Differential Dopaminergic Effects On Pupil Reward Sensitivity
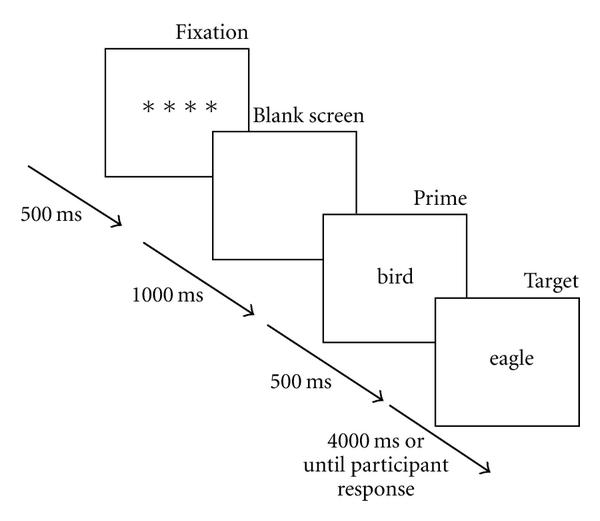
Pupillary modulation in response to monetary reward was calculated as the mean proportional difference in pupil size from the baseline pupil diameter at the beginning of each trial. As previously , the relevant epoch for reward related pupil response was taken between 1400 ms and 2400 ms after the auditory reward cue. We were interested in whether pupil dilatation was related to the potential reward on offer in each trial, and whether there were differences in pupillary dilation between PD+ICD and PD-no-ICD. Each patients pupillary reward sensitivity was calculated as the difference in mean proportional pupil change between the 50p and 0p reward conditions across the time epoch described above. Greater difference between 50p and 0p reflects greater reward sensitivity.
In both PD+ICD and PD-no-ICD, pupils dilated more in response to increasing monetary reward . In addition, there was a significant three-way interaction between drug condition, reward and group reflecting differences in the dopaminergic effect on pupil reward sensitivity in the two groups. Furthermore, there was a main between-subjects effect of group revealing overall smaller pupil responses to reward in PD+ICD , as well as a main effect of drug condition with greater overall pupil response when OFF dopamine in both groups . There were no two-way interactions.
What Are The Symptoms
Symptoms of PD vary from person to person, as does the rate of progression. A person who has Parkinson’s may experience some of these more common “hallmark” symptoms:
- Bradykinesia – slowness of movement, impaired dexterity, decreased blinking, drooling, expressionless face.
- Tremor at rest – involuntary shaking that decreases with purposeful movement. Typically starts on one side of the body, usually the hand.
- Rigidity – stiffness caused by involuntary increase in muscle tone.
- Postural instability – sense of imbalance. Patients often compensate by lowering their center of gravity, which results in a stooped posture.
Other symptoms that may or may not occur:
Freezing or being stuck in place Shuffling gait or dragging of one foot Stooped posture Cognitive impairment
What Is Dopamines Connection To Parkinsons Disease
For people with Parkinsons disease, dopamine levels are too low. As the dopamine starts to fall, signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease will begin to reveal themselves. That means the smooth, controlled body movements may be replaced by symptoms like tremor or stiffness in limbs. Fluid motions may become slow, shaky, and halted.
Dopamine levels may be significantly reduced by the time these symptoms are noticeable. Some of the earliest signs of Parkinsons disease arent as obvious, and they may occur years before the more significant motor problems arise. These symptoms include:
- difficulty concentrating
Its not clear why dopamine levels drop off in people with Parkinsons disease, but the lower the level of dopamine, the more likely you are to experience symptoms of the disorder.
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke , the symptoms of Parkinsons disease typically begin to appear when a persons brain has lost 60 to 80 percent of their dopamine-producing cells in the substantia nigra. That means the drop in dopamine may be happening long before symptoms are recognized and your doctor begins the work of trying to determine whats causing issues.
Don’t Miss: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinson’s
Downstream Effects Of Dopal Accumulation: Oxidative Stress Mitochondrial Dysfunction And Cell Death
A further analogy with DA is that also DOPAL quinones could covalently modify mitochondrial protein, possibly affecting mitochondrial physiology . In the work by Kristal et al., isolated mitochondria from mouse liver were exposed to DOPAL resulting in an increased opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore at concentrations close to physiological ones . Later studies reported that DA oxidation to quinones induced mitochondria swelling and reduced respiratory activity, suggesting the induction of the mPTP opening . An analogous effect was ascribed to DAQs derived from enzymatic oxidation of DA, specifically addressing the modulation of mPTP opening to DAQs . As a consequence, both DA and DOPAL-derived quinones could be responsible for the activation of the apoptotic pathway. On the other hand, DOPAL-induced decreased cell viability was assessed by measuring Lactate Dehydrogenase release in the extra-cellular space, which is an accepted indication of necrosis .
