What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Hospice Eligibility For Parkinsons Disease
Due to the progressive nature of Parkinsons disease, it can be challenging for families to know when their loved one is eligible for the support of hospice care. If a loved one has been diagnosed with six months or less to live or if they have experienced a decline in their ability to move, speak, or participate in the activities of daily living without caregiver assistance, it is time to speak with a hospice professional about next steps.
The Progression Pf Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons develops differently in each patient. Some deteriorate to the end stage of Parkinsons rapidly, while others remain strong and active for years, and theres no clear explanation for why.
While exercise and physical therapy can slow disease progression, theres no known cure. Even the healthiest patients will eventually decline until the end stage of Parkinsons, when they are left completely dependent on family and caretakers.
For those with loved ones whove been diagnosed with Parkinsons, it helps to know the road ahead. An awareness of whats to come makes it easier to offer help as conditions decline, and ask for help when they become too much to manage alone.
Recommended Reading: How To Slow Parkinson’s Disease
Weeks Before Death Symptoms
Several weeks before death, your loved one may start exhibit a range of behavioral changes relating to their sleeping patterns, eating habits and sociability. They may begin to sleep more often and for longer periods. They will start to refuse foods that are difficult to eat or digest, but eventually they will refuse all solid foods. Do not try to force them to eat, as it will only bring discomfort to them. Your loved one may enjoy ice during this time, since it will keep them cool while also hydrating them.
Unfortunately, your loved one may become withdrawn, less active and less communicative. They may spend more time alone introspecting and may turn down company. Some also appear to become comatose and unresponsive, but this is a symptom of withdrawal. Your loved one can still hear you, so speak in a calm, reassuring voice while holding their hand. Children may become more talkative, even if they withdraw from other activities. Its important to let your loved one set their own pace during this time. Your loved one may also start to use metaphorical language, which could be a way of coping with death. It may also be used to allude to a task they feel they need to accomplish, such as seeking forgiveness.
Common symptoms in this period also include physical changes, such as:
- Chronic fatigue
- Swelling of the abdomen, such as edema or ascites
Which Medications Can Make Confusion And Hallucinations Worse

As PD progresses, non-motor symptoms including psychosis and hallucinations become more prominent both for the patient and caregivers.9 Dopaminergic medication can exacerbate these symptoms and this can be reduced through a last in, first out approach. 27,28 Medications that have an anticholinergic effect also may cause or worsen acute confusion and the anticholinergic burden in the patients medication history should be considered.29
Don’t Miss: Primidone For Parkinson’s Disease
If You Live In South Jersey And Have Questions About The Final Stages Of Parkinsons Disease Or Hospice Care For Your Loved One Please Call Samaritan At 229
Samaritan is a member of the National Partnership for Healthcare and Hospice Innovation, a network of not-for-profit hospice and palliative providers across the country. If you know someone outside of our service area who is living with advanced illness and can benefit from hospice or palliative care, please call 1 -GET-NPHI for a referral to a not-for-profit provider in your area.
I Decline In Clinical Status Guidelines
These changes in clinical variables are listed in order of their likelihood to predict poor survival, the most predictive first and the least predictive last. No specific number of variables must be met, but fewer of those listed first and more of those listed last would be expected to predict longevity of six months or less.
