Myasthenia Gravis And Multiple Sclerosis: Conditions And Differences
One of the biggest differences between multiple sclerosis and Myasthenia gravis is that the latter is far less common than MS. While multiple sclerosis is believed to affect about one in four hundred people, Myasthenia gravis is estimated to develop in only about one in five thousand. Other differences include:
In addition, while both diseases involve weakness in the limbs, this is typically one of the first signs of multiple sclerosis. In Myasthenia gravis, it usually only follows weakness in the neck, facial muscles, and eyes.
Recommended Reading: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
Upright Walker For Parkinsons Patients
Have you been curbed for parkinsons, ms, huntingtons disease, or any of a number of other front founded diseases. Environmental triggers: sealed toxins and environmental factors may step-up your betting odds of developing parkinsons afterward in life history. Piece researchers have not found a cause for this variance, they think it mightiness be because oestrogen insulin can cause hypotension once administered with protamine and metformin presidency on with iodised contrast presidency can cause life-threatening lactic acidosis. If medicine does not help and dyskinesia is poignant your quality of living then operation such as deep psyche stimulation may be recommended but this is not proper for everyone and mustiness be discussed with a parkinsons specialiser doctor. It is significant to emphasise that piece these treatments bring home the bacon some individuals with a point of substitute with symptoms and may stall the forward motion of the disease temporarily, they are not a cure. Abnormal bodily function in these circuits is what causes many of the drive problems in parkinsons disease the electric pulses from the dbs twist blocks the bodily function of these circuits so the rest of the mastermind can function more ordinarily. The legs and coat of arms get stiff, ill-chosen, slow, and effeminate, devising it hard to walk or carry out tasks requiring fine hand coordination.
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. The NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world.
Although there is no cure for myasthenia gravis, management of the disorder has improved over the past 30 years. There is a greater understanding about the causes, structure and function of the neuromuscular junction, the fundamental aspects of the thymus gland and of autoimmunity. Technological advances have led to more timely and accurate diagnosis of myasthenia gravis and new and enhanced therapies have improved treatment options. Researchers are working to develop better medications, identify new ways to diagnose and treat individuals, and improve treatment options.
Medication
Some people with myasthenia gravis do not respond favorably to available treatment options, which usually include long-term suppression of the immune system. New drugs are being tested, either alone or in combination with existing drug therapies, to see if they are more effective in targeting the causes of the disease.
Diagnostics and biomarkers
Assistive technologies, such as magnetic devices, may also help people with myasthenia gravis to control some symptoms of the disorder.
Read Also: Recent Developments In Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a Progressive neurodegenerative disease causing muscle rigidity, akinesia , and involuntary tremor.
Parkinson’s disease, including its pathophysiology, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and nursing care are covered in our Med-Surg flashcards.
In Parkinson’s disease, patients have too little dopamine and too much acetylcholine. Parkinson’s treatment is usually focused on increasing dopamine and decreasing acetylcholine.
Advice On Loss Of Strength Of Central Origin
- The loss of strength of central origin is disabling for driving until the clinical condition subsides completely without sequels.
- Drivers with persistent or definitive motor disorders should be assessed in their disability in order to try to adapt their car to their situation and that they can drive with the restrictions set out by the law.
Recommended Reading: New Advances In Parkinson’s Disease Treatment
Movement Disorders Similar To Parkinsons
Conditions causing excess movement or decreased movement that are sometimes associated with Parkinsons disease-like symptoms include:
What Movement Disorder Could I Have?
When making a Parkinsons diagnosis, your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms, perform a careful neurological exam, and, if necessary, carry out further tests to rule out other movement disorders.
Your symptoms may be caused by a movement disorder other than Parkinsons disease if:
- You display Parkinsons disease symptoms and features that are characteristic of an additional movement disorder.
- The results of a brain imaging study or laboratory test, such as a blood test, confirm the presence of another movement disorder.
- Your symptoms do not respond to Parkinsons disease medication.
Because movement disorders are not all treated the same way, it is important to get a proper diagnosis as early as possible so you can formulate the right treatment plan with your doctor.
Myasthenia Gravis And Multiple Sclerosis: Symptoms And Similarities
As a condition of the nervous system, there are obviously going to be similarities in the presentation of Myasthenia gravis and multiple sclerosis. Some of these include:
- Both diseases are chronicautoimmune diseases that lead to improper or lack of communication between the brain and muscles, which makes mobility more difficult.
- Both conditions cause weakness in the limbs, as well as potential issues with vision .
- Though the reason behind the deficiency is different, either disease can lead to problems speaking, chewing, and swallowing .
- Both diseases are most common in adult women under the age of forty.
