Aggregation And Release Of
In the central nervous system , -syn is mainly located at the presynaptic terminal. Although the physiological functions of -syn are not fully understood, several studies have shown that it is involved in the regulation of synaptic function and plasticity, vesicle transport, and neurotransmitter release . While it is generally accepted that -syn exists as a monomer in its native state, when interacting with other proteins or under some specific stress-induced conditions, -syn may aggregate or undergo conformational changes . Lewy bodies are one of the pathological features of PD, mainly composed of -syn aggregates. A number of studies have shown that point mutations of SNCA , as well as genomic duplications or triplications containing -syn locus, can enhance the expression of pathogenic -syn, contributing to -syn aggregation and accumulation . In addition, the imbalance between the synthesis and clearance of -syn accounts for further aggregation of -syn . Degradation or clearance of -syn in the cytoplasm is mainly undertaken by the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy-lysosome pathway. The dysfunction of these degradation pathways will lead to aggregation of -syn, which will eventually contribute to the pathogenesis of PD . Excessive aggregation of -syn or failure to clear it from the cell will result in its secretion and release, which can result in neuron toxicity and -syn propagation.
Priming And Activation Of The Nlrp3 Inflammasome In Pd
While widespread inflammasome activation has been confirmed in both human PD and preclinical animal models , the mechanisms by which priming and activation of the inflammasome are triggered and/or become dysregulated remain poorly defined. In most immune cells, activation of NLRP3 is closely regulated and requires an essential priming step, which facilitates NFB-mediated upregulation of the various inflammasome components that are necessary to license assembly of the inflammasome complex when the relevant activation signal is present . Although the mechanisms by which the inflammasome priming and activation occurs in PD have not been fully elucidated, emerging evidence suggests that many of the known pathological triggers and mechanisms linked to PD are likely to be key players in this process.
Clinical Studies And Epidemiological Data On Inflammasome Activation Markers In Pd
Extensive inflammasome activation has been detected in the postmortem brains of PD patients, with elevated NLRP3 expression at both protein and mRNA levels . In a cohort of 17 PD patients, histological studies indicated significantly higher expression of NLRP3 in the substantia nigra compared to 11 healthy controls over 50% of cells were NLRP3 positive compared to only 20% of cells in healthy controls. Complementary mRNA data show an approximate 2-fold increase in gene expression of NLRP3 in mesencephalic tissues of PD patients . Similar results are observed in histological studies of ASC expression, with over twice as many cells expressing ASC in postmortem mesencephalic tissues of PD patients . Additionally, significant increase, 1-fold, in protein expression of cleaved caspase-1 p20 and ASC is observed in PD substantia nigra tissue compared to aged matched healthy controls .
Don’t Miss: Did Katharine Hepburn Have Parkinson’s
Structure Activation And Regulation Of Nlrp3 Inflammasome
Activated NLRP3 inflammasomes recruits the ASC, leading to the formation of mature caspase-1, thereby inducing the maturation and release of pro-IL-1ß and IL-18 . In addition, the activation of NLRP3 can also trigger pyroptosis. This is a kind of GSDMD-dependent programmed inflammatory cell death, which differs from apoptosis and necroptosis . NLRP3 activation induces the cleavage of GSDMD upon activated caspase-1 into its functional active form which can insert into the plasma membrane and form pores, leading to cell swelling, membrane rupture, and the further release of IL-1ß and IL-18 . Of note, several studies demonstrate caspase4/5/11 can also act on GSDMD and induce pyroptosis through directly sensing LPS, which is so-called caspase-1-independent pyroptosis .
2.3.1 The Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in PD
What Should I Know Before Participating In A Clinical Study
Read Also: What Is Stage 5 Parkinson’s
Why Should I Participate In A Clinical Study
We can only reach breakthroughs in treatment and care if people participate in the studies.
