Serotonin Reuptake Blocking Antidepressants Fluoxetine Sertraline And Paroxetine
Several other medications have been reported to cause drug-induced parkinsonism and to worsen parkinsonism in people with Parkinson disease, including the serotonin reuptake blocking antidepressants fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine. Two calcium channel blockers available in Europe and South America , which are piperazine derivatives, are thought to cause drug-induced parkinsonism by blocking dopamine receptors. Reports of parkinsonism induced by other drugs, such as lithium and amiodarone, are so rare that only after parkinsonism has developed should the possible drug effect be taken into account. Because lithium is not known to block dopamine receptors, another mechanism is likely. Some animal data implicate an effect of lithium on intercellular signalling via G-protein coupled receptors . One antidepressant, amoxapine, has dopamine receptor-blocking properties and, therefore, may induce parkinsonism. Parkinsonism as a transient side effect of alcohol withdrawal has been reported without later development of Parkinson disease, but it is unknown how common this is .
Also Check: Cleveland Clinic Parkinsons Bicycle Study 2017
Mechanism Of Action Of Available Drugs
The major classes of drugs currently available for the treatment of idiopathic Parkinsons disease are shown in Table 1. Many aim to increase dopamine in the brain, by increasing its production or altering its metabolism .
|
Table 1 |
Drugs with alter metabolism in boxed red italics
Levodopa
Levodopa is absorbed from the small intestine and transported into the brain where it is converted to dopamine. Levodopa has a short plasma half-life of about one hour. Early in Parkinsons disease, levodopa has a long duration of action which is independent of plasma concentration, but as the disease progresses, the duration of the effect reduces. The short-duration effect is strongly linked to plasma concentration and lasts, at most, hours.
Slow-release preparations are gradually absorbed, resulting in more sustained plasma concentrations. They have reduced bioavailability higher doses are required to match the benefit of an equivalent strength of a standard preparation. Rapid release preparations are taken in liquid form to enhance passage through the stomach and absorption from the small intestine.
Dopamine agonists
Apomorphine is a potent emetic so patients must be pre-treated with domperidone 20 mg three times daily orally for at least 48 hours before the first injection. Domperidone should be continued for at least a few weeks once regular intermittent treatment has commenced. The dose can then be tapered slowly as tolerance to the emetic effects of apomorphine usually develops.
What Are The Most Common Medicines Used To Treat Pd
Sinemet®
Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed and most effective medicine for controlling the symptoms of PD, particularly bradykinesia and rigidity.
Levodopa is a chemical found naturally in our brains. When given as a medicine, it is transported to the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. It is then converted into dopamine for the nerve cells to use as a neurotransmitter.
Sinemet is made up of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Levodopa enters the brain and is converted to dopamine while carbidopa prevents or lessens many of the side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and occasional heart rhythm disturbances. It is generally recommended that patients take Sinemet on an empty stomach, at least ½ hour before or one hour after meals.
There are two forms of Sinemet: controlled-release or immediate-release Sinemet. Controlled-release Sinemet and immediate-release Sinemet are equally effective in treating the symptoms of PD, but some people prefer the controlled release version. Ask your doctor which approach is best for you.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists are medicines that activate the dopamine receptor. They mimic or copy the function of dopamine in the brain.
Parlodel®, Requip®, and Mirapex® are all dopamine agonists. These medicines might be taken alone or in combination with Sinemet. Generally, dopamine agonists are prescribed first and levodopa is added if the patients symptoms cannot be controlled sufficiently.
Symmetrel®
Recommended Reading: How Does Parkinson’s Affect Daily Life
Parkinsons Medication And Alcohol: The Final Word
Whether or not you should drink alcohol while being treated for Parkinsons disease will depend on the medication youre taking. It is worth discussing this issue with your doctor, especially if you have concerns about alcohol dependence or addiction.
General health guidelines state that you should avoid drinking alcohol with any medication that makes you drowsy, sleepy or impairs your concentration. That said, many people with Parkinsons disease find that the occasional glass of wine is not harmful, as long as their doctor has agreed that they can drink in moderation.
You should always speak to your doctor before you mix Parkinsons disease medication and alcohol for the first time. You should never drive or operate heavy machinery when you have been drinking alcohol, and you should make sure you are in safe surroundings to minimize the risk of falls or injury.