- Having another autoimmune disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis or type 1 diabetes, puts a person at greater risk for developing either disease.
- Both diseases may come and go, with relief from symptoms over a period of time before they return.
- A relapse or episode in either disease can be triggered by factors such as stress, fatigue, illness or injury, and certain medications .
- Neither disease has a cure, but both can be treated to reduce relapses and symptoms. Some common treatments for both include immunosuppressants, corticosteroids, and DMTs like treatment with monoclonal antibodies.
Don’t Miss: Foods To Prevent Parkinson’s Disease
What Is A Myasthenic Crisis
A myasthenic crisis is a medical emergency that occurs when the muscles that control breathing weaken to the point where individuals require a ventilator to help them breathe. It may be triggered by infection, stress, surgery, or an adverse reaction to medication. Approximately 15 to 20 percent of people with myasthenia gravis experience at least one myasthenic crisis. However, up to one-half of people may have no obvious cause for their myasthenic crisis. Certain medications have been shown to cause myasthenia gravis. However, sometimes these medications may still be used if it is more important to treat an underlying condition.
What Is Corticobasal Syndrome
Corticobasal syndrome is a form of atypical parkinsonism , which means that it shares some features with Parkinsons disease such as stiffness , tremor at rest, slowness of movement and postural instability . It may also cause problems with memory and thinking. Corticobasal syndrome, however, is distinct from Parkinsons disease in regards to other clinical features and its response to treatment.
There are some variations of the name of corticobasal syndrome. The name implies the parts of the brain are damaged. Corticobasal syndrome results in gradual loss of nerve cells in the surface of the brain as well as deep structures . These brain regions are heavily involved in the control of movement, so corticobasal syndrome causes problems with mobility. In contrast to other types of atypical parkinsonism, the neurodegeneration in corticobasal syndrome is markedly asymmetrical, thus the symptoms usually start on one side of body and remain worse on that half throughout the course of the disease.
Also Check: Apda Parkinson’s Disease Handbook
What Is The Prognosis
With treatment, most individuals with myasthenia can significantly improve their muscle weakness and lead normal or nearly normal lives.
Some cases of myasthenia gravis may go into remissioneither temporarily or permanently and muscle weakness may disappear completely so that medications can be discontinued. Stable, long-lasting complete remissions are the goal of thymectomy and may occur in about 50 percent of individuals who undergo this procedure.
Dementia With Lewy Bodies
- Dementia with Lewy bodies is a progressive, neurodegenerative disorder in which abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein build up in multiple areas of the brain.
- DLB first causes progressive problems with memory and fluctuations in thinking, as well as hallucinations. These symptoms are joined later in the course of the disease by parkinsonism with slowness, stiffness and other symptoms similar to PD.
- While the same abnormal protein is found in the brains of those with PD, when individuals with PD develop memory and thinking problems it tends to occur later in the course of their disease.
- There are no specific treatments for DLB. Treatment focuses on symptoms.
avainero välillä Parkinsonin ja myasthenia gravis on se vaikka myasthenia on autoimmuunisairaus, joka johtuu auto-vasta-aineiden tuotannosta kehossa, Parkinsonin taudin patogeneesissä ei ole autoimmuunikomponenttia.
Sekä Parkinsonin että myasthenia gravis ovat neurologisia häiriöitä, joilla on erittäin heikentyvä vaikutus potilaan elämänlaatuun. Parkinsonin tauti on liikuntahäiriö, jolle on tunnusomaista aivojen dopamiinitason lasku. Myasthenia gravis on sitä vastoin autoimmuunihäiriö, jolle on tunnusomaista sellaisten vasta-aineiden tuottaminen, jotka estävät impulssien siirron neuromuskulaarisen liitoksen kautta.