Participating is safe and can help you
Every clinical study is reviewed thoroughly before your doctor asks you to participate. Clinical trials carry some risks, but your doctor is required by law to explain the risks to you clearly and make sure that you understand them. If your doctor tells you about the risks of participating in the study, ask yourself, What are the risks of not participating in the study? Most of the time, if you balance the possible benefits from participating against the risks, it is about the same as the risks of not being in the study.
On the other hand, the study may be of a new drug or treatment that could help you. If you dont participate, it may be years before you have a chance to try that drug.
Some people do not participate because there is no guarantee they will get the experimental therapy they might get the placebo. Again, think carefully about the risks and benefits of entering the study and getting the new treatment, entering the study and getting the placebo or not entering the study at all.
Your participation can help others
If you have PD or any other disease, the drugs, procedures and therapies you use now were scientifically tested, likely by thousands of volunteers. Participating in a clinical trial is your way to pay it forward for people diagnosed with Parkinsons in the future.
An Inhibition Of Assembly Signal And The Activation Signal Of Nlrp3 Inflammasome
Microglial activation and neuroinflammation have been proposed as the components of PD. NLRP3 inflammasome activation can partially elucidate microglia-mediated inflammation. Moreover, an increasing number of investigations are aimed at targeting NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation in activated microglia to find a therapeutic avenue for PD . The translocation of NF-B into the nucleus initiates the transcription of NLRP3 components, pro-IL-1, and pro-IL-18. In addition, mitochondrial impairment and the synthesis of ROS lead to the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. -syn aggregates simultaneously stimulates the two steps of NLRP3 activation. Thus, the negative regulation or blockage of the NF-B pathway and ROS synthesis may provide an avenue to ameliorate activated NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation. In addition, specific inhibitors of the NLRP3 inflammasome also exert beneficial effects.
3.3.1 The Inhibition of NF-B Pathway
Table 4 Molecules targeting NLRP3 and two signals of NLRP3: NF-B pathway and synthesis of ROS.
3.3.2 ROS Synthesis Blockage
Don’t Miss: How Long Can A Parkinson Patient Live
Targeting The Inflammasome In Parkinsons Disease
- 1Programme in Emerging Infectious Diseases, DukeNUS Medical School, Singapore, Singapore
- 2Department of Neurology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
- 3Department of Research, National Neuroscience Institute, Singapore, Singapore
- 4Neuroscience and Behavioural Disorders Program, DukeNUS Medical School, Singapore, Singapore
Parkinsons disease is one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases in which neuroinflammation plays pivotal roles. An important mechanism of neuroinflammation is the NLRP3 inflammasome activation that has been implicated in PD pathogenesis. In this perspective, we will discuss the relationship of some key PD-associated proteins including -synuclein and Parkin and their contribution to inflammasome activation. We will also review promising inhibitors of NLRP3 inflammasome pathway that have potential as novel PD therapeutics. Finally, we will provide a summary of current and potential in vitro and in vivo models that are available for therapeutic discovery and development.
Ask Questions And Share Your Knowledge Of Parkinsons Disease In Our Forums
We found a key immune system target, called the NLRP3 inflammasome, lights up in Parkinsons patients, with signals found in the brain and even in the blood, said Woodruff, who is an associate professor in the faculty of medicine at Queensland.
