What Is Lewy Body Dementia
LBD is a chronic, neurodegenerative cognitive disorder, and is the third most common form of dementia. Unlike most other forms of dementia, people with LBD have Lewy bodies in the brain. Lewy bodies are abnormally-folded proteins found in the nerve cells of the brain.2,3
Patients with LBD may experience memory/cognitive problems, visual hallucinations, and Parkinsonism symptoms.4
What Other Things Help
There are various ways to help a person with DLB. Speech therapy may help improve communication between people with DLB and others. Physical therapy may help strengthen and stretch stiff muscles and help to prevent falls.
Research has shown that physical exercise helps to enhance brain health and improves mood and general fitness. A balanced diet, enough sleep, and limited alcohol intake are other important ways to promote good brain health. Other illnesses that affect the brain, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol, should also be treated if present.
Lewy Bodies Dementia And Parkinsons What Does It All Mean
Here are two common scenarios that may sound familiar:
Scenario 1A patient develops a series of neurologic symptoms, is evaluated by a neurologist and is told that she has Parkinsons disease . She then visits another neurologist for a second opinion and is told she has Lewy Body Dementia .
Scenario 2A patient has his first visit with his neurologist and is told that he has PD, at a subsequent visit the diagnosis is changed to Parkinsons disease dementia , and at a follow up visit the diagnosis is changed yet again to Dementia with Lewy Bodies .
Both of these situations understandably cause great uncertainty and frustration.
Don’t Miss: Is There A Medical Test For Parkinson’s Disease
Symptoms Of Dementia With Lewy Bodies
People with dementia with Lewy bodies may have:
- hallucinations seeing, hearing or smelling things that are not there
- problems with understanding, thinking, memory and judgement this is similar to Alzheimer’s disease, although memory may be less affected in people with dementia with Lewy bodies
- confusion or sleepiness this can change over minutes or hours
- slow movement, stiff limbs and tremors
- disturbed sleep, often with violent movements and shouting out
- fainting spells, unsteadiness and falls
These problems can make daily activities increasingly difficult and someone with the condition may eventually be unable to look after themselves.
Understanding Lewy Body Dementia
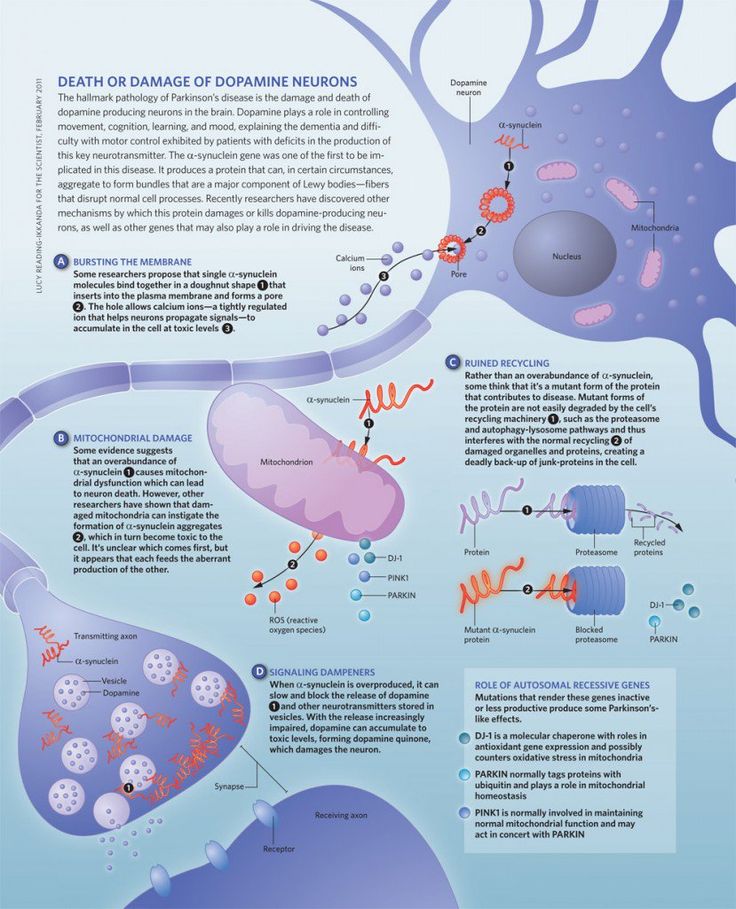
Lewy body dementia symptoms are so similar to those of other forms of dementia that LBD can be misdiagnosed. This might make more sense when you consider that there are many types of dementia.