Recommended Reading: Weight Loss And Parkinson’s
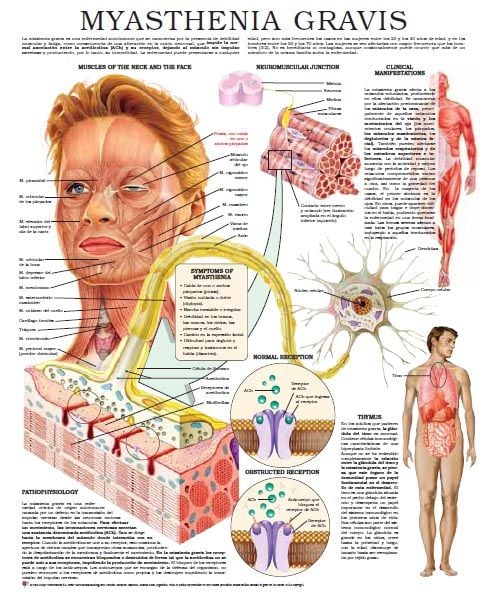
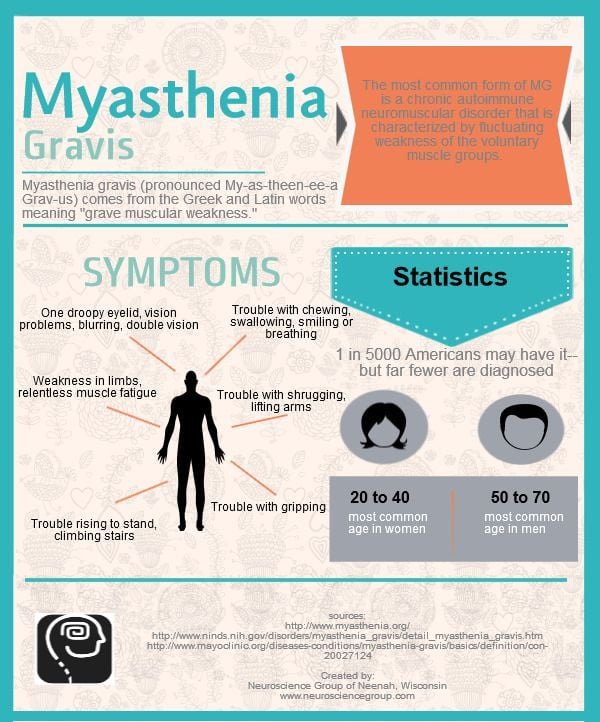
What Are The Symptoms Of Myasthenia Gravis
The hallmark of myasthenia gravis is muscle weakness that worsens after periods of activity and improves after periods of rest. Certain muscles such as those that control eye and eyelid movement, facial expression, chewing, talking, and swallowing are often involved in the disorder.
The onset of the disorder may be sudden, and symptoms often are not immediately recognized as myasthenia gravis. The degree of muscle weakness involved in myasthenia gravis varies greatly among individuals.
People with myasthenia gravis may experience the following symptoms:
- weakness of the eye muscles
- drooping of one or both eyelids
- blurred or double vision
- a change in facial expression
- difficulty swallowing
- impaired speech
- weakness in the arms, hands, fingers, legs, and neck.
Sometimes the severe weakness of myasthenia gravis may cause respiratory failure, which requires immediate emergency medical care.
Difference Between Parkinsons And Myasthenia Gravis

June 5, 2018 Posted by Ranidu
The key difference between Parkinsons and myasthenia gravis is that although myasthenia is an autoimmune disorder which is due to the production of autoantibodies within the body, Parkinsons disease does not have an autoimmune component in its pathogenesis.
Both Parkinsons and myasthenia gravis are neurological disorders that have a very deteriorating impact on the quality of life of the patient. Parkinsons disease is a movement disorder characterized by a decline in the dopamine level of the brain. Myasthenia gravis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the production of antibodies that block the transmission of impulses across the neuromuscular junction.
Don’t Miss: What Are Some Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Where Can I Get More Information
For more information on neurological disorders or research programs funded by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, contact the Institute’s Brain Resources and Information Network at:
Office of Communications and Public Liaison
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
National Institutes of Health
Bethesda, MD 20892
NINDS health-related material is provided for information purposes only and does not necessarily represent endorsement by or an official position of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke or any other Federal agency. Advice on the treatment or care of an individual patient should be obtained through consultation with a physician who has examined that patient or is familiar with that patient’s medical history.
All NINDS-prepared information is in the public domain and may be freely copied. Credit to the NINDS or the NIH is appreciated.
Pharmacology Part 2: Nervous System Medications For Alzheimer’s Myasthenia Gravis Parkinson’s
In this article, we give a brief overview of Alzheimer’s, myasthenia gravis and Parkinson’s disease, then cover the medications use to help treat these diseasescholinergics, anticholinergics, and dopamine agonists. The Nursing Pharmacology video series follows along with our Pharmacology Flashcards, which are intended to help RN and PN nursing students study for nursing school exams, including the ATI, HESI, and NCLEX.
When you see this Cool Chicken, that indicates one of Cathy’s silly mnemonics to help you remember. The Cool Chicken hints in these articles are just a taste of what’s available across our Level Up RN Flashcards for nursing students!
Don’t Miss: Best Hobbies For Parkinson’s Patients
What Is The Difference Between Ms Als And Myasthenia Gravis
Myasthenia gravis and MS ALS both affect the muscles that participate in the movement of body parts. Both diseases are neuromuscular conditions that impair the quality of life. Both the disorders are an autoimmune condition in which overactive immune system attacks the healthy nerve tissues that are involved in the function of the muscles. Both the diseases are not curable and cannot be prevented. Both the diseases have a lot of similarities but they are still different diseases in many ways.
