When Brain Mri Is Recommended To Help Diagnose Parkinsonism
Differentiating atypical parkinsonism from Parkinsons disease can be a challenge in patients presenting with symptoms in early disease stages. A diagnosis cannot be made from a brain magnetic resonance imaging scan, but brain MRI can be of added value when there is uncertainty about the clinical diagnosis.
The appropriateness of and the added diagnostic value of a brain MRI scan in the work-up of parkinsonism is described in a newly published article in the Journal of Parkinsons Disease. Lead author Frederick J.A. Meijer, MD, PhD, a neuroradiologist in the department of radiology and nuclear medicine at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, The Netherlands, offers advice on the scanning protocol to use, and also discusses its diagnostic value with respect to specific abnormalities that can be seen.
The authors of the article, who also include neurologists from the Radboud University Medical Center and Donders Institute for Brain, Cognition and Behavior, conducted a 3-year long prospective study on the contribution of routine brain MRI to the differential diagnosis of parkinsonism.1 Based on this research, the authors refuted clinical guidelines recommending standard use of cerebral MRI for all patients presenting with parkinsonism.
3T brain MRI including DTI tractography in a patient presenting with parkinsonism.
What Is A Datscan
A DaTscan is an imaging drug, also called Ioflupane I 123 or phenyltropane, that acts as a radioactive tracer for dopamine transporters within the brain. This drug was approved by the FDA in 2011. It may help distinguish the diagnosis of essential tremor from Parkinson’s syndromes, like Parkinsons disease or Parkinsons disease dementia.
The drug is administered during the SPECT scan. This scanning technique gathers images of a particular area in the brain called the striatum, a cluster of neurons in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum helps facilitate the transportation of dopamine.
DaTscan is injected into the patients bloodstream and eventually circulates to the brain. The tracer attaches itself to a molecule found on dopamine neurons in the striatum called the dopamine transporter . The patient then undergoes a SPECT scan which will produce an image of the dopaminergic neuron terminals that remain available in the striatum.
In patients with a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, or parkinsonism , this area of the brain will show dark. This indicates the loss of dopamine-containing nerve cells within the brain, a hallmark of the disease.
Humanistic Considerations In Ioflupane Imaging
SPECT imaging with ioflupane may have an impact on patient-reported quality of life through enabling timely diagnosis that can lead to prompt and appropriate treatment. Patients who remained untreated after a PD diagnosis experienced deteriorations in mobility, activities of daily living, emotional well-being, social support and bodily discomfort.,
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Come And Go
Pd Risk Prediction Modeling
Table 3 shows the risk estimation PD model using SBR and biological biomarkers. It was observed that the value of p for RC, plasma, and serum was greater than 0.05 hence, these features were not contributing to the results obtained by this model. However, these features are of great importance as discussed in the literature hence, these features cannot be ignored. To satisfy this constraint, an interaction term is introduced, instead of working with those individual features.
Deviance Table for SBR and Biological Biomarkers
| AIC | 103.42 |
DF is the degree of freedom that represents the amount of information in the data. Adj Dev is the measure of variation for different components of the model . Adj mean measures how much deviance a term or model explains for each DF. Chi-square value determines whether a term or model is associated with response. p-Value specifies the significance level to reject or accept the null hypothesis. Deviance R-Sq and AIC are the measures of how well the model fits the data, and relative quality of model. Higher value for deviance R-Sq and smaller value for AIC are preferred to represent the degree of fitness of the data to the model.
Table 3 reflects the calculated 8-predictor model. Subsequently, it was observed that p-value was less than 0.05 and R-Sq value was significantly high for 8-predictor model. It shows that the logistic model is fitting the data. The obtained model can be expressed as PPD = exp/), where
4.2.1 Goodness-of-Fit Test
How A Diagnosis Is Made
The bedside examination by a neurologist remains the first and most important diagnostic tool for Parkinsons disease . Researchers are working to develop a standard biological marker such as a blood test or an imaging scan that is sensitive and specific for Parkinsons disease.