You May Like: How To Calm Parkinson’s Tremors
More About Carbidopa / Entacapone / Levodopa
1. Product Information. Stalevo 150 . Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ.
2. Product Information. Stalevo 50 . Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ.
3. Hauser RA Levodopa/carbidopa/entacapone . Neurology 62 : S64-71
4. Product Information. Stalevo 100 . Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ.
5. Giner V, Rueda D, Salvador A, Hernandez JC, Esteban MJ, Redon J Comments, opinions, and brief case reports: thrombocytopenia associated with levodopa treatment. Arch Intern Med 163 : 735-6
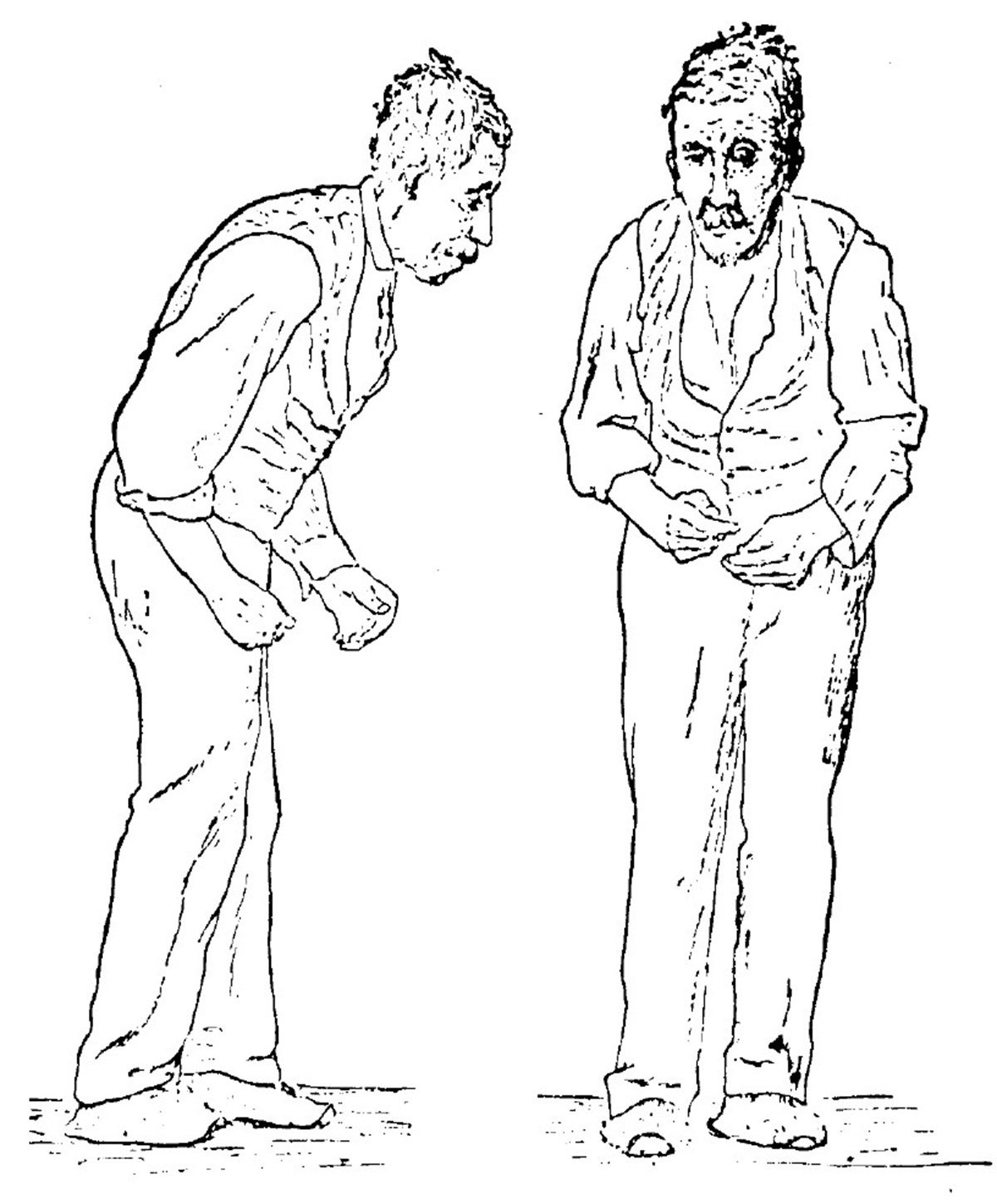
The four main symptoms of Parkinsons are:
- Tremor, which means shaking or trembling. Tremor may affect your hands, arms, or legs.
- Problems with balance or walking.
Tremor may be the first symptom you notice. Its one of the most common signs of the disease, although not everyone has it.
More importantly, not everyone with a tremor has Parkinsons disease.
Tremor often starts in just one arm or leg or on only one side of the body. It may be worse when you are awake but not moving the affected arm or leg. It may get better when you move the limb or you are asleep.
In time, Parkinsons affects muscles all through your body, so it can lead to problems like trouble swallowing or constipation.
In the later stages of the disease, a person with Parkinsons may have a fixed or blank expression, trouble speaking, and other problems. Some people also lose mental skills .
People usually start to have symptoms between the ages of 50 and 60. But sometimes symptoms start earlier.
How Can Hospice Help Patients With Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons is a chronic progressive disease of the nervous system that affects movement. Tremors are the most noticeable symptom of the disease, usually beginning in the hands. Both genetic and environmental factors are believed to cause Parkinsons. About 1 million people in the United States are affected by this disease.
