it, often causing a mold-toxic person to feel misunderstood by their family and peers however, science has taught us that this hot-wired feeling is caused by the excessive electrical activity in the brain due to mold toxicity. With the understanding that those experiencing excito-neurotoxicity say that it feels like they have been plugged into an electrical socket, its easy to see why they feel aggravated or aggressive. Over time, as mold toxicity worsens in a patient, the over-electrified brain feeling causes a confusing emotional combination of anxiety and also depression. With this volatility of emotions, its no wonder mold toxic patients grow irritable and exhibit rage.
Read More About How Irritability and Rage Affect Health Here
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery For Parkinson’s Disease At Ucla
If you’ve been diagnosed with Parkinson’s, your doctor will first prescribe medication. There are many drugs available that improve symptoms, but they have many side effects, including nausea, hallucinations and impulsive behavior. Some patients respond well to medications for years before seeing side effects. In these patients, the drugs may start to wear off quickly, or they may become extremely sensitive to the drugs and experience too much movement
Deep brain stimulation is a surgical option available to patients who are intolerant of medications or who experience serious side effects. This procedure involves implanting electrodes, or wires, deep inside the brain to change irregular brain activity. As a result, it improves motor function in patients with Parkinson’s disease. It is used more often to treat Parkinson’s disease than any other movement disorder.
Recommended Reading: Va Parkinson Disease Rating Scale
What Medications And Treatments Are Used
Medication treatments for Parkinsons disease fall into two categories: Direct treatments and symptom treatments. Direct treatments target Parkinsons itself. Symptom treatments only treat certain effects of the disease.
Medications
Medications that treat Parkinsons disease do so in multiple ways. Because of that, drugs that do one or more of the following are most likely:
Several medications treat specific symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Symptoms treated often include the following:
- Erectile and sexual dysfunction.
- Hallucinations and other psychosis symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation
In years past, surgery was an option to intentionally damage and scar a part of your brain that was malfunctioning because of Parkinsons disease. Today, that same effect is possible using deep-brain stimulation, which uses an implanted device to deliver a mild electrical current to those same areas.
The major advantage is that deep-brain stimulation is reversible, while intentional scarring damage is not. This treatment approach is almost always an option in later stages of Parkinson’s disease when levodopa therapy becomes less effective, and in people who have tremor that doesnt seem to respond to the usual medications.
Experimental treatments
Researchers are exploring other possible treatments that could help with Parkinsons disease. While these arent widely available, they do offer hope to people with this condition. Some of the experimental treatment approaches include:
What Were The Basic Results
Exposing wild Drosophila flies to low dose 1-octen-3-ol caused movement problems within the first 24 hours and 50% to die by 16.9 days. The control group all survived for at least 27 days, by which time the entire 1-octen-3-ol group had died.
In the second part of the study, exposure to 1-octen-3-ol reduced the number of all types of dopamine nerves except for one. This caused a reduction in dopamine levels of 28% compared to flies that were not exposed. It also increased the level of the waste product of dopamine, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid by 40%.
In the human embryonic kidney cells, very low levels of 1-octen-3-ol did not have an effect, whereas low and higher levels caused a difficulty in transporting dopamine into the cells.
They found that overexpression of a different genetic neurotransporter cell in flies brains was protective against the effects of 1-octen-3-ol.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Loss Of Appetite
Surgery For People With Parkinsons Disease
Deep brain stimulation surgery is an option to treat Parkinsons disease symptoms, but it is not suitable for everyone. There are strict criteria and guidelines on who can be a candidate for surgery, and this is something that only your doctor and you can decide. Surgery may be considered early or late in the progression of Parkinsons. When performing deep-brain stimulation surgery, the surgeon places an electrode in the part of the brain most effected by Parkinsons disease. Electrical impulses are introduced to the brain, which has the effect of normalising the brains electrical activity reducing the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The electrical impulse is introduced using a pacemaker-like device called a stimulator. Thalamotomy and pallidotomy are operations where the surgeon makes an incision on part of the brain. These surgeries aim to alleviate some forms of tremor or unusual movement, but they are rarely performed now.