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Pivotal Pathological Mechanism Of Parkinsons Disease
Mitochondria are complex cytosolic organelles of eukaryotic cells whose primary function is the generation of cellular energy in the form of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Mammalian mitochondria contain between 2 and 10 mitochondrial DNA molecules encoding 22 transfer RNAs, two ribosomal RNAs, and 13 polypeptides, each of which is part of the respiratory chain and the oxidative phosphorylation system . The mitochondrial respiratory chain contains four protein complexes that form the site of oxidative phosphorylation. This site is responsible for NADH and FADH2 oxidation, co-occurring with the movement of protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space. This movement produces an electrochemical gradient denoted as mitochondrial membrane potential . This gradient stimulates the ATP synthase to reduce molecular oxygen and synthesize ATP. This step is fundamental in aerobic metabolism and constitutes the primary provider of ATP at the final stage of cellular respiration . Nevertheless, the biological function of mitochondria goes far beyond energy production and includes the metabolism of lipids and amino acids and the support of intermediate metabolic pathways, such as the Krebs cycle.
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Cause Hip Pain
The Role Of Dopaminergic Medications Including Agonists In Impulse Control Disorders
The pupillary reward sensitivity findings were independent of total LEDD at the group level and did not significantly correlate with it across patients. However, there were some effects that suggest a potential impact of dopamine agonists. Across the patient groups, DA-LEDD was significantly correlated with pupil reward sensitivity when OFF dopaminergic medication and with respect to the mean of ON and OFF. But increased DA-LEDD did not predict increased proportional pupil change ON medication or crucially the difference between ON and OFF.
The results of many different studies have pointed to the possibility that ICDs in Parkinsons disease might develop in response to dopamine agonist treatment interacting with underlying Parkinsons disease pathophysiology and possibly personality traits . ICDs have been associated with the use of non-ergolinic oral dopamine agonists, such as rasagiline, ropinirole and pramipexole , as well as ergoline-derivatives such as cabergoline . However, there is no straightforward dose-dependent relationship across individuals , suggesting other factors are important for the overt manifestation of impulsive behaviour. These may include impaired learning from negative feedback, greater novelty seeking, enhanced delay discounting, rapid decision-making without sufficient evidence, reduced inhibitory control, and increased risk taking under conditions of ambiguity .
Linking The Catecholaldehyde Hypothesis To Synuclein
A pivotal study by Burke et al. in 2008 demonstrated that in vitro DOPAL incubation with Syn monomers triggers a dose-dependent protein aggregation. Similarly, SDS-resistant aggregates of Syn were detected by Western Blot in lysates from SH-SY5Y cells after administration of DOPAL in the medium. The process was observed also in vivo upon direct DOPAL injection into rat SNpc, which resulted in dopaminergic neuron loss and accumulation of Syn high molecular weight species . Since then, other groups provided further insights into the DOPAL-dependent Syn aggregation process. Inhibition of DA uptake into synaptic vesicles by reserpine administration to dopaminergic PC12 cells, induced DA cytosolic build-up with consequent cytotoxic accumulation of DOPAL and induction of Syn oligomerization . Furthermore, redox active metal ions i.e. Cu, Fe, Mn, whose levels are increased in parkinsonian SNpc , were shown to accelerate DOPAL-induced Syn oligomerization in PC12 cells . On the same ground, in vitro assays revealed a modulating effect of N-terminal acetylation and familial mutations on DOPAL-induced Syn oligomerization .
Fig. 4
You May Like: Exercise For Freezing In Parkinson’s
Precision Medicine In A Preventive Approach
The failure of current therapies for PD may be due to the heterogeneity of syndromes collectively referred to as PD. While all converge in the massive loss of DA neurons in the midbrain alongside the appearance of Lewy bodies, different etiologies of PD have been found. Some of these etiologies specifically affect the DA neurons, while others may overlap with comorbid conditions such as AD and other synucleinopathies. Based on this idea, the multiple hit hypothesis was proposed, in which the basis for selective neuronal death is a combination of toxic stress, induced by DA oxidation or mitochondrial dysfunction, co-occurring with inhibition of neuroprotective responses, such as follows after the loss of parkin function .