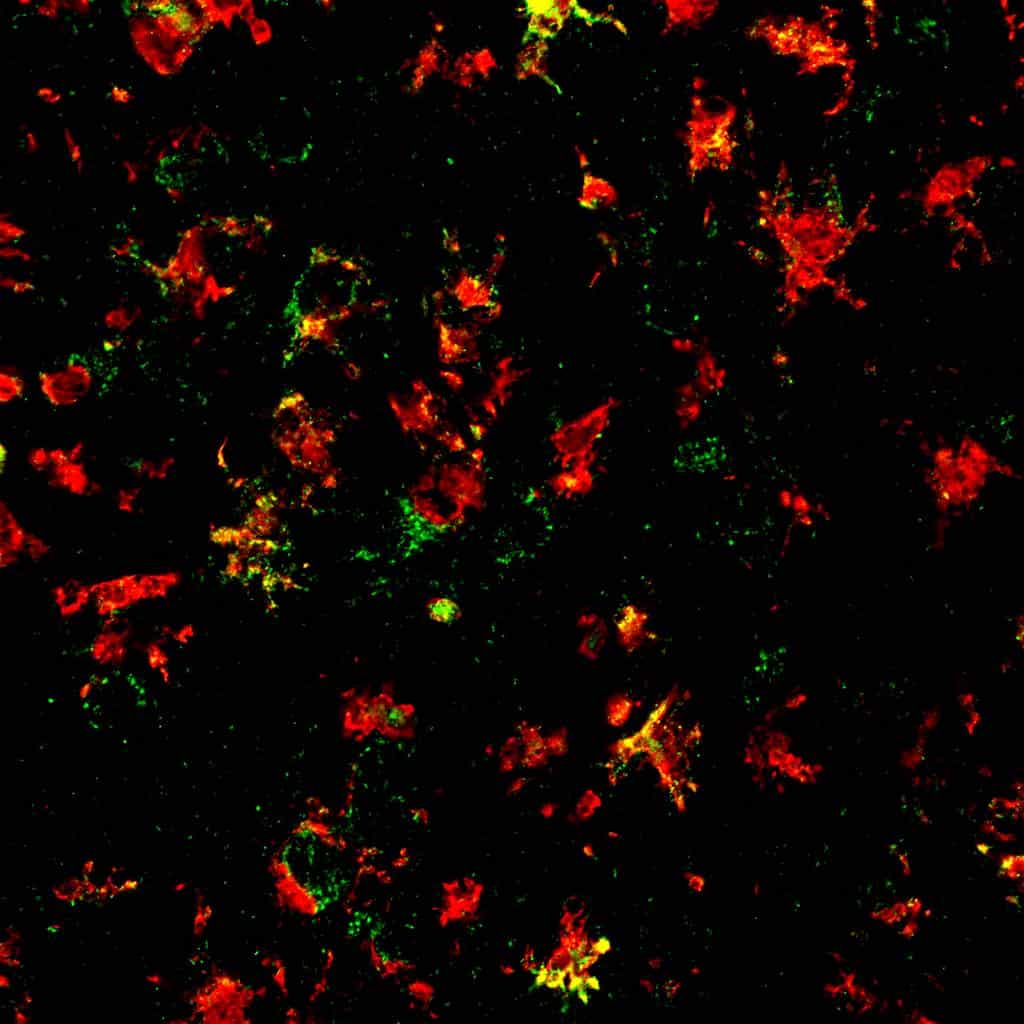
An activated NLRP3 inflammasome was associated with the release of the pro-inflammatory molecule interleukin -1beta and ASC protein, which is also involved in the inflammatory response, in mouse cells, along with increased levels of activated caspase-1 an enzyme responsible for the generation of active IL-1beta in the substantia nigra of Parkinsons patients.
The team found that low doses of MCC950, a small-molecule inhibitor of NLRP3, completely suppressed inflammasome activation in mouse microglia as well as ASC protein release. Importantly, once-daily, oral administration of MCC950 inhibited inflammasome activation, alpha-synuclein clumping, and loss of dopamine-producing neurons in a mouse model of Parkinsons disease, while also easing their motor deficits.
These findings suggest that microglial NLRP3 may be a sustained source of neuroinflammation that could drive progressive dopaminergic neuropathology and highlight NLRP3 as a potential target for disease-modifying treatments for , the researchers wrote in the study.
Gordon added that the team is now exploring approaches such as repurposing medications to target processes implicated in inflammasome-mediated disease progression.