A neurologist will make the diagnosis based on:
- A detailed history of symptoms, medical problems, current and past medications. Certain medical conditions, as well as some medications, can cause symptoms similar to Parkinsons.
- A detailed neurological examination during which a neurologist will ask you to perform tasks to assess the agility of arms and legs, muscle tone, gait and balance, to see if:
- Expression and speech are animated.
- Tremor can be observed in your extremities at rest or in action.
- There is stiffness in extremities or neck.
- You can maintain your balance and examine your posture.
Read Also: New Treatment For Parkinson’s 2021
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Dont Miss: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
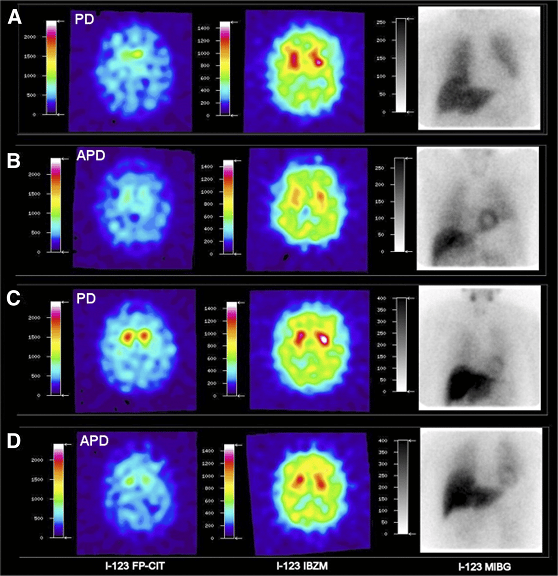
Datscan: A Test To Help In The Diagnosis Of Parkinsons
In 2011, the Food and Drug Administration approved an imaging test to help diagnose PD. In this test, a radioactive tracer, Ioflupane 123I, also known as DaTscan, is injected into the blood, where it circulates around the body and makes its way into the brain. It attaches itself to the dopamine transporter, a molecule found on dopamine neurons. Several hours after the tracer has been injected, special imaging equipment scans the head to detect the presence of DaTscan.
People with PD will typically have a smaller signal in a part of the brain called the striatum, where the ends of the dopamine neurons are meant to be. Here is a normal scan on the left, which would indicate a healthy dopamine system, next to an abnormal scan on the right, which would indicate an unhealthy dopamine system.
It is important to note that conventional MRI imaging will appear normal in PD and is therefore not helpful in confirming the diagnosis. Other atypical parkinsonian conditions, such as vascular parkinsonism however, can have abnormalities on MRI, so the test may be done to rule out other diagnoses.
Read Also: Average Life Expectancy Parkinson’s
Computing The Specific Binding Ratio
The 123I-Ioflupane SPECT radiotracer produces low-level, non-specific dopamine transporter bindings in addition to the intended specific dopamine transporter bindings. In this study, SBR was computed for seven striatal and extra-striatal regions. The SBR is defined as the ratio between the concentrations of the specific binding radioactivity of target ROI to the non-specific binding radioactivity of the reference region,. The non-specific binding uptake is estimated from a brain region devoid of 123I-Ioflupane, which was chosen as the occipital region. The occipital region was specified by image co-registration with the Desikan-Killiany anatomical atlas using procedures described in ROI specifications. SBR was calculated for seven regions according to the following formula: SBR=/-1.
Brain Imaging In Parkinsons Disease
Traditional brain imaging with CT and MRI scans do not show changes in the brain when someone has Parkinsons disease and are generally not helpful in diagnosis. A new kind of brain scan, called a DaT scan, does show changes in persons with Parkinsons disease and may someday become an important tool in diagnosing Parkinsons.
The dopamine transporter, or DaT, scan uses a chemical that labels the dopamine transporter in the area of the brain known as the striatum. Dopamine is a neurochemical that is decreased in persons with Parkinsons disease.