It may help to think of dementia as one large “umbrella” that slowly robs people of their ability to think, talk, remember, and use their bodies. Many diseases crowd underneath this umbrella, including:
- Alzheimers disease
- Struggle with incontinence
With dementia with Lewy bodies, cognitive changes may appear earlier than, about the same time, or shortly after any physical changes surface.
You May Like: Theracycle For Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s Dementia Vs Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Have you ever wondered if there was any difference between dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease dementia? If you’ve ever heard the symptoms of these two disorders, they sound surprisingly alike. That’s because they’re both types of Lewy body dementia: dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease dementia .
What Happens In Dlb
People with DLB may have trouble focusing, remembering things, staying awake during the day, or staying asleep at night. They may become more frustrated or confused because of the lack of sleep. They may also hallucinate and see people, objects, or animals that are not there.
Some people with DLB will need help with walking, while others may have hunched posture or trouble using their hands and feet because of stiff muscles. People with DLB may appear to be better and need less help on some days, only to become worse and more confused again and need more help the next day or in a few days. This is because their energy level and focus will vary.
DLB is a disease that changes with time. A person with DLB can live for many years with the disease. Research suggests that a person with DLB may live an average of 57 years with the disease, although this can vary from person to person.
You May Like: Tardive Dyskinesia And Parkinson’s
Coping With Cognitive Changes
Some medications used to treat Alzheimer’s disease also may be used to treat the cognitive symptoms of LBD. These drugs, called cholinesterase inhibitors, act on a chemical in the brain that is important for memory and thinking. They may also improve hallucinations, apathy, and delusions. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved one Alzheimer’s drug, rivastigmine, to treat cognitive symptoms in Parkinson’s disease dementia. Several other drugs are being tested as possible treatments for LBD symptoms or to disrupt the underlying disease process.
Managing The Effects Of Dementia With Lewy Bodies
A person with dementia with Lewy bodies might:
- have recurring visual hallucinations see things that are not there
- experience disturbed sleep known as Rapid Eye Movement sleep disorder, in which people are restless and can experience intense dreams/nightmares
- experience sudden changes and fluctuations in alertness people may stare blankly into space for periods of time, seem drowsy and lethargic and spend a lot of time sleeping
- have slowed movement, difficulty walking, shuffling or appear rigid
- experience tremors usually in the hands whilst at rest
- have problems with balance and be prone to falls
- bladder and bowel problems
- difficulties with swallowing
Memory is often less affected than with other types of dementia but people may be at more risk of mood and behaviour changes such as apathy, anxiety, depression, delusions and paranoia. One type of delusion, known as Capgras syndrome, in which the person believes that a friend or relation has been replaced by an imposter can be particularly difficult for families. Other symptoms may include changes in blood pressure, body temperature and impaired sense of smell.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease And Paraquat
What Is The Life Expectancy For People With Lewy Body Dementia
The average life expectancy of Lewy body dementia is five to eight years after the initial diagnosis. But some people with LBD live up to 20 years after their diagnosis.
This short average life expectancy could be due to a lack of knowledge regarding LBD among healthcare providers and the population and difficulty in distinguishing it from other similar conditions. This often leads to a delay in diagnosis, which delays the onset of specific therapy.
Diagnosing Lewy Body Dementia: For Professionals
Lewy body dementia can be difficult to diagnose. Talking to both patients and caregivers helps doctors make a diagnosis. It is important to ask the patient and their care partners about any symptoms involving thinking, movement, sleep, behavior, or mood. Certain medications can worsen LBD symptoms be aware of all current medications and supplements the patient is taking.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is often hard to diagnose because its early symptoms may resemble those of Alzheimer’s disease or a psychiatric illness. As a result, it is often misdiagnosed or missed altogether. As additional symptoms appear, making an accurate diagnosis may become easier.
The good news is that doctors are increasingly able to diagnose LBD earlier and more accurately, as researchers identify which symptoms and biomarkers help distinguish it from similar disorders.
Visiting a family doctor is often the first step for people who are experiencing changes in thinking, movement, or behavior. If a persons primary doctor is not familiar with LBD, they may have patients seek second opinions from specialists, like a geriatric psychiatrist, neuropsychologist, or a geriatrician to help diagnose LBD. If a specialist cannot be found in your community, ask the neurology department at a nearby medical school for a referral. Neurologists generally have the expertise needed to diagnose LBD.