You May Like: Cbd And Parkinson’s Disease
Immune Cell Subsets Linked To Inflammasome Activation In Pd
In a cohort of 43 PD patients and 24 healthy controls, NLRP3 expression was elevated in activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells of the PD patients, indicating increased caspase-1 and mature IL1 compared to internal controls such as GAPDH. This indicates that peripheral immune cells are primed in PD for activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Additionally, -synuclein levels in PD patients blood are higher compared to healthy controls when compared, there was a positive correlation between -synuclein in the blood and the increase of inflammasome markers in PD patient PBMCs. This was additionally correlated to the Hoehn and Yahr staging scale which reflects on PD progressive symptoms .
Platelets play a key role in inflammasome regulation, boosting NLRP3 activation in macrophage cells. In cell cultures, co-culturing of human macrophages, neutrophils, or monocytes with platelets significantly increased IL1 production resulting from a combination of LPS, ATP, and Nigericin treatments. Though not yet fully understood, NLRP3 transcription and inflammasome activation is enhanced because of factors released by platelets .
Indirect Inhibitors Of Nlrp3
Apart from direct NLRP3 inhibition, several other compounds are shown to regulate NLRP3 indirectly via modulating its transcription, inflammasome priming, protein expression or post-translational modifications. Therefore, these compounds suppress NLRP3 activity and IL-1 release independently of their direct effect on any components in the NLRP3 inflammasome.
NLRP3 driven neuroinflammation has been found to be critical in neurodegenerative diseases. Though some of the NLRP3 inhibitors are entering early clinical stages, more investigations are required to robustly test the NLRP3 inhibitors efficacy and discover new inhibitors targeting inflammasome pathway. Given that the involvement of inflammasome NLRC4, AIM2, and NLRP1 in diseases is emerging, molecules that block multiple inflammasome is a promising therapeutic strategy, for instance inhibiting ASC formation. Hence, targeting multiple layers of inflammasome will be a promising next generation anti-inflammatory approach to effectively control excessive inflammation.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson Disease Treatment In India
Microglial Activation In Pd
Microglia are resident mononuclear phagocytes of the central nervous system. They serve as immunological surveillants in healthy individuals, maintaining the homeostasis of the brain microenvironment by shaping neural circuits, fine-tuning synapse plasticity, and interacting with neurons . During injury, microglia serve as immune defenders, and are responsible for phagocytosis and the elimination of microbes, dead cells, and protein aggregates by expressing a wide range of immune receptors . However, it remains unclear whether they play a beneficial or detrimental role in neurodegenerative diseases, particularly in PD.
Effects Of Osteopathic Manipulative Treatment On Gait Biomechanics In Parkinson’s Disease
Sorry, in progress, not accepting new patients
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder that puts individuals at high risk for injuries and long-term disabilities as a result of a fall or other trauma. Injuries sustained from falls account for many deaths as well as thousands of hospital admissions and nursing home stays every month. Quality of life and even longevity itself is reduced due to the resulting surgeries, immobility, complications and even cognitive impairments that can follow. The proposed study will explore beneficial impact of a treatment modality that may significantly reduce the morbidity of this condition by comparing 6 weeks of OMT versus 6 weeks light touch intervention versus 6 weeks care as usual to improve gait in individuals with PD. Gait will be measured at mid-treatment, post-treatment and 4-week follow-up.
La Jolla, California
Read Also: Treatment For Parkinson’s Psychosis
Why Are Clinical Studies Important
All types of research are critical for improving care. Basic science research tests done in a laboratory can help us learn more about the human body and the causes of PD. Basic research can also point scientists in promising directions as they develop and refine treatments.
Clinical studies are essential because through them, discoveries made in the laboratory can help people with PD today and in the future. The Parkinsons Foundation is at the forefront of PD research and clinical studies are central to our vision. The Foundations Parkinsons Outcomes Project was the first study of its kind and continues to be the largest clinical study. Every year, insights from the study help optimize PD care, leading to better quality of life for people with PD today and better health for people with PD tomorrow.