Don’t Miss: Jimmy Choi Parkinson’s Treatment
How Is It Treated
At this time, there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease. But there are several types of medicines that can control the symptoms and make the disease easier to live with.
You may not even need treatment if your symptoms are mild. Your doctor may wait to prescribe medicines until your symptoms start to get in the way of your daily life. Your doctor will adjust your medicines as your symptoms get worse. You may need to take several medicines to get the best results.
Levodopa is the best drug for controlling symptoms of Parkinson’s. But it can cause problems if you use it for a long time or at a high dose. So doctors sometimes use other medicines to treat people in the early stages of the disease.
The decision to start taking medicine, and which medicine to take, will be different for each person. Your doctor will be able to help you make these choices.
In some cases, a treatment called deep brain stimulation may also be used. For this treatment, a surgeon places wires in your brain. The wires carry tiny electrical signals to the parts of the brain that control movement. These little signals can help those parts of the brain work better.
There are many things you can do at home that can help you stay as independent and healthy as possible. Eat healthy foods. Get the rest you need. Make wise use of your energy. Get some exercise every day. Physical therapy and occupational therapy can also help.
What Is An Advance Decision To Refuse Treatment
During the course of an individuals advance care planning discussion they may indicate that they wish to make an advance decision to refuse certain treatments.
This is a separate document to that of the ACP and must be instigated by a professional who is competent in this process. They are required to follow the guidance available in the Code of Practice for the Mental Capacity Act on Advance Decision to Refuse Treatment in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland professionals must follow guidance available in the Adults With Incapacity Act .
- An Advance Decision to Refuse Treatment allows the person who is 18 years of age or over to specify what treatments they would not want and would not consent to later in life. In Scotland the age of advanced directives is 16. They cannot demand certain treatments or refuse basic care, ie offers of food and water by mouth, warmth, shelter and hygiene. But clinically assisted nutrition and hydration given by intravenous, subcutaneous or gastroscopy are considered medical interventions and can be refused. These decisions can be withdrawn if the individual gains or retains capacity.
- All healthcare providers must respect the individuals advance decision and ensure it is incorporated into the person-centred care planning. They will also have discussed who is to be made aware of the ADRT and where they wish to store it in the home. A copy of the document should be stored in their healthcare notes and their GP made aware.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Getting Parkinson’s Disease
Adjusted Odds Ratios For Motor Deterioration
Multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that delirium and body temperature were significantly associated with motor deterioration after systemic inflammation . The adjusted odds ratios were 15.89 for delirium and 2.78 for body temperature . The HosmerâLemeshow test showed no significance and predictive accuracy was 89.7%.
How Is Pneumonia Treated
Bacterial pneumonia can be treated with antibiotics usually by mouth. For more severe pneumonia, you may need to go to the hospital to be treated. Hospital treatment may include oxygen therapy to increase oxygen in the blood, intravenous antibiotics, and fluids. Pain relievers and medicine to reduce fever may also be given. With treatment, bacterial pneumonia usually begins to improve within 24-48 hours.
Viral pneumonia is usually less serious. A stay in the hospital is rarely needed. Antibiotics cannot be used to treat viral pneumonia, but may be given to fight a bacterial infection that is also present. Other drugs, such as those listed above, may be used to lessen symptoms. If you are given antibiotics, make sure you take all of the medicine, even if you feel better. If you stop taking the medicine too early, the infection can come back and may be harder to treat.
For both viral and bacterial pneumonia:
- Drink warm fluids to relieve coughing.
Don’t Miss: How Long Do Parkinson’s Patients Live After Diagnosis
Interacting With Parkinsons Disease
Here are a few simple, but effective strategies to employ when faced with understandably uncomfortable scenarios:
- Change the subject. When symptoms manifest, sometimes talking about something else can help calm patients down. Whether its a recollection from their past or just a different topic, changing the conversation can turn chaos into calm.
- Take it outside. Fresh air and sunlight can help improve oxygen flow and trigger mood stabilizers in the brain.
- Get busy. Having an activity, especially something patients find meaningful, can help set them on a more even keel. Old hobbies or household tasks generally work best in these instances.
- Have a snack. Most of us get cranky when were hungry or thirsty patients with Parkinsons are no different. A light snack, some water or juice can help stabilize behaviors.