APA ReferenceSmith, E. . Can You Drink Alcohol with Parkinsons Disease Medication?, HealthyPlace. Retrieved on 2021, August 28 from https://www.healthyplace.com/parkinsons-disease/treatment/can-you-drink-alcohol-with-parkinsons-disease-medication
Dont Miss: Weighted Silverware
What Are The Causes
Drug-induced parkinsonism is caused by medications that reduce dopamine levels in the brain. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that works to control bodily movements.
Dopamine is also part of the brains reward system. It helps you feel pleasure and enjoyment, and it supports your ability to learn and focus.
Medications that bind to and block dopamine receptors are called dopamine antagonists. These medications arent used to treat Parkinsons disease. Rather, theyre used to treat other conditions that might seriously impact your quality of life.
If your doctor has prescribed a medication that causes unwanted side effects, you may have options. You may also decide that the side effects are worth it if the medication effectively treats your condition.
Some medications that cause drug-induced parkinsonism include:
You May Like: How Long Does Dbs Work For Parkinson’s
The Role Of Antiparkinson Medication In The Pathogenesis Of Psychotic Symptoms In Pd Patients
The pathogenesis of psychosis related to PD is currently viewed as a complex of medication- and disease-related factors. Among medication-related factors, the use of dopaminergic drugs is particularly considered as a significant risk factor for the development of these symptoms. The ability of drugs that enhance dopaminergic transmission, such as amphetamine, to induce psychotic symptoms and the blockade of dopaminergic D2 receptors as the mechanism of action of antipsychotic medications help support the dopaminergic role of pathogenesis in drug-induced psychosis in PD . Also, historically, psychotic symptoms in PD patients were rarely described in treatment-naïve patients .
The causal relationship between levodopa and dopaminergic medications and psychosis has not been definitely established. The results of experimental and clinical studies are conflicting . In an animal model of PD, Fox et al. confirmed the propensity of levodopa and dopamine agonists to induce psychosis-like behavior in primates . However, in a clinical study by Aarsland et al., no correlation between the prevalence of psychotic symptoms and the type, duration, and dose of antiparkinson drug therapy was found . More recently Rai et al. found no correlation between psychotic symptoms and the class, dose, or duration of antiparkinson medications in patients with PD . Contrastingly, Papapetropoulos and Mash demonstrated that all antiparkinson drugs can induce psychosis in PD patients .
Side Effects With Levodopa
To avoid use in individuals with known allergy or hypersensitivity to Mucuna pruriens or components.
There have been some side effects of mucuna. In a study of patients with Parkinsons disease, a derivative of Mucuna pruriens caused minor adverse effects, which were mainly gastrointestinal in nature.
Isolated cases of acute toxic psychosis have been reported1, probably due to levodopa content. Therefore, as with Sinemet and Madopar, its use should be avoided in patients with psychosis or schizophrenia
Also Check: Laser Light For Parkinson’s Disease
Antagonists Of At1 Receptor For Angiotensin Ii
The mechanism behind the hypotensive effect of antagonists of AT1 receptor for angiotensin II is associated with the binding of the drug to AT1 receptor for angiotensin II in adrenal glands and smooth muscles of the blood vessels. This prevents the vasoconstrictive effect of angiotensin II and aldosterone release. Of note, the antagonists of AT1 receptor for angiotensin II do not modulate the metabolism of bradykinin, noradrenalin and substance P .
Data from the Polish ministerial database suggest that the antagonists of AT1 receptor for angiotensin II do not interact with anti-parkinsonian agents, apart from an insignificant interaction between sartans and bromocriptine or cabergoline, which is associated with the enhancement of their hypotensive effect . In contrast, Lexicomp® and Stockleys® include significant interactions between MAO-B inhibitors and antagonists of AT1 receptor.
Table presents the interactions between the antagonists of AT1 receptor for angiotensin II most frequently used in the treatment of arterial hypertension and anti-parkinsonian agents, stratified according to their significance.