Parkinsons Drug Makers Target Inflammasome
Hyperstimulated immune cells in the brain are emerging as a hallmark feature of most neurodegenerative disordersand Parkinsons disease is no exception. In patients with the progressive movement disorder, those immune cells, called microglia, react to the presence of -synuclein-containing protein clumps by dialing up inflammatory signals that not only contribute to the gradual death of dopamine-producing neurons but also recruit more pathological proteins, creating a vicious cycle of neuroinflammation and -synuclein buildup in the brain.
The inflammasome could be driving the progressive neuronal loss seen in the brains of Parkinsons disease patients. .
To break the cycle, a Dublin-based startup called Inflazome is aiming to disrupt the NLRP3 inflammasome, a multiprotein complex that serves as a sensor of cell stress and abnormal proteins. Last year, the companys foundersMatt Cooper, a chemist from the University of Queensland in Brisbane, Australia, and Luke ONeill, an immunologist at Trinity College Dublindemonstrated a clear link between -synuclein aggregation and inflammasome activation in the brain microglia of mice with a Parkinsons-like condition. Most notably, they showed the defect could be remedied with an NLRP3 inhibitor called MCC950.
According to Cooper, who serves as CEO, Inflazome will likely first pursue an indication outside of the central nervous system but, of the 54 diseases on the companys long list, Parkinsons remains a top priority.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Freezing And Driving
The Relationship Between Tlrs
TLRs are pattern recognition receptors located on the cell membrane that can induce a series of signal cascades to activate an immune response to stimulation in vivo and in vitro after recognition of PAMPs and DAMPs . Microglia can express all members of the TLR family, with TLR2 and TLR4 being the most widely studied . The pathological -syn released by neurons, as an endogenous DAMPs, can act as ligands of TLR2, and then are transported to lysosomes for degradation or participate in the spread of pathogenic -syn . Studies have found that in TLR2-/-mice, -syn accumulation in neurons is reduced, accompanied by a decrease in microgliosis and astrogliosis . The -syn released by neurons can also be taken up by astrocytes through TLR4, causing the release of inflammatory factors and further promoting the activation of microglia . TLR4 on the surface of microglia are involved in the phagocytosis of -syn, because TLR4 ablation cause damaged phagocytosis of -syn ,and the absence of TLR4 leads to the inhibition of inflammasome activation .
Inflammasome Activation In Parkinsons Disease
Issue title: The immune System in Parkinsons Disease
Guest editors: Bastiaan R. Bloem, Patrik Brundin, Eng King Tan, Ashley Harms, Cecilia Lindestam Arlehamn and Caroline Williams-Gray
Article type: Review Article
Authors: Jewell, Shannona | Herath, Ashane M.a | Gordon, Richarda b *
Affiliations: UQ Centre for Clinical Research, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia | School of Biomedical Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Richard Gordon, PhD, DABT, 508 UQCCR Building 71/918, Royal Brisbane Hospital Campus, Brisbane, Queensland 4029, Australia. Tel.: +61 7 33466081 E-mail: .
Keywords: NLRP3, Parkinsons disease, inflammasome, immune system, inflammation, microglia, neurodegeneration
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-223338
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 12, no. s1, pp. S113-S128, 2022
Abstract
Don’t Miss: Most Common Parkinson’s Medications
In Vivo Models Of Parkinsons Disease
Though in vitro models provide significant convenience and streamlining for PD research, the research on PD pathogenesis and the screening for potential therapeutics cannot be substantiated and validated without robust PD animal models. The common PD animal models involve the use of neurotoxins such as MPTP , 6-OHDA , and pesticides/herbicides including rotenone, paraquat, and maneb . Besides chemical inducers, transgenic animal models are also used to investigate the phenotypes of specific mutations in PD-related genes such as PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 , DJ-1, and Parkin . Overexpression of wild-type or variants of -synuclein is also a strategy commonly explored to model the important role of -synuclein in PD pathogenesis .