Difficult as it is, getting an accurate diagnosis of LBD early on is important so that a person:
Also Check: Diagnostics For Parkinson’s Disease
Treating Movement Symptoms In Lewy Body Dementia
LBD-related movement symptoms may be treated with medications used for Parkinson’s disease, called carbidopa-levodopa. These drugs can help make it easier to walk, get out of bed, and move around. However, they cannot stop or reverse the disease itself. Side effects of this medication can include hallucinations and other psychiatric or behavioral problems. Because of this risk, physicians may recommend not treating mild movement symptoms with medication. Other Parkinson’s medications are less commonly used in people with LBD due to a higher frequency of side effects.
People with LBD may benefit from physical therapy and exercise. Talk with your doctor about what physical activities are best.
How Lewy Body Dementia Progresses

Lewy body dementia and Alzheimer’s disease are both forms of dementia. Lewy body dementia, however, progresses somewhat differently from Alzheimer’s disease. Notably, the symptomsespecially memory losscan fluctuate greatly with LBD. Alzheimer’s tends to worsen more steadily.
One of the hallmarks of Lewy body dementia is the fluctuation of cognitive functioning. Often, a person may function fairly well one day and be totally disengaged with a profound loss of memory the next.
Understanding this variation in cognition can be helpful for caregivers. Without this knowledge, it may seem like the person with Lewy body dementia is “forgetting” on purpose.
This fluctuation can also make it feel like the person is moving back and forth from one stage to another. In reality, the variation in functioning is a normal feature within each stage of the disease.
Read Also: Mrna Vaccine And Parkinson’s Disease
How Does Lewy Body Disease Progress
Lewy body disease differs from Alzheimers disease in that the progression of the disease is usually more rapid. However, like Alzheimers disease it is a degenerative condition, eventually leading to complete dependence. Death is usually a result of another illness, such as pneumonia or an infection. The average lifespan after the onset of symptoms is about seven years.
How Is Lewy Body Dementia Diagnosed
There are no medical tests that can diagnose Lewy body dementia with 100% accuracy. Specialists, including neurologists, geriatric psychiatrists, neuropsychologists and geriatricians, make the diagnosis of probable LBD based on the combined results of tests and patient symptoms.
Your healthcare provider will perform a thorough neurological and physical examination. You or your loved one will also complete mental status and neuropsychological tests. These tests check thinking abilities, including memory, word-finding, attention and visual-spatial skills. Your doctor will ask you and your family about your mental status and the history of your symptoms. Be sure to tell your healthcare provider of any physical, cognitive, memory, emotional, behavioral, movement, sleep or physical changes you or your loved one is having. Also, tell your healthcare provider about any of your current medications, supplements, vitamins, herbal products and frequently used over-the-counter products. These will be reviewed to see if they might be a cause of your or your loved ones symptoms.
Depending on your symptoms, your doctor may also test your blood. If your doctor needs more information, brain imaging studies may be performed.
If you have cognitive deficiency severe enough to impair daily life in the presence of any following clinical features, your doctor may suspect diagnosis of LBD:
Read Also: Ed Begley Jr Parkinson’s
Medications At The End Of Life
Many participants described stopping DLB medications near EOL. Occasionally this was associated with a decline:
I would swear in a court of law that the galantamine worked for her And when I couldnt get her to take it is really when I started noticing the decline.
Hospice commonly provided morphine for pain, breathing, or overall comfort. Many participants felt that morphine resulted in a peaceful death, but several participants described morphine as insufficient to address pain or causing paradoxical symptoms. Often hospice needed to supplement morphine with benzodiazepines. Multiple participants described using haloperidol from hospice comfort packs. In one case, this resulted in a severe reaction:
He looked at the strings hanging down from the overhead lights and he thought they were a noose. I mean, it wasnt anything you know, anything I was worried about. I was just relating to how things had been going. And she suggested Haldol. And I didnt research it About two, two and a half hours since he had his Haldol He was suddenly sitting upright Every muscle in his body was clenched. His mouth was clenched. It was opening and closing, opening and closing. His tongue was thrusting out. He almost bit his tongue off at one point and he was groaning and moaning, and he was in terrible pain His temperature skyrocketed From there, his kidneys shut down, and he was gone by Tuesday morning.