Identifying Early Pd Patients
Eligibility criteria included individuals with a first Read Code of a definitive PD diagnosis in GP data . The Read Code system is a hierarchical system that covers most clinical terms, including diagnoses and drugs.24 The Read Codes indicating a definitive PD diagnosis were used and validated in a previous study.25 Patients were excluded for the following reasons: less than 40 years of age, taking any antiparkinsonian drug before PD diagnosis, no prescription of any antiparkinsonian drug within one year after PD diagnosis, a first code of PD within 6 months from SAIL registration date, death within a year of PD diagnosis, and previous antipsychotic use within the year prior to PD diagnosis, as antipsychotics can cause Parkinson-like symptoms which could be mistakenly diagnosed as PD.26
You May Like: Cause For Parkinson’s Disease
Key Aspects Of Drug Induced Parkinsonism
- Drug induced Parkinsonism is relatively less likely to produce the problem of tremor than its counterpart idiopathic Parkinsons disease.
- DIP is highly symmetric, but doctors usually fail to distinguish the 2 syndromes in case of an individual therapy.
- The problem of DIP persists in patients for a few weeks to up to many months even when a patient stops the consumption of respective offending drug.
- Drug induced Parkinsonism has a longstanding and a significant effect on the daily lives of a patient. Hence, doctors should essentially stay cautious while prescribing the drugs of depaminergic receptor blockers to their patients.
Also Read:
Antipsychotics To Treat Parkinsons Psychosis Need Further Research Report Says
The antipsychotics Clozaril and Nuplazid are potential treatments for Parkinsons disease psychosis in patients with idiopathic Parkinsons disease , whose cause is unknown. However, their use is currently limited and further research is necessary, according to a review of various trials.
Results of a meta-analysis of studies of antipsychotics used to treat PDP were shared in a letter titled, Antipsychotics for the management of Parkinsons disease psychosis, published in the International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry last April.
Up to 40% of patients with iPD develop PDP. Psychotic symptoms include visual hallucinations and delusions. PDP causes severe distress and agitation, which makes it harder for caregivers to provide care for these patients and often requires admission to nursing homes.
Antipsychotics are one of the options for treatment of PDP, but many antipsychotics cause deterioration in motor function. The letter reported on studies of antipsychotics that do not affect motor function in treating PDP.
Seroquel has often been used without demonstrated effectiveness, and over 50% of patients dropped out of trials because of adverse effects including somnolence and orthostatic hypotension, a drop in blood pressure when a person suddenly stands up from a lying or sitting position. Seroquel was not shown to reduce psychotic symptoms in PDP and neither was Zyprexa , even though they do not affect motor function.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease And Weed
Antipsychotic Drugs Called Neuroleptics
Drug-induced parkinsonism is due primarily to drugs that block dopamine receptors, particularly the D2 receptors . These drugs are most often the antipsychotic drugs, called neuroleptics, such as haloperidol, chlorpromazine, and trifluoperazine, but include metoclopramide, a gastrointestinal motility enhancer, and the antiemetics prochlorperazine and droperidol. In addition, medications that block synthesis of dopamine, such as alpha-methyl para-tyrosine and alpha-methyl dopa or deplete dopamine also induce parkinsonism. In these cases the pathophysiology is presumably due to diminished dopamine receptor stimulation, resulting in a pharmacologic state closely resembling Parkinson disease.
However, the atypical antipsychotics also block D2 receptors. Yet there is no apparent correlation between the degree of this blockade and the risk for inducing parkinsonism. The explanation for this is uncertain. One current hypothesis is the fast off theory, postulating that the duration of the D2 blockade, rather than the percentage of receptors blocked, determines the likelihood of parkinsonism . A competing theory is that the ratio of 5 HT-2a receptor blockade versus the dopamine D2 receptor blockade is critical because of the interplay between the serotonin and dopamine systems in the brain. An older theory relating extrapyramidal side effects to anticholinergic activity is considered untenable because the concomitant use of anticholinergics does not eliminate the problem.
Medications Used For Treating Psychosis
Antipsychotic agents are designed to balance abnormal chemical levels in the brain. Up until the 1990s, the use of antipsychotics in PD was controversial because the drugs used until that time work by reducing excess dopamine. This alleviated psychosis but caused dramatic worsening of PD motor symptoms.
Fortunately, medications that are better tolerated by people with PD are now available. Today, there are three antipsychotic medications considered relatively safe for people with PD: quetiapine , clozapine and the newest agent, pimavanserin . They cause limited worsening of PD while treating hallucinations and delusions.