The dopamine transporter, which moves dopamine in and out of cells, is also decreased in the striatum in persons with Parkinsons disease and related disorders. The chemical that labels the transporter is injected into the vein and can be imaged by using something called single photon emission computerized tomography, or SPECT scanning. This technique has been registered in the European Union since 2000 for differentiating a diagnosis of essential tremor and a parkinsonian syndrome. It was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2011 for this same indication and recently became available at the OHSU Brain Institute.
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Cause Vision Problems
Mechanisms Underlying Fluctuations And Dyskinesias
PD patients show reduced putamen 18F-dopa uptake whether they have sustained or fluctuating motor responses to levodopa, but mean uptake is 20% lower in the latter group . There is, however, considerable overlap of individual levels of putamen 18F-dopa uptake in fluctuator and nonfluctuator cohorts, and so, loss of putamen dopamine terminal function cannot be the sole factor responsible for determining the timing of onset of motor complications.
11C-raclopride PET studies have reported that putamen D2 binding is initially increased by up to 20% in de novo PD but that after 6 mo of treatment with levodopa, D2 receptor availability returns to normal . 11C-SCH23390 PET reveals normal striatal D1 binding in de novo PD, whereas patients chronically exposed to levodopa show a 20% reduction . Striatal dopamine D1 and D2 receptor availability has been compared in dyskinetic and nondyskinetic groups of PD patients with similar clinical disease duration and severity who were receiving a similar daily dose of levodopa . Similar levels of D1 and D2 receptor binding were found, suggesting that onset of motor fluctuations and dyskinesias in PD is not driven by alterations in striatal postsynaptic dopamine receptor availability.
Diffusion Mri For The Study Of Parkinsons Disease
Diffusion changes in PD has been the subject of many studies over the years. They are generally based on two measures accounting for mean diffusivity and fractional anisotropy . These measures describe the diffusion of water molecules in the brain, MD accounts for the their overall displacement and FA indicates the orientation of diffusion. The meta-analysis proposed by Cochrane and Ebmeier, 2013 put into evidence important discrepancies between the diffusion scans of PD patients across studies between 1946 and 2012, notably regarding acquisition parameters, analysis methods and the introduction of medication. Most studies focused on the SN as Region Of Interest and often reported FA reductions in different segments with a slight tendency towards the caudal segment. However, no significant association was detected between disease severity and FA values. The first studies were carried out on small cohorts and presented opposing results. We can notably cite the work of Schwarz et al., 2013 where, in contrast to the work of Du et al., 2011, no differences were found in SN for FA values between PD patients and controls but a significant increase of MD in the SN was reported.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Double Vision
You May Like: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s Disease
Whats A Nuclear Medicine Scan
A nuclear medicine scan uses small amounts of radiation to create pictures of tissues, bones, and organs inside the body.
The radioactive material collects in certain areas of your body, and special cameras find the radiation and make images that help your medical team diagnose and treat cancer and other illnesses.