- Adjust the ambience. Sometimes, something as simple as a rooms brightness or temperature can contribute to a patients acting out. Too much noise can overstimulate too little light can cause anxiety excessive heat or cold can trigger anger. Adjusting lighting and temperatures, turning the volume down on the TV or the radio, or simply offering a cozy blanket may help restore the peace.
- Ask for help. Looping in a patients doctor may reveal underlying medical conditions, like urinary tract infections, behind the sudden shifts in behavior.
Stage Four: Symptoms Are Severe And Disabling And You Often Need Assistance To Walk Stand And Move
Stage Four Parkinsons disease is often called advanced Parkinsons disease. People in this stage experience severe and debilitating symptoms. Motor symptoms, such as rigidity and bradykinesia, are visible and difficult to overcome. Most people in Stage Four arent able to live alone. They need the assistance of a caregiver or home health aide to perform normal tasks.
You May Like: Medications For Parkinson’s Disease And Side Effects
Your Home And Lifestyle
- Modify your activities and your home. For example, simplify your daily activities, and change the location of furniture so that you can hold on to something as you move around the house.
- Eat healthy foods, including plenty of fruits, vegetables, grains, cereals, legumes, poultry, fish, lean meats, and low-fat dairy products.
- Exercise and do physiotherapy. They have benefits in both early and advanced stages of the disease.
Pharmacologic Issues At End
As PD progresses there are fewer dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra as well as a progressively lower capacity to store exogenous levodopa and convert it to dopamine for storage and release in the remaining neurons. Additionally, as the dose requirements of levodopa increase, the patients functioning is inhibited before his next dose of medication . This usually takes place 24 hours after a levodopa dose and may appear as sensory , psychiatric or autonomic symptom, or progression of motor symptoms or dystonia . This is called end of dose wearing off. Wearing off has not been fully explored, but may be connected to pharmacokinetic changes, and shortening of striatal levodopa half-life resulting from progressive degeneration of nigrostriatal dopaminergic terminals . To treat motor symptoms it is necessary to deliver medication effectively. Patients with advanced PD often notice that protein-rich meals will diminish the effectiveness of levodopa doses . This can be alleviated by reducing protein intake during daytime and limiting protein intake at night to 40 grams . There are some strategies to Improve absorption of Levodopa include: advise patients to take levodopa before meals, on an empty stomach , advise patients to avoid protein-rich meals and bulk-forming foods , advise patients against lying down, and encourage them to move around, after ingesting a dose , and advise patients to mix levodopa, crushed into a powder, into sparkling liquid .
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Make You Tired
What Are The Considerations For Pain Management In The Last Days Of Life In Pd
It is important to consider that pain can be a risk factor for, and associated with, many other symptoms which might be the presenting features in a patient with complex or advanced PD. These include a new or worsened confusion, hallucinations, agitation and symptoms of depression or apathy.
As well as being an underlying cause of another symptom, pain can also be the symptom of other features of PD, such as rigidity, dyskinesia, but also non-motor features, for example, depression and fatigue.
Identifying whether pain is at the root of the presenting complaint and what might be causing the pain is therefore the most important part of the initial history from the patient and the carer. Then using the clinical examination to confirm findings from the history and identify any features not already elicited such as abnormal posturing, or dystonia.
A recent review into the pathophysiology and treatment of pain in PD suggests simple analgesia with paracetamol and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs but advises caution with opiate analgesia as constipation is a recognised problem in PD patients.25 The review mentions, however, the lack of evidence for many widely used analgesics specifically in PD.26
Recommended Reading: Beginning Of Parkinsons Symptoms
Bowel Issues In Parkinsons
Recently, I was doing an interview about Parkinsons troublesome issues and I had to admit that by far my most troublesome and annoying problem is related to the effects of my gut. This is true for the majority of us living with this disease. Whether it be a direct or indirect consequence of our illness is irrelevant in my opinion when the effect is the same. Plus to be honest I am not sure anyone of us can tell the difference most of the time.
As I have re-discovered the agony of suffering from one of these ailments over the last several months when I had several bouts of ileus. In my opinion, there is nothing worse than having stomach pain, bloating, nausea, indigestion, and gas to make life miserable.
Below are all the plausible GI symptoms all of us can experience throughout our journey with PD.1 The most common symptoms are those related to poor motility or dysmotility and can be compounded by the effect of the medication.
Also Check: On Off Phenomenon In Parkinsons Disease
Read Also: Parkinson Disease Treatment Brain Surgery