This said, the bright side of PDs multifactorial etiology provides an opportunity for more personalized treatment regimens. Precision medicine is driven to improve specific molecular alterations and treat particular subtypes of PD . Personalized medicine is not a novel treatment approach outside of PD, and it is currently used in an array of conditions, such as oncology and cystic fibrosis . The slow development of PD gives a unique opportunity to study the patients genome and environmental factors to target the causes of the disease in each specific group of patients .
What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons warning signs can be motor symptoms like slow movements, tremors or stiffness. However, they can also be non-motor symptoms. Many of the possible non-motor symptoms can appear years or even decades ahead of motor symptoms. However, non-motor symptoms can also be vague, making it difficult to connect them to Parkinson’s disease.
Non-motor symptoms that might be early warning signs include:
- Sleep problems such as periodic limb movement disorder , rapid eye movement behavior disorder and restless legs syndrome.
Don’t Miss: Questions About Parkinson’s Disease
Be Honest With Yourself And Your Doctor
It is important to discuss alcohol consumption with your doctor to make sure you are approaching it safely. Elements of PD, including motor symptoms such as bradykinesia and dyskinesia , will vary from person to person, so its important to make decisions based on your medical history.
Taking into account environmental factors such as how central alcohol is to your social life can affect the decisions you make. Be honest with your doctor about your habits and preferences remember, your doctor wants to work with you to make your symptoms as manageable as possible, not to judge or shame you.
As you decide how alcohol may fit into your life post-diagnosis lifestyle, there are many factors to consider, such as the type of alcoholic beverage, your other risk factors, and your neurologists recommendations specific to your medical history. Most importantly, monitor how you feel when you drink alcohol and be willing to have open and honest conversations about drinking with your doctor and other important people in your life.
I am not even a big drinker, but miss the odd one, wrote a MyParkinsonsTeam member. So, I had an alcohol-free beer, which tasted OK, to be honest.
Reward Processing In Impulse Control Disorders
Previous work has suggested that when cued with monetary rewards, PD+ICD patients have reduced tolerance for delayed gratification. In our study, patients had less time to evaluate the rewarding stimuli before a response was required. The subjective valuation and associated behavioural response reflect autonomic response to, and invigoration of reflexive responses by, reward cues. Therefore, the oculomotor behaviours we observed are likely to index incentive salience , or implicit sensitivity to rewarding stimuli, as opposed to conscious decision-making. From this perspective, heightened wanting of rewards translates to heightened sensitivity for extrinsic rewards as well as a lower salience threshold for initiation of a reflexive behavioural response to obtain the reward. However, our findings suggest that the underlying incentive salience, or reward sensitivity, is not directly modulated by dopamine in PD+ICD because the autonomic pupil response to reward did not decrease when OFF dopamine. Additionally, the fact that pupillary reward sensitivity is predictive of future emergence of ICDs suggests that enhanced incentive salience of extrinsic rewards might even precede the behavioural disinhibition which characterizes pathological impulsive behaviour.
Recommended Reading: What Tests Are Done To Diagnose Parkinson’s
Comparison With Healthy Controls
Relative to controls, nondepressed PD patients showed a significantly lower value-independent gambling bias during the OFF session, U = 111, p = 0.001, but not during the ON session, U = 177, p = 0.08. This is consistent with the significant effect of medication in the nondepressed PD group, mentioned earlier. Relative to controls, PD patients with a depression showed a significantly lower value-independent gambling bias during the ON session, U = 151, p = 0.033, but not during the OFF session, U = 160, p = 0.06. Note however that, within this patient group, there was no significant medication effect on the value-independent gambling bias parameter.
Relative to controls, median loss aversion parameter estimates were quite low in patients. However, direct comparisons with controls revealed that this reduction was significant only in nondepressed PD patients OFF medication, U = 150, p = 0.019. The median loss aversion parameter from nondepressed patients ON medication, U = 169, p = 0.056, and from PD patients with a depression OFF, U = 228, p = 0.75, or ON medication, U = 176, p = 0.12, did not differ from that of controls. There were no differences in terms of the inverse temperature parameter between controls and either group of PD patients .