Other terms your doctor might use for a nuclear medicine scan are:
- Radionuclide imaging
What Are The Limitations Of The Test
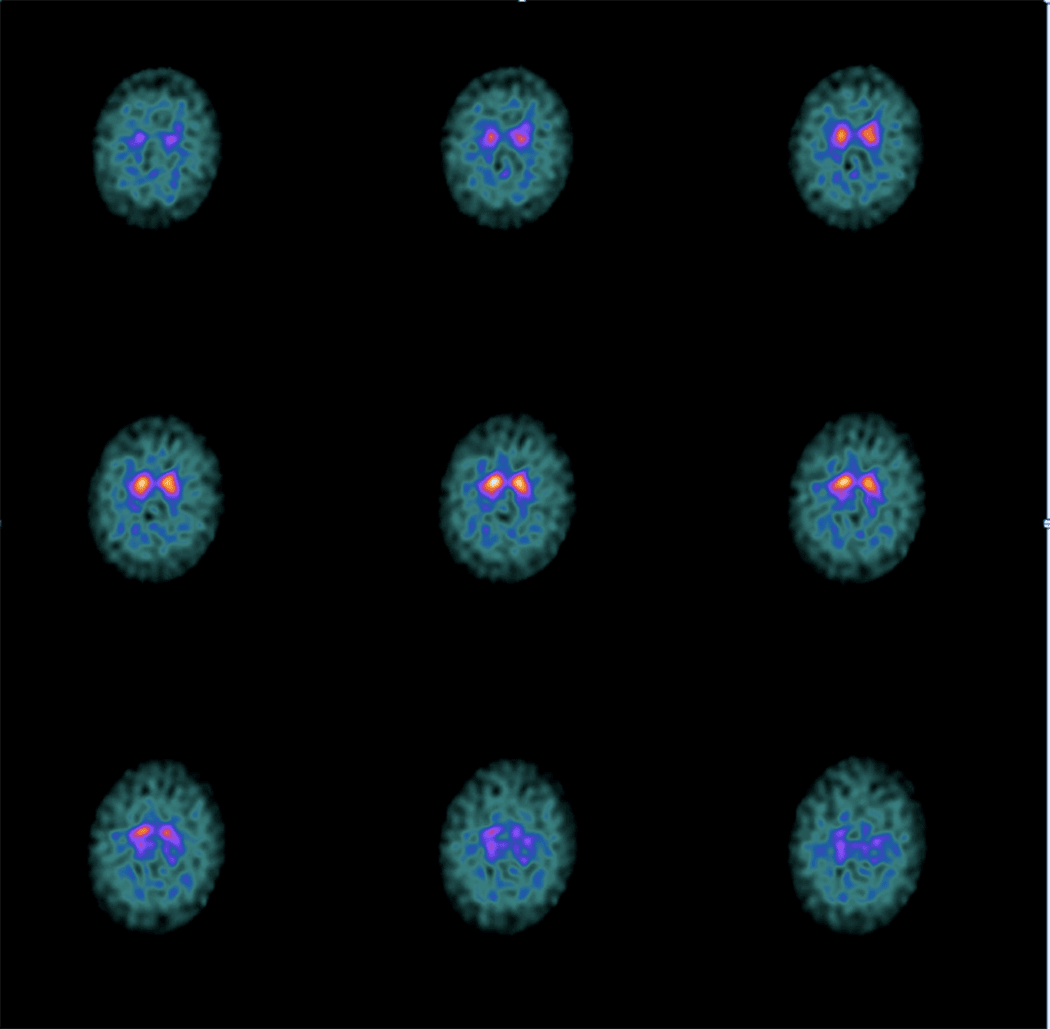
Currently, DaTscan that is in clinical use is not quantitative, which means that the test is not designed to determine how impaired the dopamine system is just whether it is or not. This means that the test is not used to tell you whether the disease has progressed over time and is not used to follow a patients disease. It also is not used currently as a clinical test to screen for the disease before motor symptoms are evident. Because of these limitations, the search continues for additional measurable indicators, known as biomarkers, to help diagnosis and manage PD.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Stiffness In Morning
Imaging Structural Change In Atypical Pd
MRI can play a valuable role in discriminating atypical parkinsonian syndromes, such as multiple-system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy, from typical PD. Atrophy of the lentiform nucleus is a feature of these atypical disorders, but volumetric MRI has not proved sensitive enough to be of diagnostic value . In contrast, diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor MRI is highly sensitive to changes in striatal structure and potentially useful for discriminating atypical from typical parkinsonian disorders. Diffusion-weighted MRI has been reported to detect raised water-proton apparent diffusion coefficients in the putamen in 90%100% of patients with clinically probable multiple-system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy, whereas apparent diffusion coefficients in the putamen are normal in PD . Multiple-system atrophy can be discriminated from progressive supranuclear palsy by the presence of an altered water diffusion signal in the middle cerebral peduncle . These studies have all involved well-established atypical cases, however, and it remains to be seen how well diffusion-weighted MRI will perform with early gray cases in prospective series where clinical diagnostic uncertainty is still present.