Also Check: Yoga And Parkinson’s Disease
Pimavanserin Is Associated With Better Physician
Neurology Reviews
MIAMIAs a treatment for Parkinsons disease psychosis, pimavanserin is associated with significantly improved outcomes, compared with quetiapine and other therapies, according to research presented at the Second Pan American Parkinsons Disease and Movement Disorders Congress. The data suggest that use of pimavanserin is associated with significantly improved treatment outcomes, both within and beyond six months of treatment, said Conrad Tenenbaum, PhD, Senior Associate at BluePrint Research Group in Princeton, New Jersey, and colleagues.
Conrad Tenenbaum, PhD
More than half of patients with Parkinsons disease develop related psychosis. According to Dr. Tenenbaum and colleagues, most clinicians prescribe quetiapine for Parkinsons disease psychosis, but clinicians report that pimavanserin is more likely to provide adequate control of symptoms. To probe this discrepancy, Dr. Tenenbaum and colleagues investigated current treatments and outcomes for patients with Parkinsons disease psychosis to improve disease management.
You May Like: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinsons
Antipsychotics To Deal With Psychotic Symptoms
Psychotic symptoms remain present in approximately half of the patients dealing with Parkinsons disease. These symptoms create detrimental effects on the quality of life lead by patients and their caregivers, while result in mortality in some cases. Pathogenesis associated with psychotic symptoms in Parkinsons disease is complicated and usage of antipsychotics i.e. dopaminergic medications involve many risk factors. Treatment for psychotic symptoms in patients dealing with Parkinsons disease is complicated because of the property of any antipsychotic medicine to make motor symptoms worse.
Recommended Reading: What Other Diseases Mimic Parkinson’s
Epidemiology And Risk Factors
Psychosis in PD generally occurs late in the disease, although there may be a bimodal onset, with early onset associated with motor fluctuations and large doses of drugs, and more commonly a late onset associated with cognitive impairment. Hospital based studies show prevalence rates of 8%40% for hallucinations in patients receiving long term treatment for PD.
Old age, cognitive impairment, history of depression, and sleep disorders are important risk factors for the development of psychosis in PD. Several drugs, including those used in treating PD can worsen or even precipitate psychosis in PD. The relation between the drug dose and psychosis in PD is complex. Underlying genetic susceptibility may be important. Interestingly, a recent study did not find antiparkinsonian drugs a risk factor for psychosis.
Overview Of Pdp Management
Physical Versus Emotional Control:The intertwining pathophysiology of psychosis and PD through dopaminergic pathways presents healthcare professionals and patients with the unfortunate choice between physical and emotional stability. Dopaminergic agents that treat the symptoms of PD and maintain physical control are predominately associated with the triggering of psychosis symptoms through D2-receptor activation.9,11 This swing to emotional instability could be broadly treated in one of two ways. One option is to stop the anti-PD agent however, this is not feasible for most patients because physical instability and motor symptoms would return. Alternatively, an antipsychotic could be added, but nearly all typical and atypical antipsychotics work via D2-receptor antagonism, potentially tipping the scale toward physical instability. Accordingly, methods used in practice involve dose reduction of offending agents, as tolerated, or the use of an atypical antipsychotic with low D2-receptor affinity.9,11
Read Also: Pants For Parkinson’s Patients
Specific Warning About Mucuna
We assume that all contraindications, interactions, precautions and side effects that we know about synthetic levodopa should be considered when taking levodopa from mucuna.
Specific contraindications include thinning of the blood , and care should be taken with antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory drugs because mucuna increases clotting time.
Mucuna should not merge with anticoagulants or with antiplatelet drugs such as clopidogrel. Caution should be exercised and the additive effect should be taken into account if it is associated with acetylsalicylic and NSAIDs .
We should also be careful with antidiabetic medicines: mucuna lows glycemic index, and thus is to be considered a potential additive effect. Other interactions are possible, so always consult your regular doctor.
On the one hand, it can be argued that mucuna has been used for many centuries in India and has been available for several years online without a prescription, and yet serious problems have not been revealed. But that is just an observation.
Regarding Sinemet and Madopar, we have thousands of controlled studies, while publications on mucuna are still scarce. One must therefore use greater caution when choosing mucuna. While the future appears to be positive, we need the confirmation of more scientific studies.