Correcting Cholinergic Deficits In Parkinsons Disease: Cotinine A Potential Therapeutic Agent
The cholinergic system plays a broad role in controlling neurotransmitter release, reducing neuroinflammation, and promoting neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity in the brain. The binding of acetylcholine to nicotinic ACh receptors occurs throughout the brain, including within striatum and other constituents of the mesolimbic, mesocortical, nigrostriatal, and frontostriatal loops. nAChRs are pentameric ligand-gated ion channels composed of -subunits or containing and -subunits . Presynaptic nAChRs mediate neurotransmitter release and postsynaptic receptors increase neuronal firing rates and thus facilitate long-term potentiation.
Epidemiological studies have shown lower rates of PD development in people consuming tobacco products, which suggests that the nicotinic receptors may play an essential role in preventing PD and that one or more tobacco-derived compounds may be neuroprotective . Various studies using cellular models have shown a neuroprotective effect of nicotine that diminished dopaminergic neuronal damage . Other reports have shown that both nicotine and its main derivative, cotinine, have a neuroprotective effect against 6-hydroxydopamine -induced toxicity in cultured differentiated SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells expressing nAChRs .
Don’t Miss: Shoes For People With Parkinsons
Strategies For The Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease: Beyond Dopamine
- 1Laboratorio de Neurobiología, Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud, Universidad San Sebastián, Concepción, Chile
- 2Department of Biological Sciences, University of Limerick, Limerick, Ireland
- 3Health Research Institute, University of Limerick, Limerick, Ireland
- 4Department of Psychology and Neuroscience, Center for Neuroscience, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO, United States
- 5Research & Development Service, Bay Pines VA Healthcare System, Bay Pines, FL, United States
Parkinsons disease is the second-leading cause of dementia and is characterized by a progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra alongside the presence of intraneuronal -synuclein-positive inclusions. Therapies to date have been directed to the restoration of the dopaminergic system, and the prevention of dopaminergic neuronal cell death in the midbrain. This review discusses the physiological mechanisms involved in PD as well as new and prospective therapies for the disease. The current data suggest that prevention or early treatment of PD may be the most effective therapeutic strategy. New advances in the understanding of the underlying mechanisms of PD predict the development of more personalized and integral therapies in the years to come. Thus, the development of more reliable biomarkers at asymptomatic stages of the disease, and the use of genetic profiling of patients will surely permit a more effective treatment of PD.
Where Is It Made In The Brain
Dopamine is produced in the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, and hypothalamus.1 You may not remember these complicated names. That is fine! It is probably more important to know what these areas of the brain do:1,4-6
- The substantia nigra is part of the brain known as the basal ganglia. This part of the brain is responsible for making movement possible.
- The ventral tegmental area is the part of the brain that is responsible for reward and reinforcement.
- The hypothalamus has many functions. It is responsible for sleep, appetite, body temperature, and sexual arousal, among other things. The hypothalamus helps control the autonomic nervous system.
Read Also: Cane With Laser For Parkinson’s
What Are Some Possible Side Effects Of The Dopamine Receptor Agonists
Dopamine agonists have many of the side effects of other dopaminergic agents. These include hallucinations and orthostatic hypotension . Leg swelling can also occur. Dopamine agonists can induce sleepiness as well as sleep attacks and must be used with great caution in those patients who are driving. Compulsive behavior is a well described side effect and could take the form of over-shopping, over-eating, gambling or hyper-sexuality.
In some patients, a withdrawal syndrome can be experienced as the dopamine agonist is lowered and stopped. Symptoms of the withdrawal syndrome can include anxiety, pain, depression, and even suicidality. Patients should be warned about the possibility of experiencing withdrawal when a dopamine agonist is tapered so if they experience these symptoms, they can modify how the medication is weaned off.
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
If you have Parkinsons disease, the best thing you can do is follow the guidance of your healthcare provider on how to take care of yourself.
- Take your medication as prescribed. Taking your medications can make a huge difference in the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. You should take your medications as prescribed and talk to your provider if you notice side effects or start to feel like your medications aren’t as effective.
- See your provider as recommended. Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule for you to see them. These visits are especially important to help with managing your conditions and finding the right medications and dosages.
- Dont ignore or avoid symptoms. Parkinsons disease can cause a wide range of symptoms, many of which are treatable by treating the condition or the symptoms themselves. Treatment can make a major difference in keeping symptoms from having worse effects.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Someone Live With Parkinson’s Dementia