FIGURE 3.
How Does The Datscantm Work
The radiopharmaceutical, or tracer, which is used in DaTSCANTMis Iodine-123 Ioflupane. It is injected into the vein after administering a thyroid blocking agent in the form of oral potassium iodide. This is to prevent unnecessary accumulation of the radiopharmaceutical in the thyroid gland.
The DaTSCANTM binds to the presynaptic dopamine transporters in the brain, in particular the striatal region of the brain. In Parkinsons disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies there is a marked reduction in dopaminergic neurons in the striatal region. The tracer binds to the dopamine transporters and gives a semi-quantitative measure and spatial distribution of the transporters.
The scan itself is a single photon emission computed tomography scan of the brain. The patient lies down on the examination couch with their head positioned in the headrest. Often a gentle head restraint is used to minimise motion. The gamma camera rotates around the patients head for approximately 30-45 minutes. During this time, it is important that the patient lies still as a three-dimensional image of the distribution of the dopamine receptors in the brain is being created.
Most patients will tolerate the scan very well, and we are used to performing the scans in patients with a tremor. In patients with suspected dementia, it is very useful to liaise with a carer to make sure the patient can attend the appointment. It is also reassuring for the patient to have their carer next to them during the scan.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease And Foot Pain
What Role Does Datscan Have In The Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
Many patients with Parkinsons disease are frustrated and sometimes frankly suspicious about how it is diagnosed. As a neurologist, over the years Ive heard comments like:
- All the doctor did was have me make some movements with my hands and legs and watch me walk and then he told me I had Parkinsons disease! How is that possible?
- I dont believe my diagnosis. Arent there a bunch of other diseases it could be?
- How can they know for sure? I want a test to prove whether I do or do not have Parkinsons disease!
I understand how some patients and care partners can feel this way so I want to address this concern and discuss the role and limitations of a test that is available, known as DaTscan.
Functional Imaging And Atypical Pd
Imaging presynaptic dopaminergic terminal function with either striatal 18F-dopa uptake or a DAT SPECT marker shows high sensitivity for detecting atypical parkinsonian syndromes but only poor specificity for discriminating them from typical PD . The typical gradient of loss of dopaminergic function in PD, where the head of the caudate is relatively spared, is less evident in progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration patients . In progressive supranuclear palsy, there is a more symmetric pattern of nigrostriatal dysfunction than in other parkinsonian syndromes.
In contrast, measurements of resting glucose metabolism can be helpful for separating typical from atypical parkinsonian syndromes. In typical idiopathic PD, lentiform nucleus glucose metabolism is preserved or raised, whereas it is reduced in most atypical cases .
FIGURE 5.
18F-FDG PET images of PD and multiple-system atrophy patient. Multiple-system atrophy patient shows significant striatal reduction of glucose metabolism. MSA = multiple-system atrophy.
You May Like: Best Bed For Parkinson’s Patients
Accuracy Of Ioflupane In Pd
Perlmutter and Eidelberg make the point that after several years, follow-up of individuals with negative DAT SPECTs revealed that some develop PD or another PS. The published 95% sensitivity/specificity of ioflupane suggests that ioflupane will not be 100% accurate in predicting the diagnosis. In fact, readers of the scans performed in the pivotal trials failed to achieve total agreement, further confirming that results of the scan cannot be 100% accurate. This is important to keep in mind when reviewing ioflupane results, considering them in the overall diagnostic and decision-making process, and in discussing them with patients.
Nevertheless, the overall error rate appears to be low. Recent audit data indicate that of 743 ioflupane cases performed at a UK National Centre of Excellence for PD over a 9-year period, there were five false-positive and two false-negative results yielding a specificity of 98.6%, sensitivity of 99.4%, positive predictive value of 98.7%, negative predictive value of 99.4% and overall accuracy of 99.1% for ioflupane result versus final clinical diagnosis.