Also Check: Can You Be Tested For Parkinsons
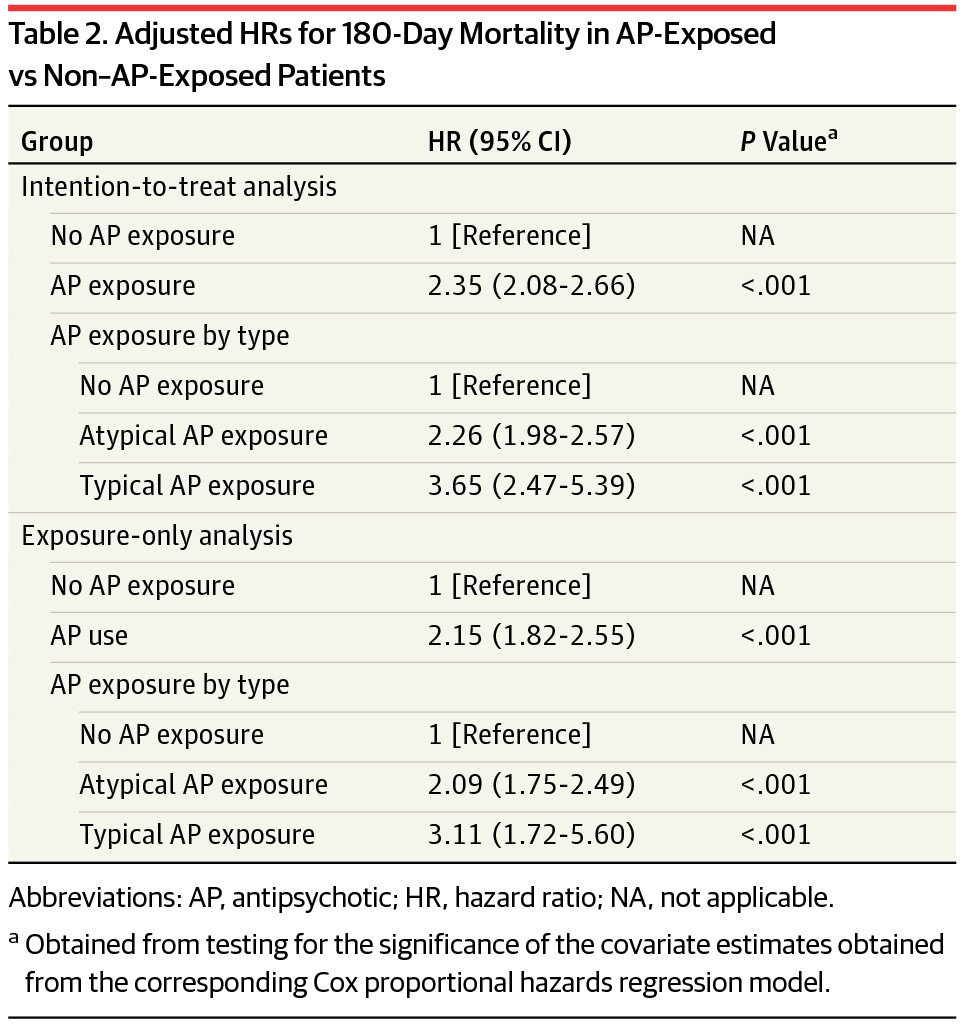
Antipsychotics For The Management Of Psychosis In Parkinson’s Disease: Systematic Review And Meta
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 02 January 2018
- CT1 SHO in General Medicine, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust, Queen’s Medical Centre, Nottingham, UK
- Oluwademilade A. Onalaja
- Stratford Healthcare, Arden Street, Stratford-Upon-Avon, UK
- *
Antipsychotics can exacerbate motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease psychosis.
To systematically review the literature on the efficacy and acceptability of antipsychotics for Parkinson’s disease psychosis.
Randomised controlled trials comparing an antipsychotic with placebo were systematically reviewed.
The final selection list included nine studies using quetiapine , clozapine , olanzapine and pimavanserin . A narrative synthesis and meta-analyses were presented for each antipsychotic. Clozapine demonstrated superiority over placebo in reducing psychotic symptoms. Quetiapine and olanzapine did not significantly improve psychotic symptoms. All three antipsychotics may exacerbate motor symptoms. Quetiapine studies were associated with high drop-out rates due to adverse events. Pimavanserin is a novel treatment that warrants further investigation.
Further research is needed. Clozapine and pimavanserin appear to be a promising treatment for Parkinson’s disease psychosis.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Runny Nose Treatment