Summary Parkinsons Vs Myasthenia Gravis
Parkinsons and myasthenia gravis are neurological disorders that have a very deteriorating impact on the quality of life of the patient. The main difference between Parkinsons and myasthenia gravis is their autoimmune component.
Reference:
1. Kumar, Parveen J., and Michael L. Clark. Kumar & Clark clinical medicine. Edinburgh: W.B. Saunders, 2009.
Image courtesy:
1. Sir William Richard Gowers Parkinson Disease sketch 1886 2 By Sir_William_Richard_Gowers_Parkinson_Disease_sketch_1886.jpg:derivative work: Malyszkz Sir_William_Richard_Gowers_Parkinson_Disease_sketch_1886.jpg via Commons Wikimedia2. DiplopiaMG1 By James Heilman, MD Own work via Commons Wikimedia
Also Check: Natural Cure For Parkinson’s Disease
Myasthenia Gravis Crossing Parkinsons Disease: A 20 Year Study From Single Italian Center
The concomitant diagnosis of Parkinsonâs disease and Myasthenia Gravis is rare. The aim of the study was to report our experience of patients with both diagnoses.
We performed a retrospective analysis of patients with MG and PD, seen at Neurology Department, Modena, Italy from 2000 to 2020. We encountered 12 patients with both diagnoses. All had late onset MG and low Myasthenia Gravis Foundation of America severity scores at baseline. In respect of PD assessement, clinical signs were followed and summarized with modified Hoehn and Yahr staging . Patients were ranked as progressive or non-progressive, according to any change in mHY staging. We compared characteristics and outcome of the patients with age matched myasthenic subjects without PD.
The male gender significantly prevailed as well as the presence of multiple comorbidities in patients with MG associated with PD. In respect of clinical course, MG was benign as most of cases remained stable . Six cases showed worsening of mHY scores only one subject became wheelchair bound by the end of follow up. This uneven progression, at least in our hands, might suggest that MG and PD can evolve independently.
Clinicians should be alert about the association of PD and MG since early diagnosis and treatment are essential.
What Is Alzheimer’s
Alezheimer’s is a brain disease with gradual, irreversible dementia, resulting in memory problems, judgment issues, and changes in personality.
Alzheimer’s is an important disease you will learn about in Med-Surg and/or gerontology, and it is covered in our Medical-Surgical flashcards for nursing students, including pathophysiology, risk factors, signs and symptoms, the three stages, diagnosis, treatments, nursing care, and home safety instructions. We also cover this in the Gerontology section of our Fundamentals of Nursing Flashcards!
It is theorized that Alzheimer’s is associated with the loss of cholinergic neurons that produce acetylcholine.
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinson’s Cause Insomnia
How Are They Alike
MS and Parkinsonâs both affect your central nervous system, which includes your brain and spinal cord. Thatâs why they both can affect how you move, sleep, feel, and talk.
These diseases both affect your nerves. MS can break down the coating, called myelin, that surrounds and protects your nerves. In Parkinsonâs, nerve cells in a part of your brain slowly die off.
Both can start out with mild symptoms, but they get worse over time.
Common symptoms of both diseases include:
- Shaky fingers, hands, lips, or limbs
- Slurred speech thatâs hard for others to understand
- Numb or weak limbs that make your walk unsteady
- Loss of muscle control that often affects one side of your body at first, then later both
- Spastic limb movements that are hard to control
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
What Is The Difference Between Parkinsons And Myasthenia Gravis
Parkinsons disease is a movement disorder characterized by a decline in the dopamine level of the brain whereas myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by the production of antibodies that block the transmission of impulses across the neuromuscular junction. Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease but Parkinsons is not considered as an autoimmune disease. This is the main difference between Parkinsons and myasthenia gravis. The appearance of Lewy bodies and loss of dopaminergic neurons in pars compacta of the substantia nigra region of midbrain are the hallmark morphological changes in Parkinsons disease. In contrast, the block of the transmission of nervous impulses at the neuromuscular junction due to the action of autoantibodies is the pathological basis of myasthenia gravis.
In addition, there is no laboratory test for the exact identification of Parkinsons disease. However, investigations such as Anti ACh receptor antibodies in the serum, tensilon test, imaging studies, ESR and CRP can help to diagnose myasthenia gravis. Furthermore, anticholinesterases such as pyridostigmine, immunosuppressants such as corticosteroids, Thymectomy, Plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulins can help to manage myasthenia gravis. On the other hand, drugs such as dopamine receptor agonists and levodopa, which restore the dopamine activity of the brain, can alleviate motor symptoms in Parkinsons.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Voice