Dont Miss: Bicycle Therapy For Parkinsons Disease
Caring For A Person With Lewy Body Dementia
On this page:
As someone caring for a person with Lewy body dementia , you will take on many different responsibilities over time. You do not have to face these responsibilities alone. Many sources of help are available, from adult day centers and respite care to online and in-person support groups.
Below are some actions you can take to adjust to your new roles, be realistic about your situation, and care for yourself.
You May Like: The 4 Classic Features Of Parkinson’s Disease Are
Are There Medicines To Treat Dlb
Though there is no cure for DLB yet, there are medications that help manage the symptoms. These medications are called cholinesterase inhibitors, and they can help if a person with DLB is having memory problems. Some examples of these medicines are donepezil, rivastigmine and galantamine. If a person with DLB has movement symptoms they may be treated with medications used for Parkinsons disease, such as levodopa. Sleep problems may be managed by sleep medications including melatonin.
Because people with DLB are usually very sensitive to medications, any new medication, even one that is not being used for the brain, needs to be reviewed with the persons provider to avoid potential contraindication.
Surgical Intervention For Patients With Lewy Body Dementia
Surgical interventions are a common area of concern for patients and caregivers. Dementia in and of itself, and a diagnosis of LBD in particular, does not preclude necessary surgical interventions. This can become more of a gray area when optional procedures such as knee or hip replacements are considered. Clearly, arthritic joints can severely limit QOL but there is a balance when considering potential repercussions from anesthesia and the rehabilitation potential with a pre-existing cognitive and functional impairment. The relationship between general anesthesia and LBD specifically has not been robustly examined. Patients with LBD may respond poorly to certain anesthetics and experience postoperative delirium and/or functional decline . Patients with Parkinsons disease need careful oversight of their drug dosing regimen so it is impacted as little as possible pre- and postoperatively . A discussion with both the surgeon and anesthesiologist prior to surgery about the LBD diagnosis is prudent.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s And Freezing Up
Parkinsons Disease With Dementia Versus Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Some patients with Parkinsons disease experience no or only subtle cognitive decline, and their primary limitation is their motor disorder. However, other patients with Parkinsons disease develop dementia as a consequence of the disease. When dementia develops after an established motor disorder, we call the disease Parkinsons disease with dementia . In contrast, when dementia develops prior to or at the same time as the motor disorder, we call the disease DLB. Although the initial sequence of symptoms differs in PDD and DLB, as the disorders progress, the symptoms and the underlying brain changes are much more similar than they are different. As such, many researchers and clinicians think of PDD and DLB as being on a continuum of a similar disease process rather than as two distinct entities.
Dementia With Lewy Bodies And Parkinson Disease Dementia
, MD, PhD, Department of Neurology, University of Mississippi Medical Center
Dementia with Lewy bodiesParkinson disease dementia
Dementia is chronic, global, usually irreversible deterioration of cognition.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is the 3rd most common dementia. Age of onset is typically > 60.
Lewy bodies are spherical, eosinophilic, neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions composed of aggregates of alpha-synuclein, a synaptic protein. They occur in the cortex of some patients who have dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurotransmitter levels and neuronal pathways between the striatum and the neocortex are abnormal.
Lewy bodies also occur in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson disease Parkinson Disease Parkinson disease is a slowly progressive, degenerative disorder characterized by resting tremor, stiffness , slow and decreased movement , and eventually gait and/or… read more , and dementia may develop late in the disease. About 40% of patients with Parkinson disease develop Parkinson disease dementia, usually after age 70 and about 10 to 15 years after Parkinson disease has been diagnosed.
Both dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease dementia have a progressive course with a poor prognosis.
Also Check: Parkinsonian Syndrome Vs Parkinson’s Disease
Common Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
The disease of Lewy Body Dementia affects cognitive response, changes physical and sleep pattern along with changing behavioral features. Some people may start developing the disorder in movement in the initial stage that further leads to dementia. This is often termed as Parkinsons disease dementia.
Another group of people may start developing cognitive disorder with two or more distinctive features of dementia. There are very few people that come up with neuropsychiatric symptoms. These include hallucinations, behavioral problems, and complex mental activities.
Generic symptoms of Lewy Body Dementia include:
- Impaired thinking like loss of execution, planning, processing and/or ability to understand visual information
- Fluctuation in alertness, attention, and cognition
- Sudden tremors, stiffness, and difficulty in walking
- Changes in bodily functions like blood pressure, temperature regulation bowel and bladder function.